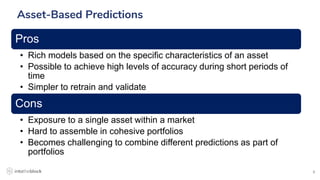
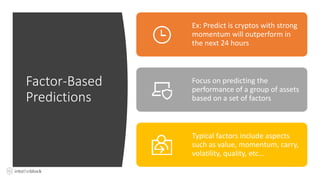
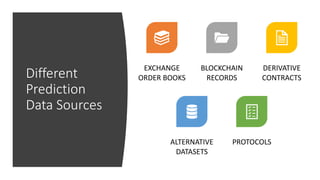
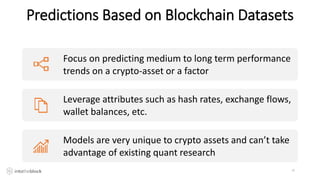
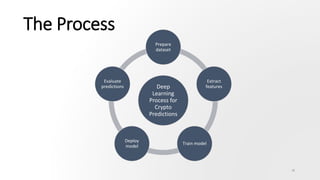
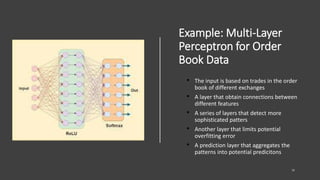
The document discusses the challenges and methodologies in predicting the performance of crypto assets using deep learning techniques. It highlights two primary approaches: asset-based predictions targeting specific assets and factor-based predictions focusing on groups of assets, alongside various data sources for predictions such as order books and blockchain data. Additionally, it addresses common myths about predictive models and outlines the deep learning process for developing these models in the context of crypto-asset trading.