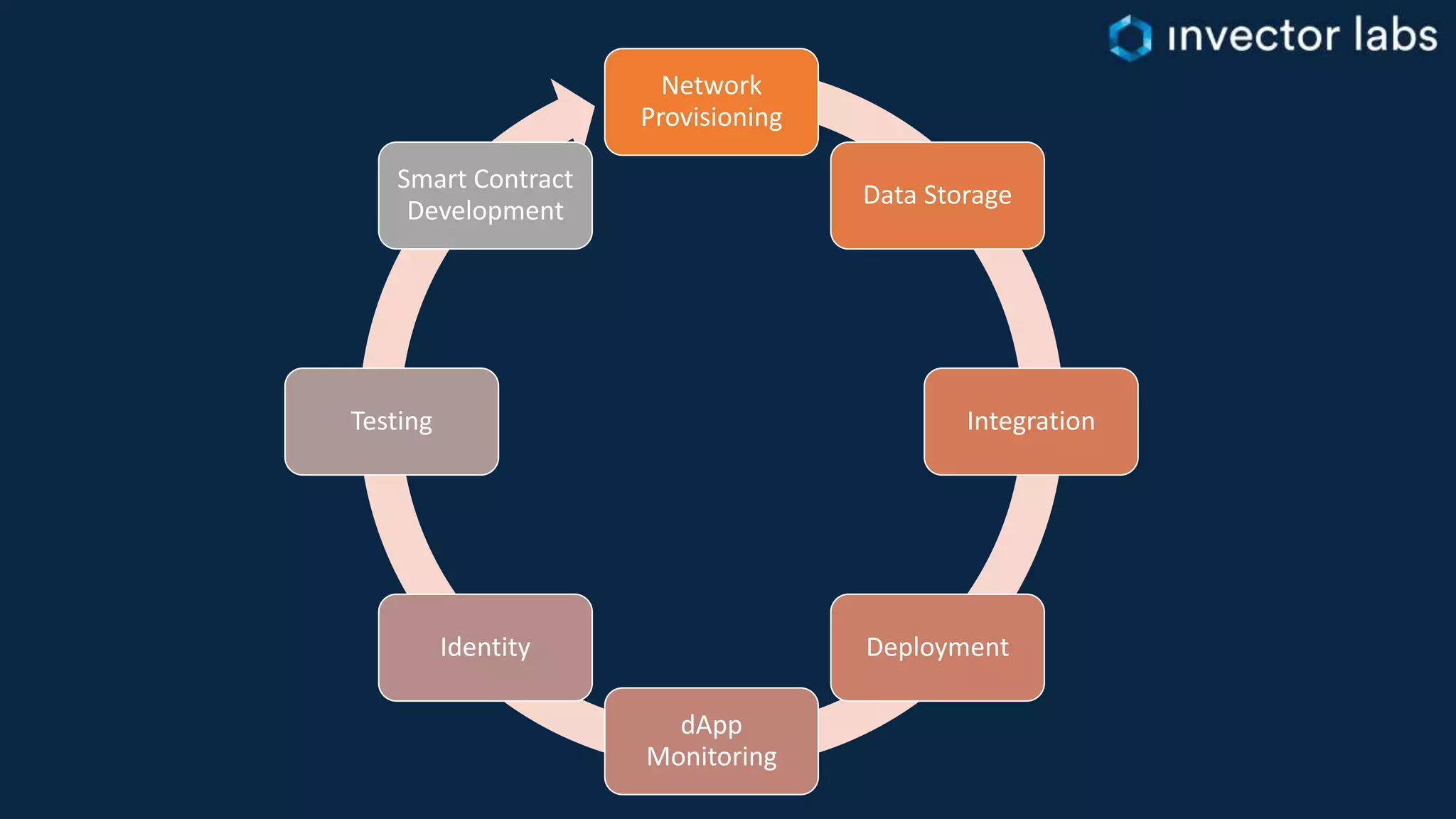
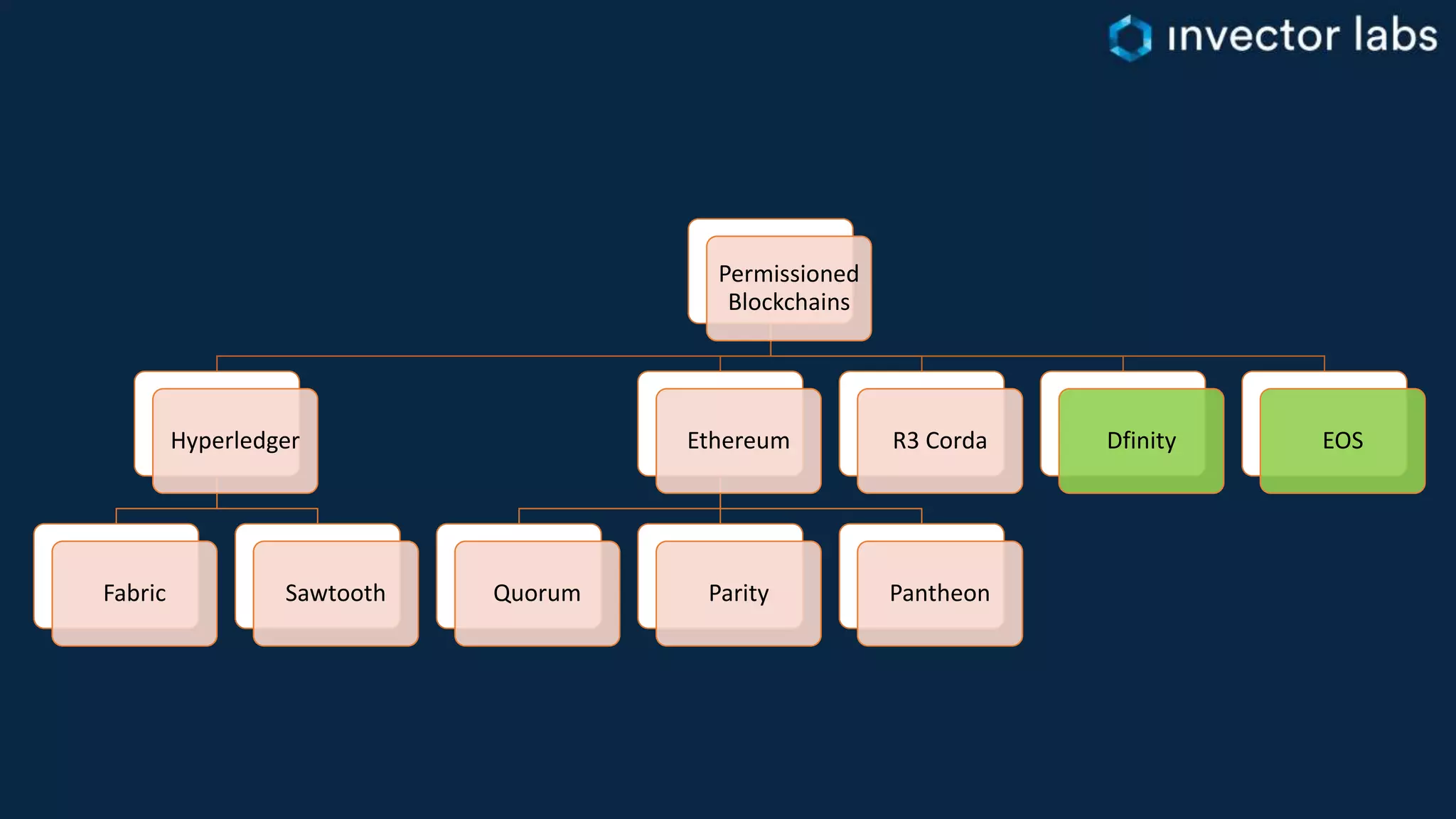
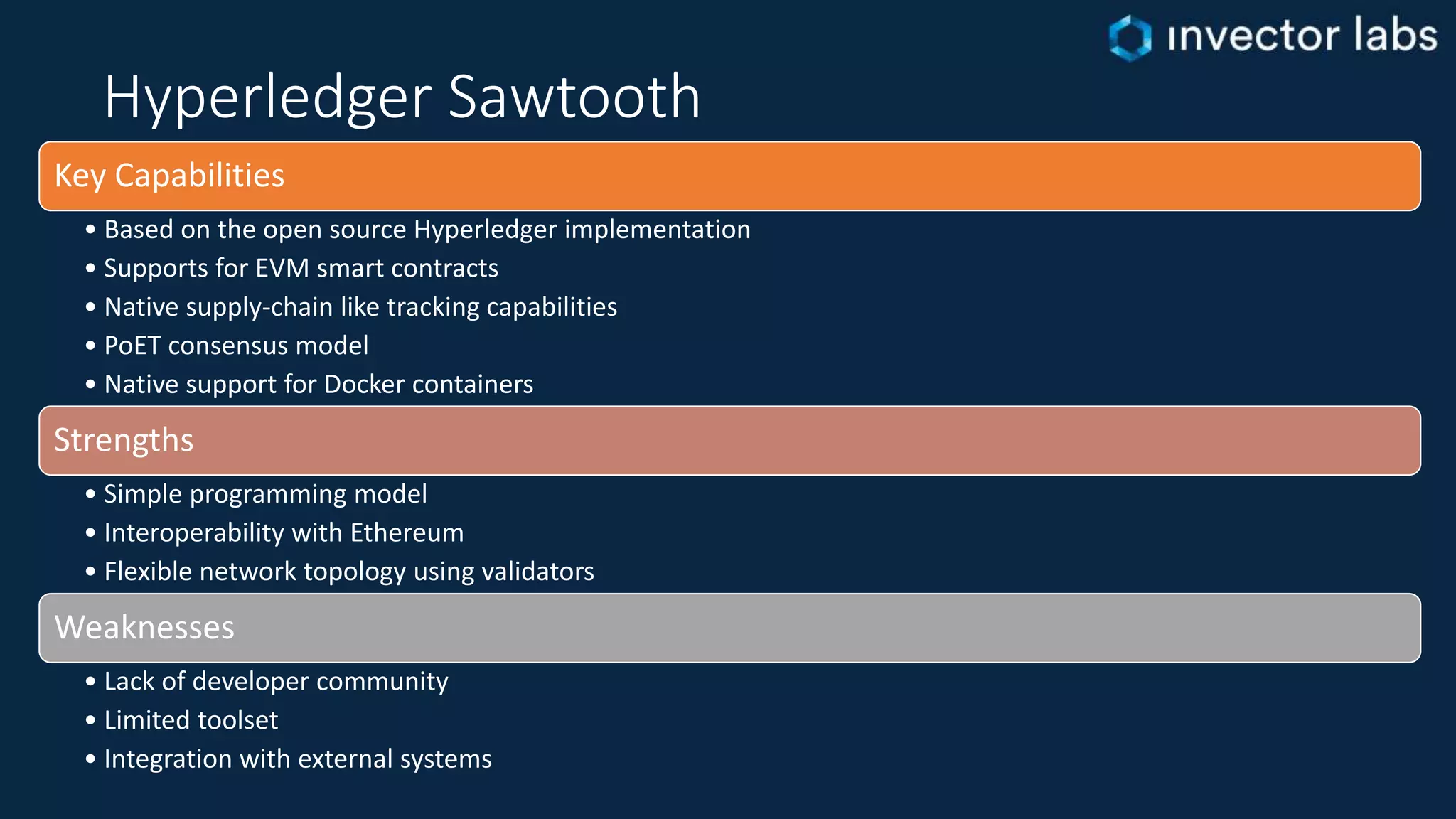
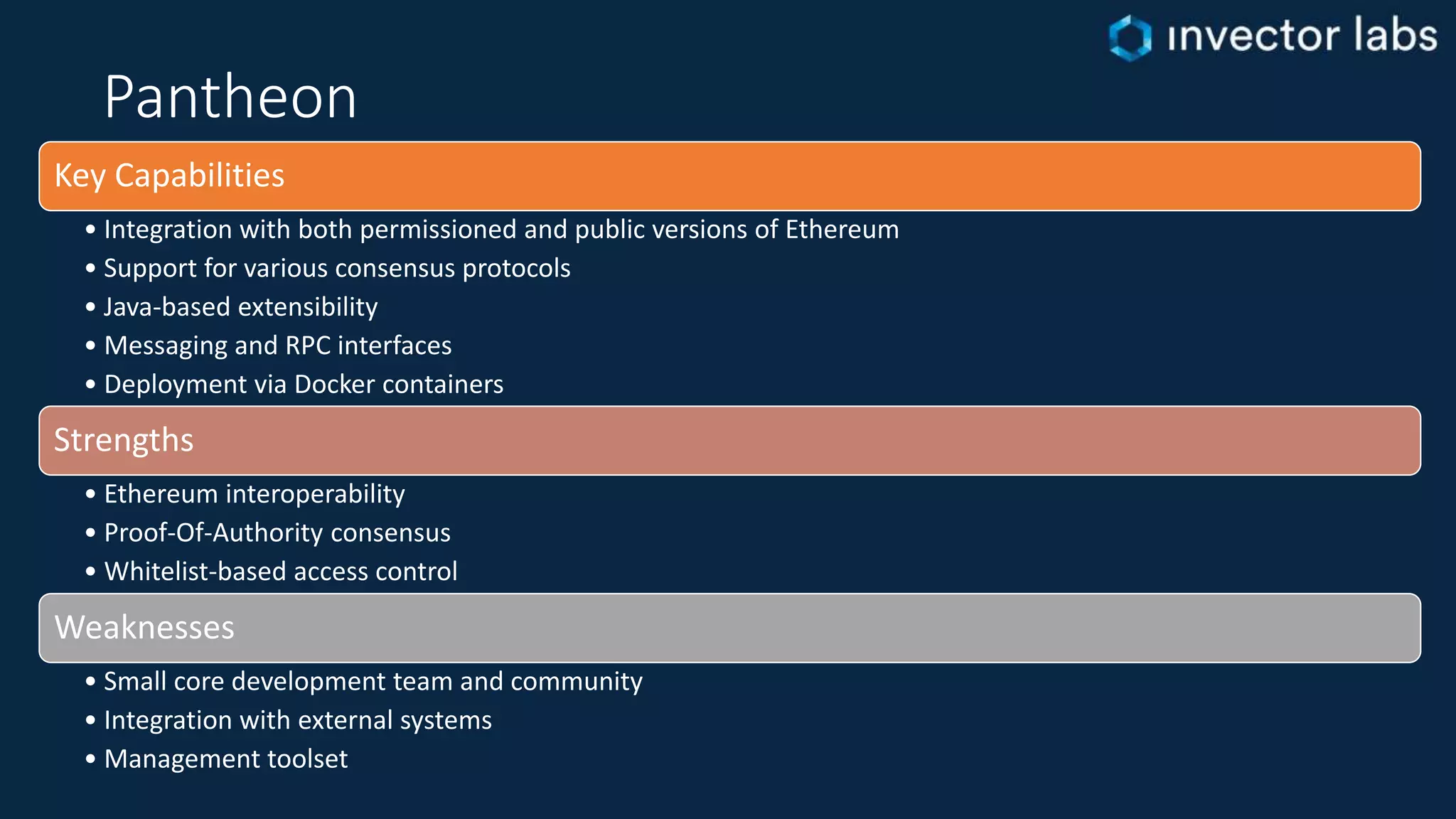
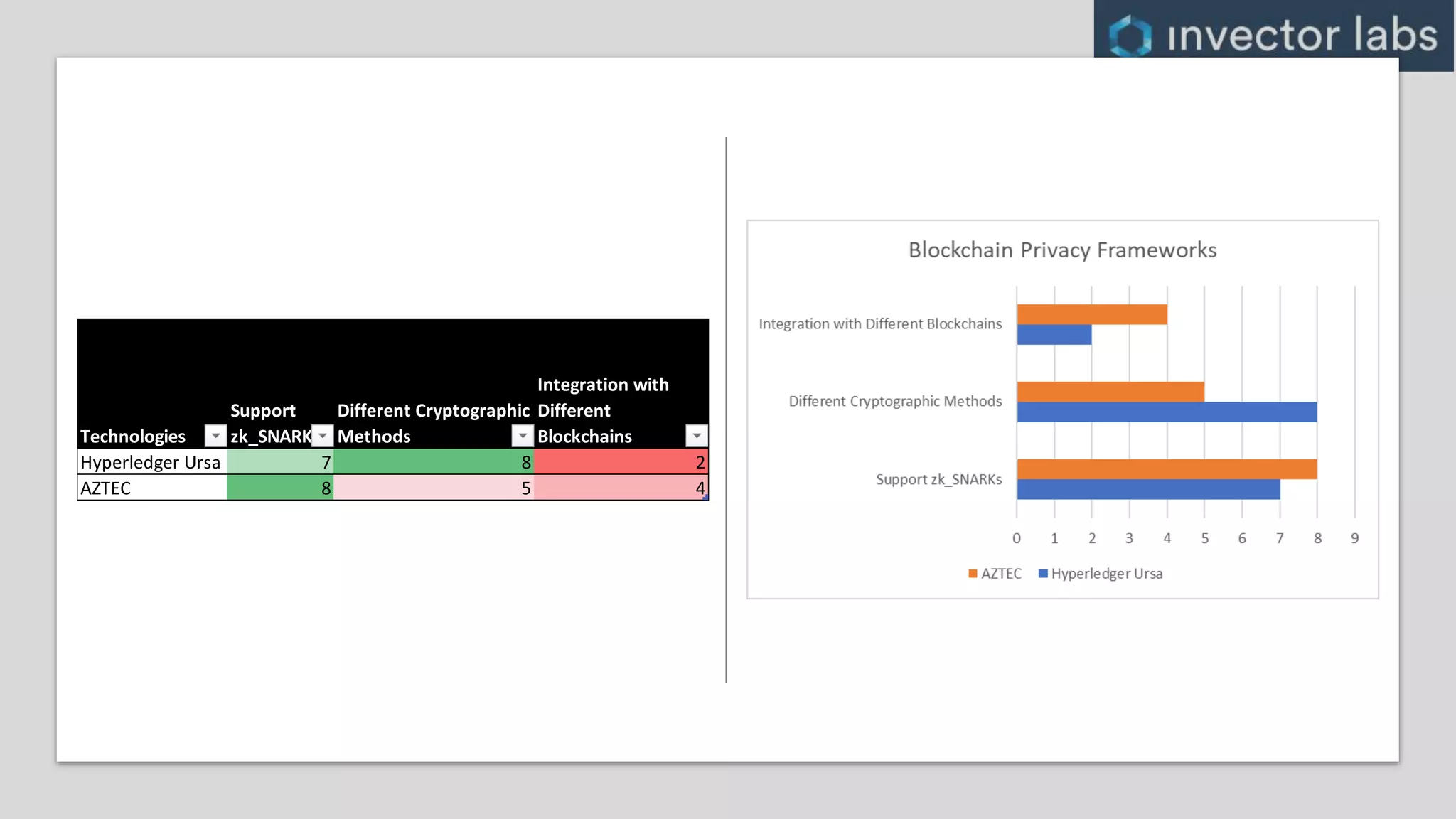
The document discusses key considerations for enterprise blockchain implementations, including selecting a blockchain platform, runtime, and complementary technology stacks. It analyzes popular permissioned blockchain platforms like Hyperledger Fabric, Sawtooth, and Corda and cloud services from Azure, AWS, IBM and others. It also reviews relevant technology stacks for integration, testing, data storage, access and security. The conclusion recommends starting small and iterating when establishing a blockchain strategy to address challenges of real-world solutions.