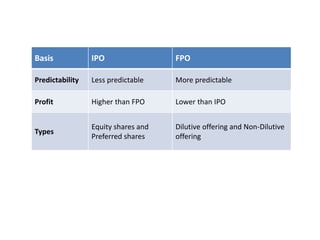
The primary market is where companies issue shares to the public for the first time to raise capital, facilitated by investment banks that set a price range and oversee sales. It includes methods such as public issues (IPOs and FPOs), rights issues, private placements, and preferential allotments, each with distinct characteristics and regulatory requirements. The primary market allows companies to raise funds quickly and gives investors opportunities for early investment, although it may carry higher risks due to limited information and historical trading data.