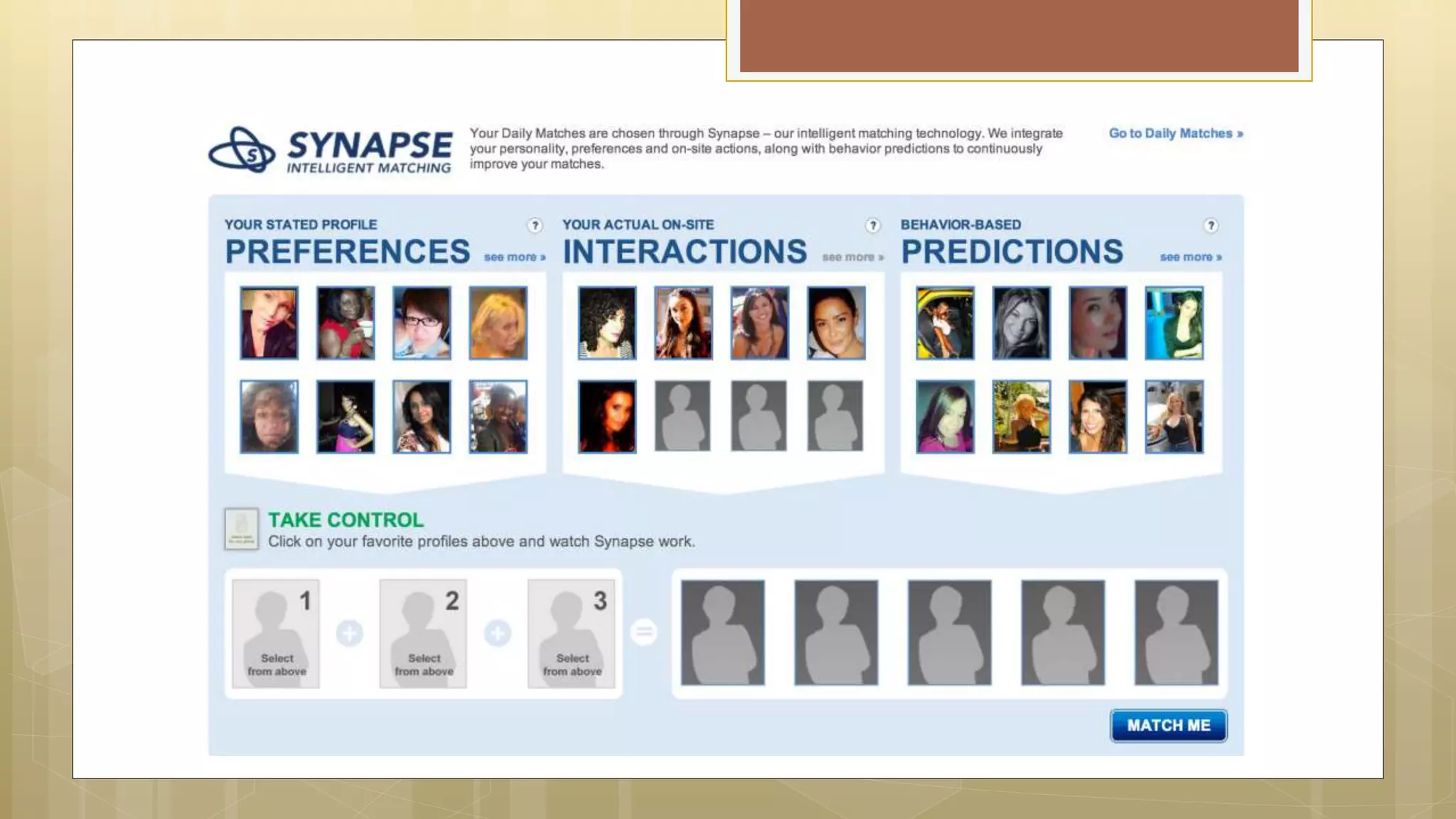
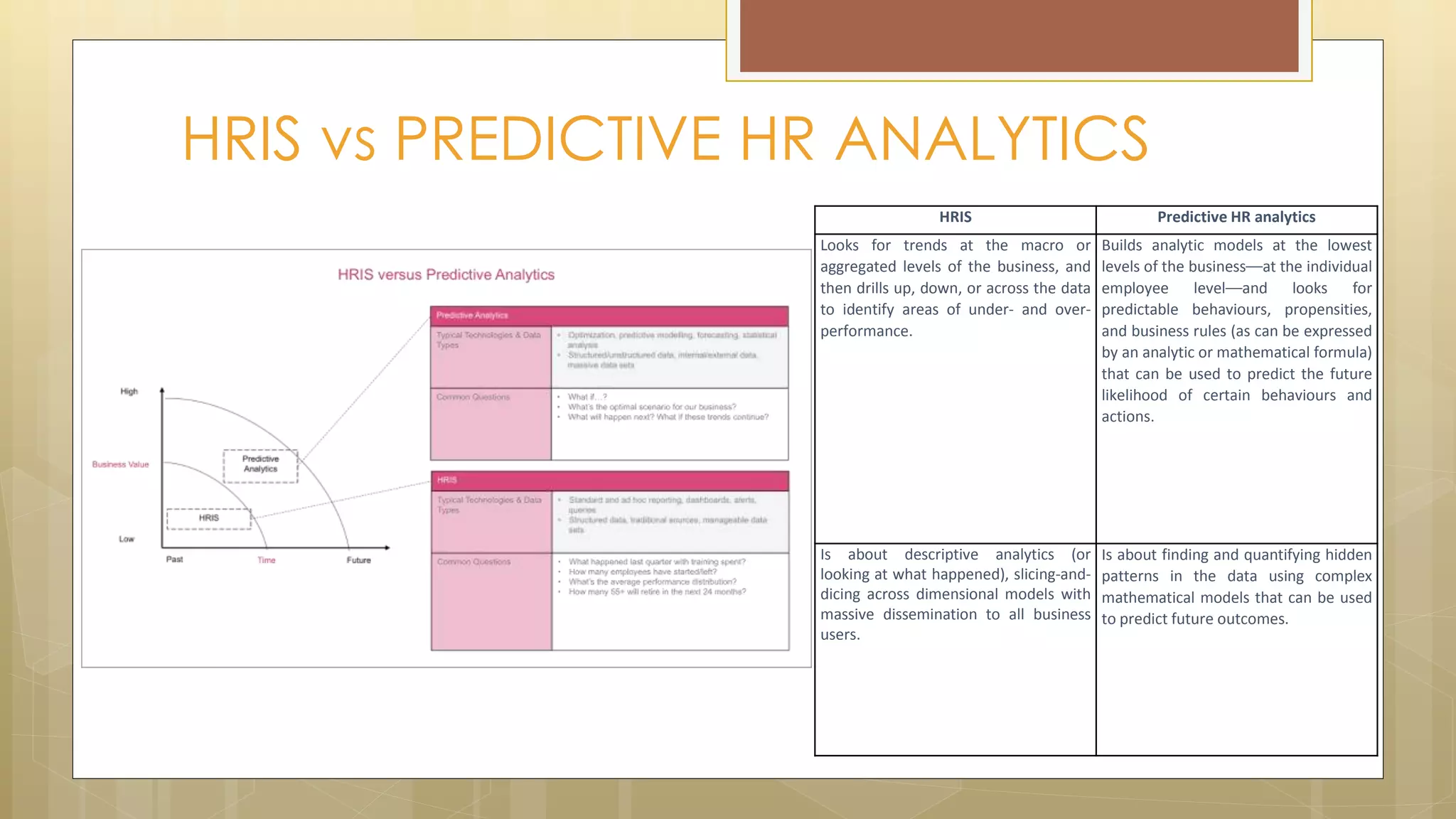
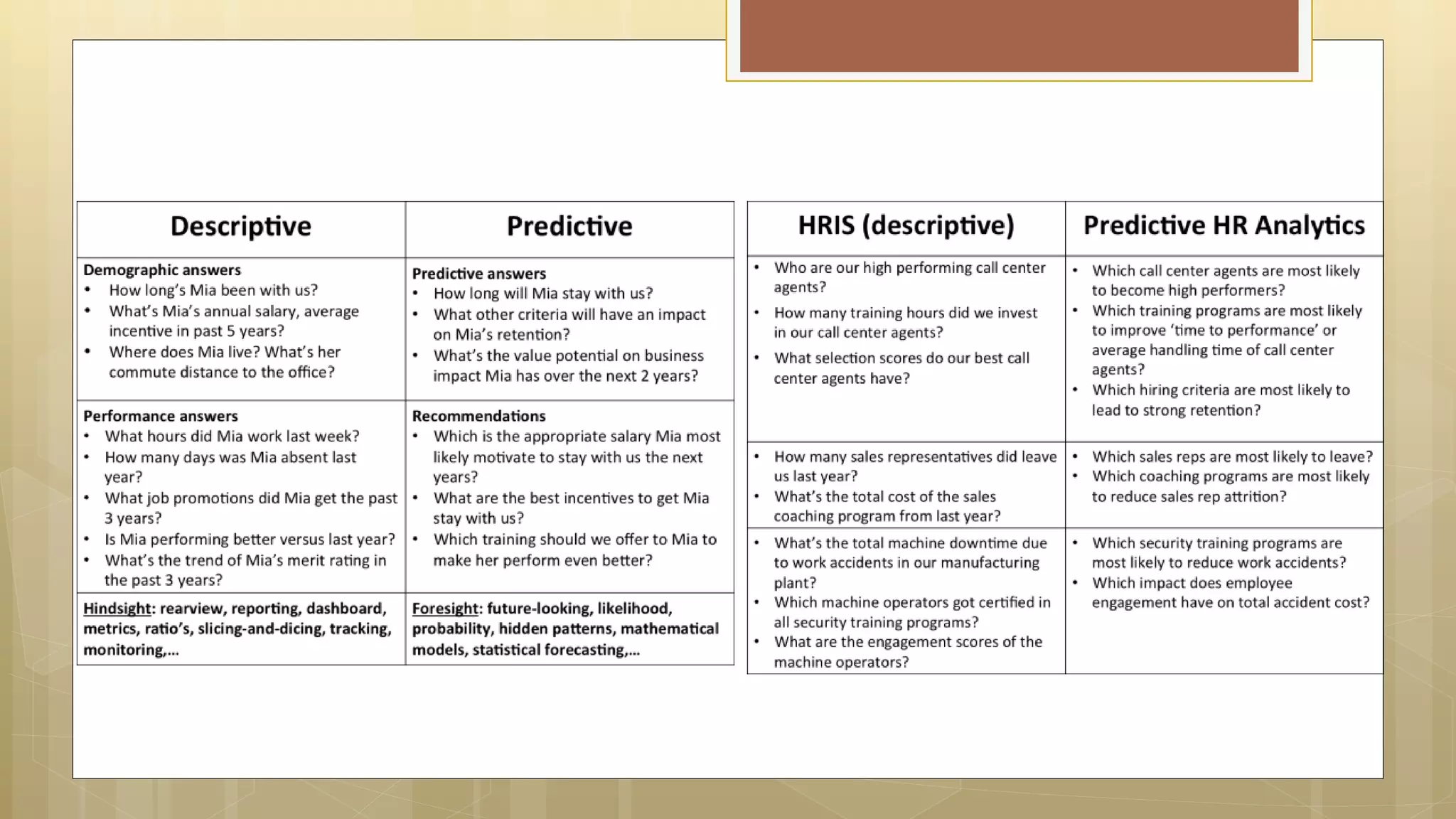
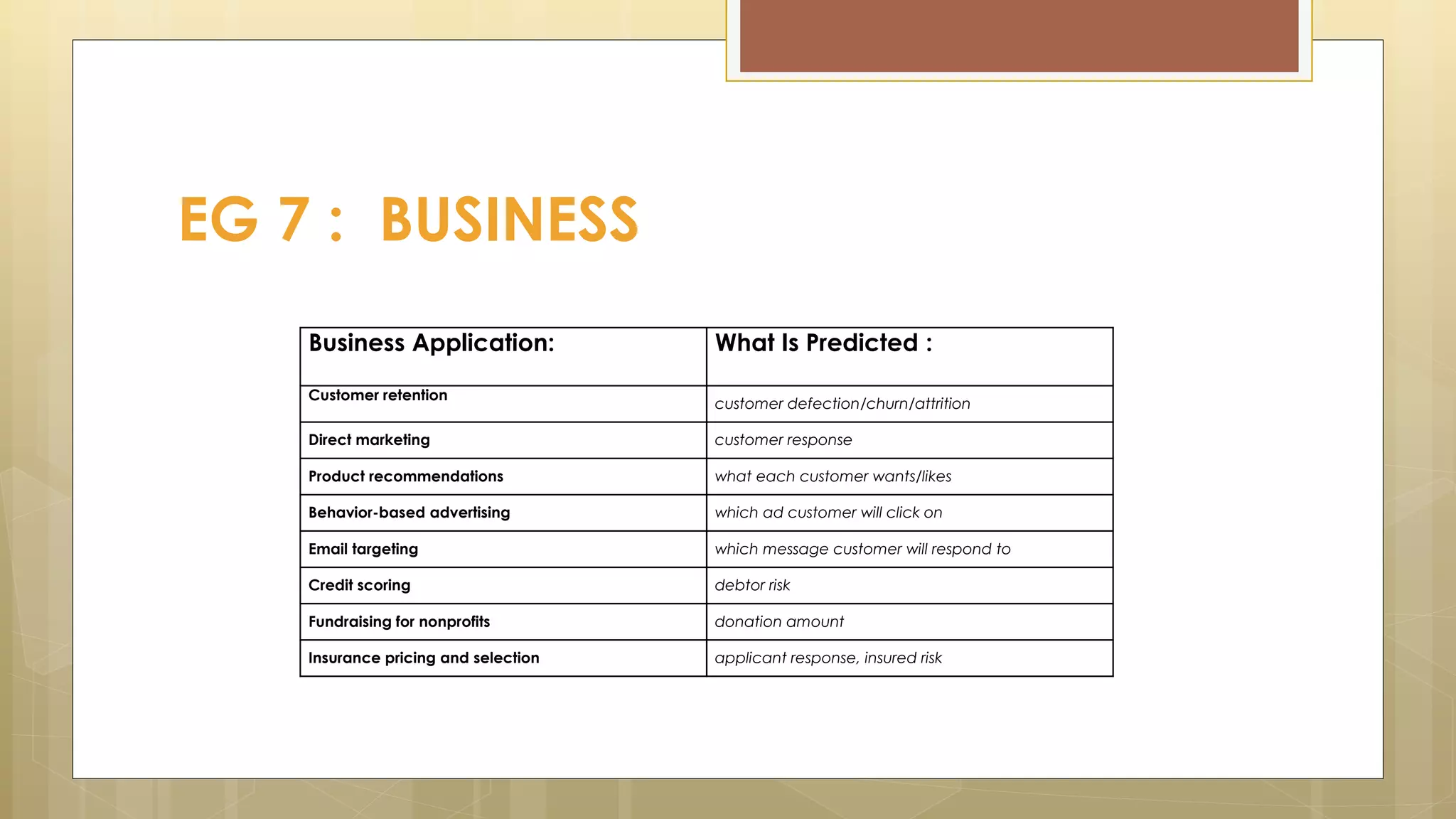
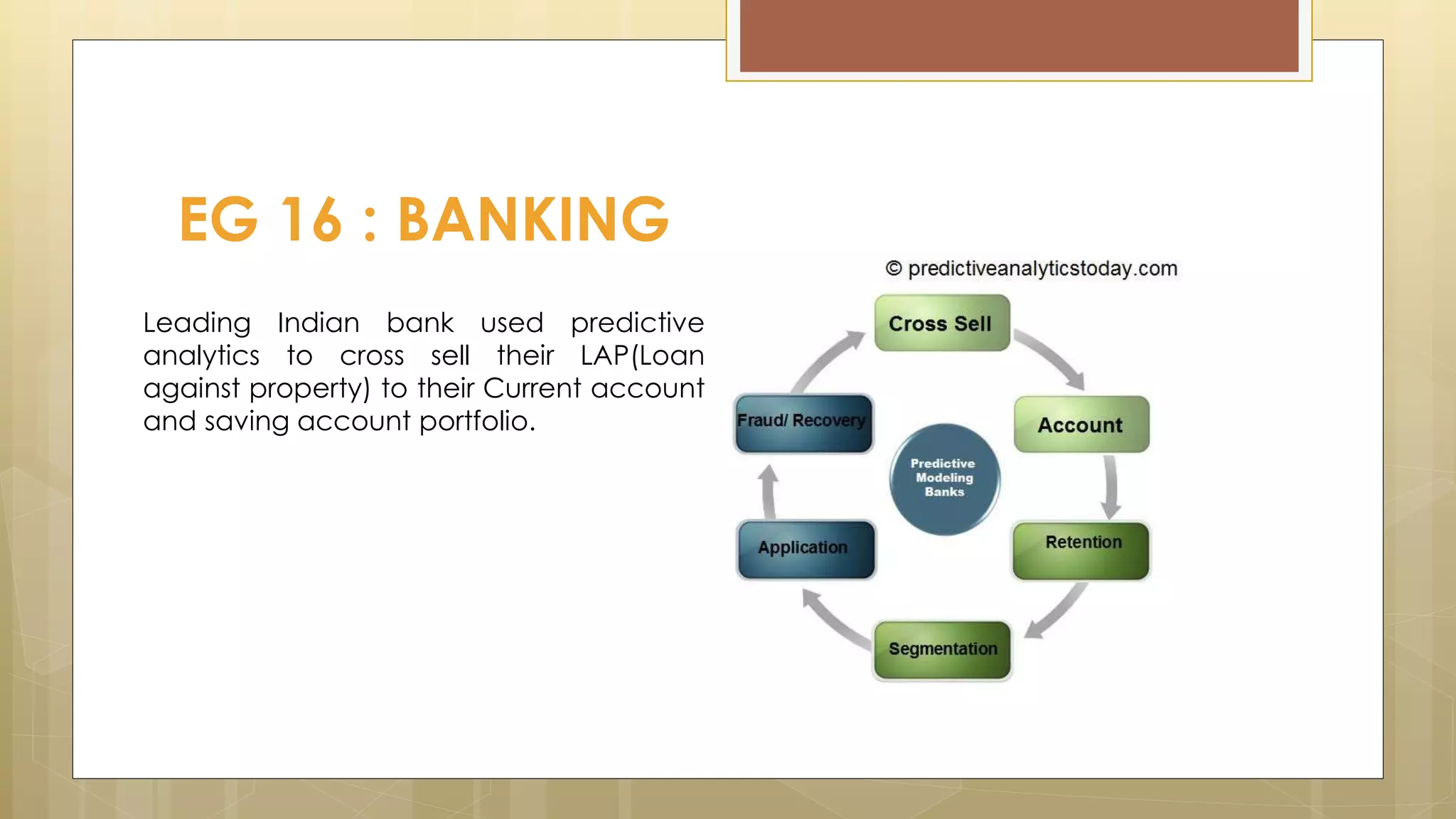
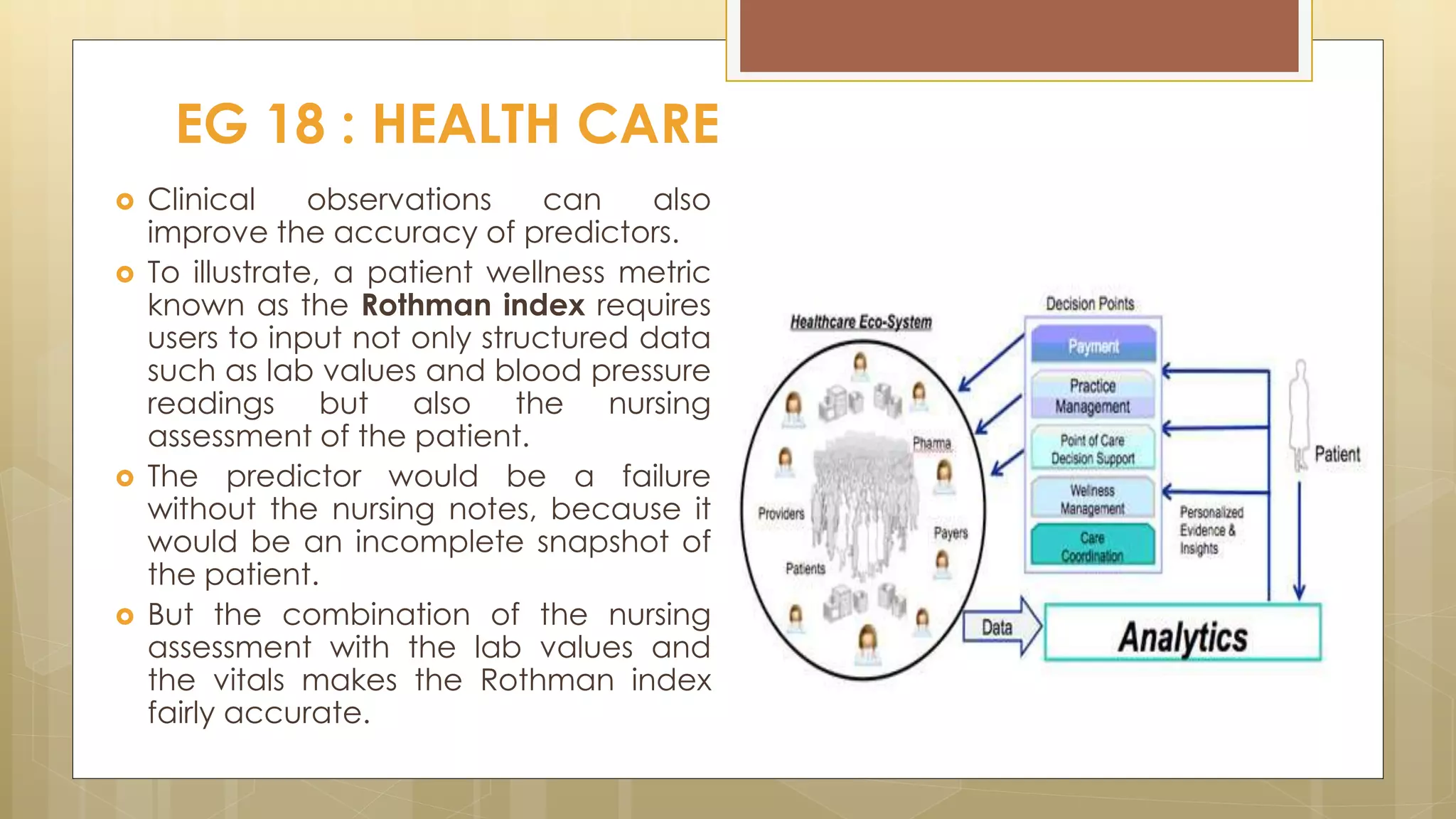
Prasad Narasimhan discusses various applications of predictive analytics across different domains including business, marketing, operations, collections, customer segmentation, telecom, sports, social media, and insurance. Predictive analytics uses statistical techniques to analyze current and historical data to predict future events or outcomes. It has various uses such as predicting customer churn, credit risk, response to marketing campaigns, fraud detection, and more. The document provides examples of how predictive analytics is applied in areas like customer retention, cross-sell, collections, credit risk management, and churn prediction in telecom.