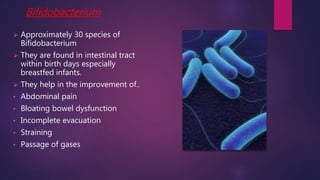
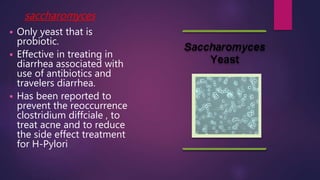
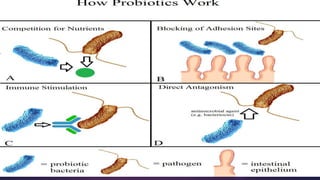
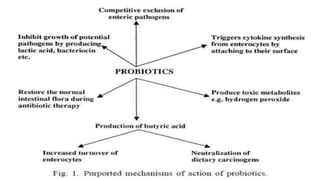
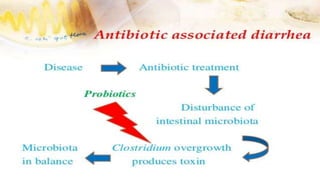
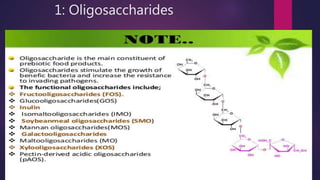
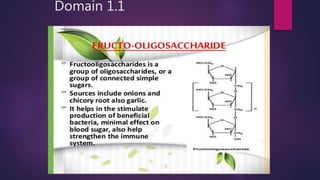
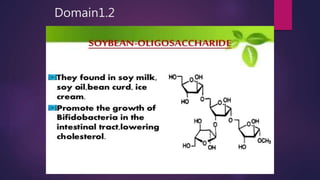
The document discusses probiotics and prebiotics. It defines probiotics as living microbes that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Common probiotic bacteria include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus, Bacillus, and Saccharomyces. Probiotics help prevent infections, support digestion, and may reduce cancer risk by altering gut bacteria. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. Common prebiotics are oligosaccharides and inulin.