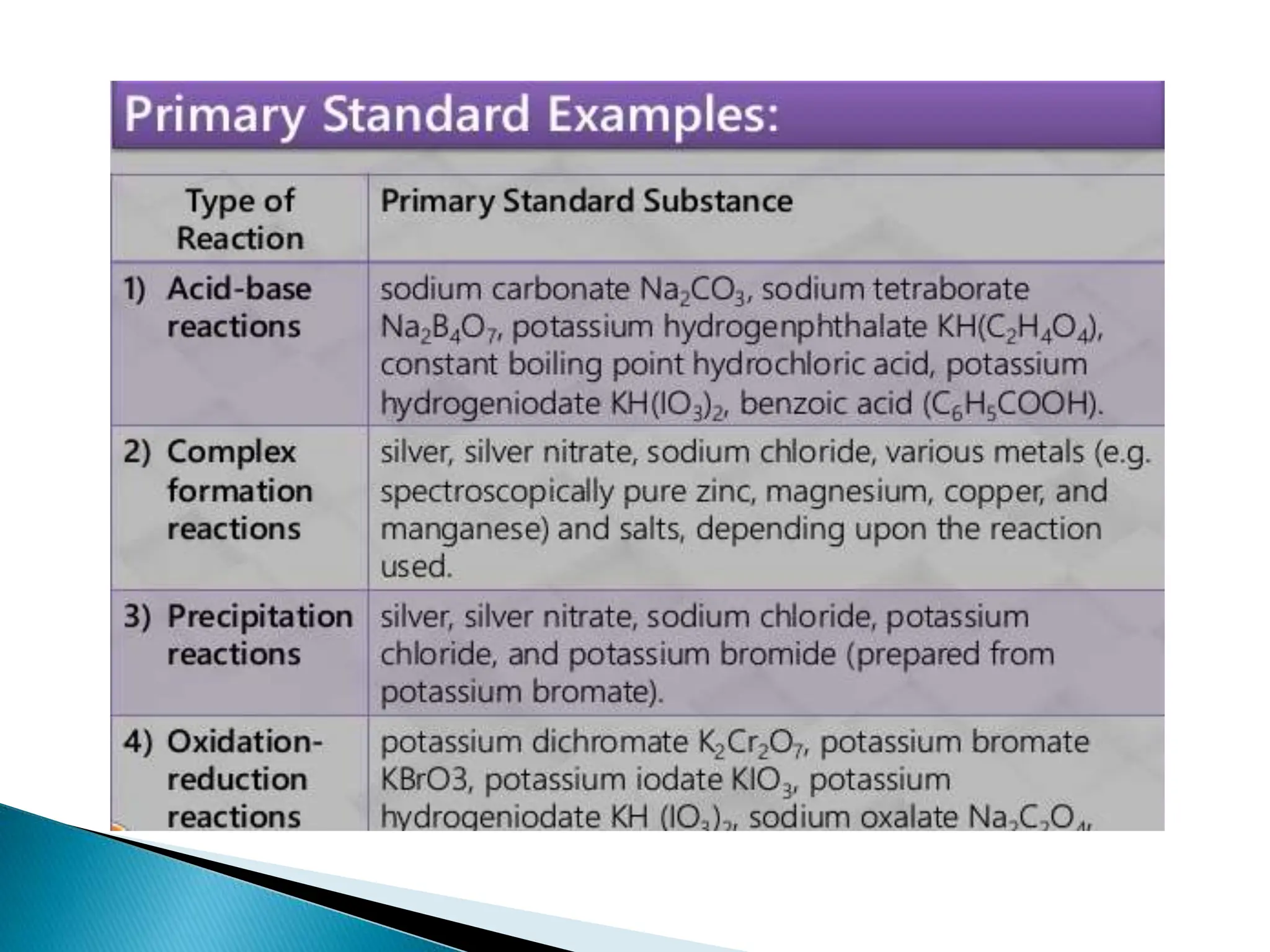
This document discusses primary and secondary standards used in pharmaceutical analysis. It defines a primary standard as a highly pure reagent or chemical used to prepare standard solutions of known concentration that do not require further standardization. Primary standards should be stable, pure, and soluble. Secondary standards are substances whose concentration has been determined by comparison to a primary standard. Secondary standards have less purity and stability than primary standards but their solutions remain stable for long periods of time. The document provides examples of properties primary and secondary standards should possess.