Embed presentation
Download to read offline






![SURFACE AREA
b = area of a base
p = perimeter of a base
h = height of the prism
Surface Area
= 2(½ X 8 X 3) + [(8+5+5) X 12]
= 240 cm2
Area = 2b + ph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prismpresentation-150625032629-lva1-app6891/85/Prisms-presentation-9-320.jpg)


![EXAMPLE:
Finding the volume of the oblique prism.
Volume of the oblique prism
= [ ½ x (8+4) x 9 ] x 15
= 54 x 15
= 810 cm2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prismpresentation-150625032629-lva1-app6891/85/Prisms-presentation-12-320.jpg)
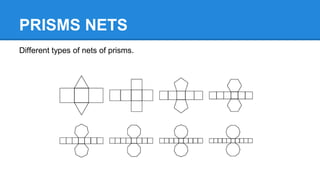
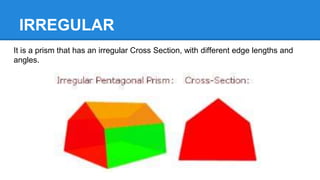
A prism is a solid geometric shape with identical cross-sectional areas and two faces that are identical, parallel polygons. There are different types of prisms including triangular, rectangular, pentagonal, and hexagonal prisms. To solve prisms, you calculate the surface area as 2 times the area of the base plus the perimeter of the base times the height, and the volume as the area of the base times the height. Prisms can also be regular, irregular, right, or oblique depending on the shape of their cross-sections and angles. The document provides examples of calculating surface areas and volumes of various prisms.








![SURFACE AREA
b = area of a base
p = perimeter of a base
h = height of the prism
Surface Area
= 2(½ X 8 X 3) + [(8+5+5) X 12]
= 240 cm2
Area = 2b + ph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prismpresentation-150625032629-lva1-app6891/85/Prisms-presentation-9-320.jpg)


![EXAMPLE:
Finding the volume of the oblique prism.
Volume of the oblique prism
= [ ½ x (8+4) x 9 ] x 15
= 54 x 15
= 810 cm2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prismpresentation-150625032629-lva1-app6891/85/Prisms-presentation-12-320.jpg)