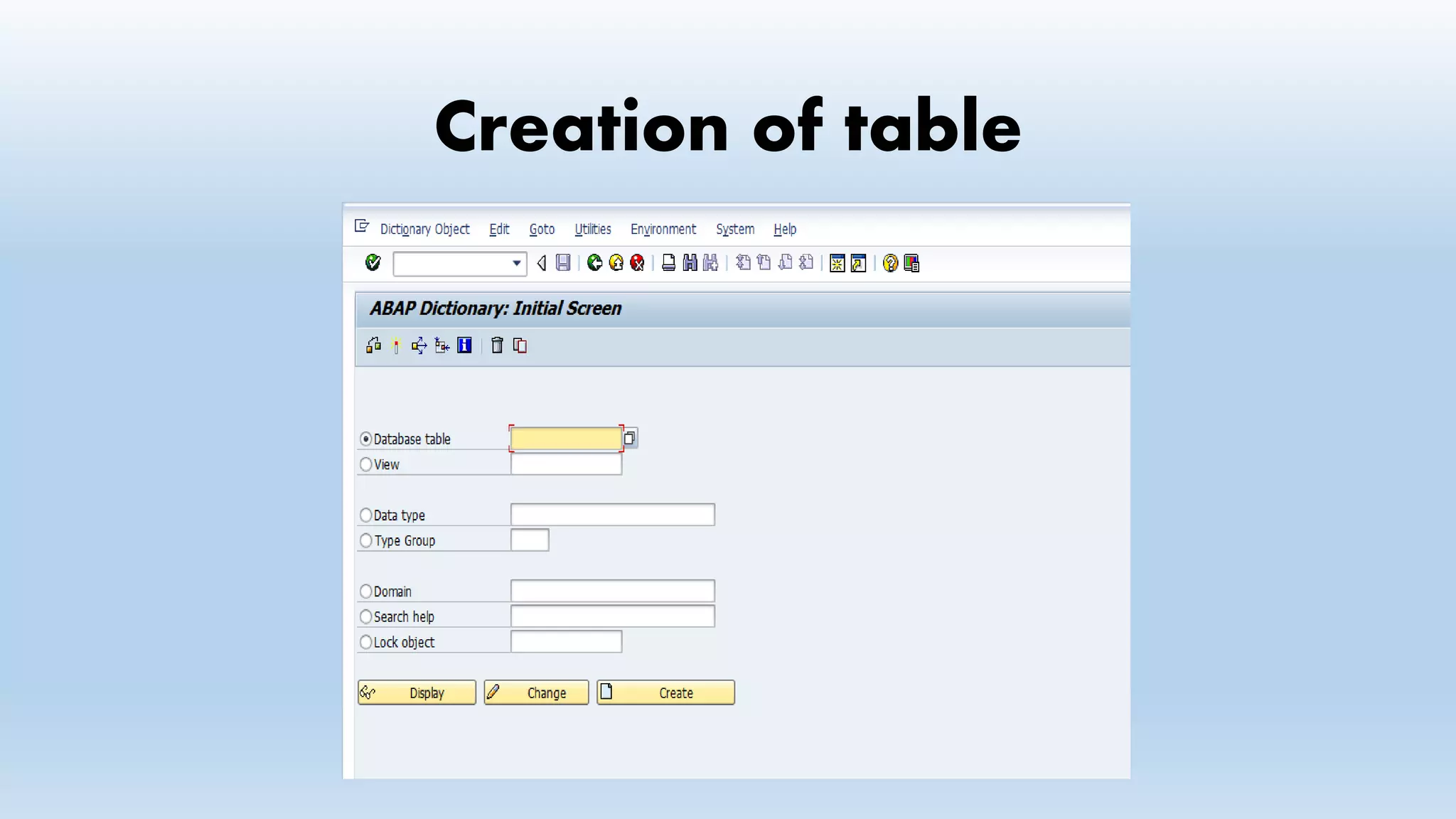
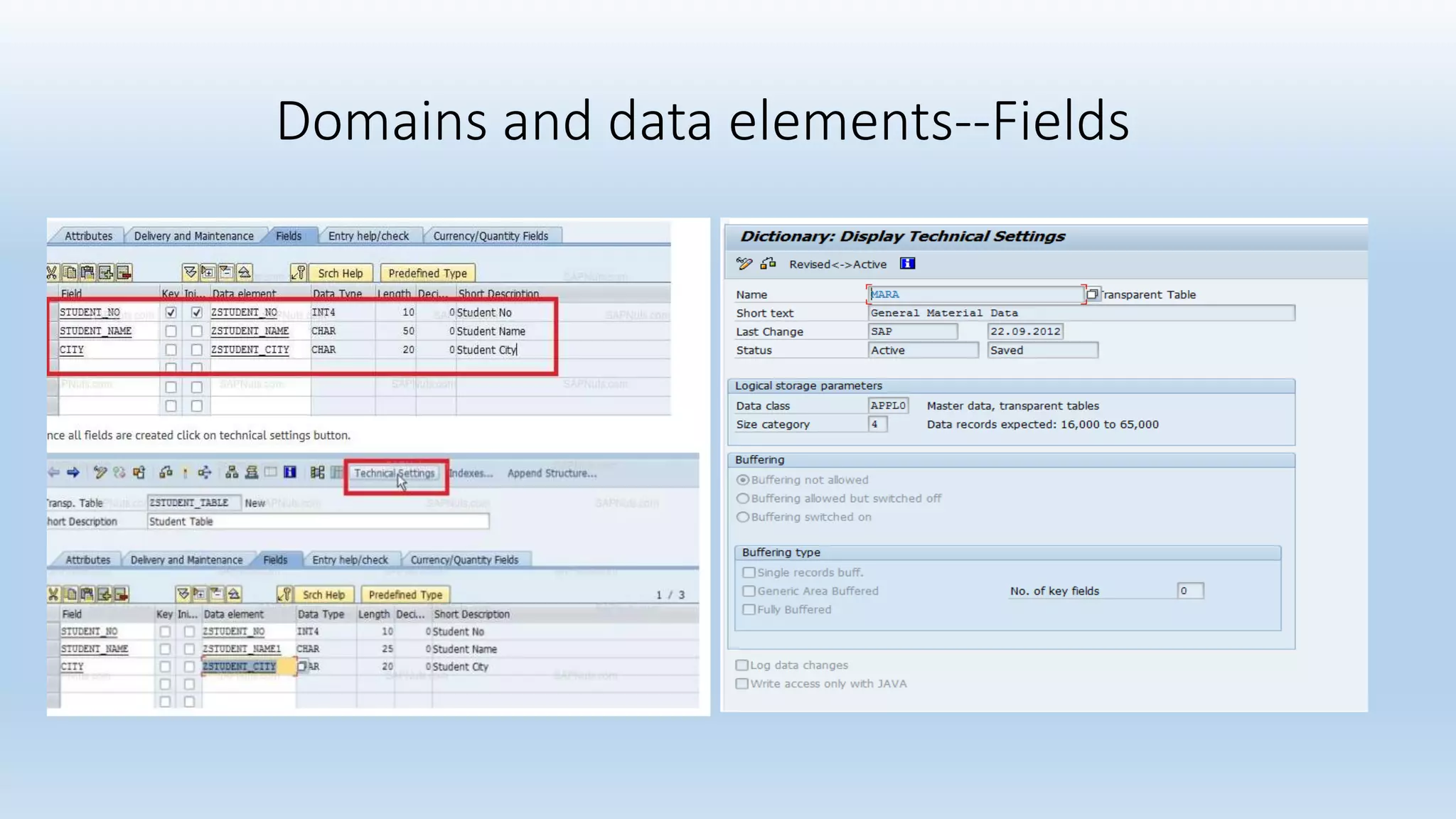
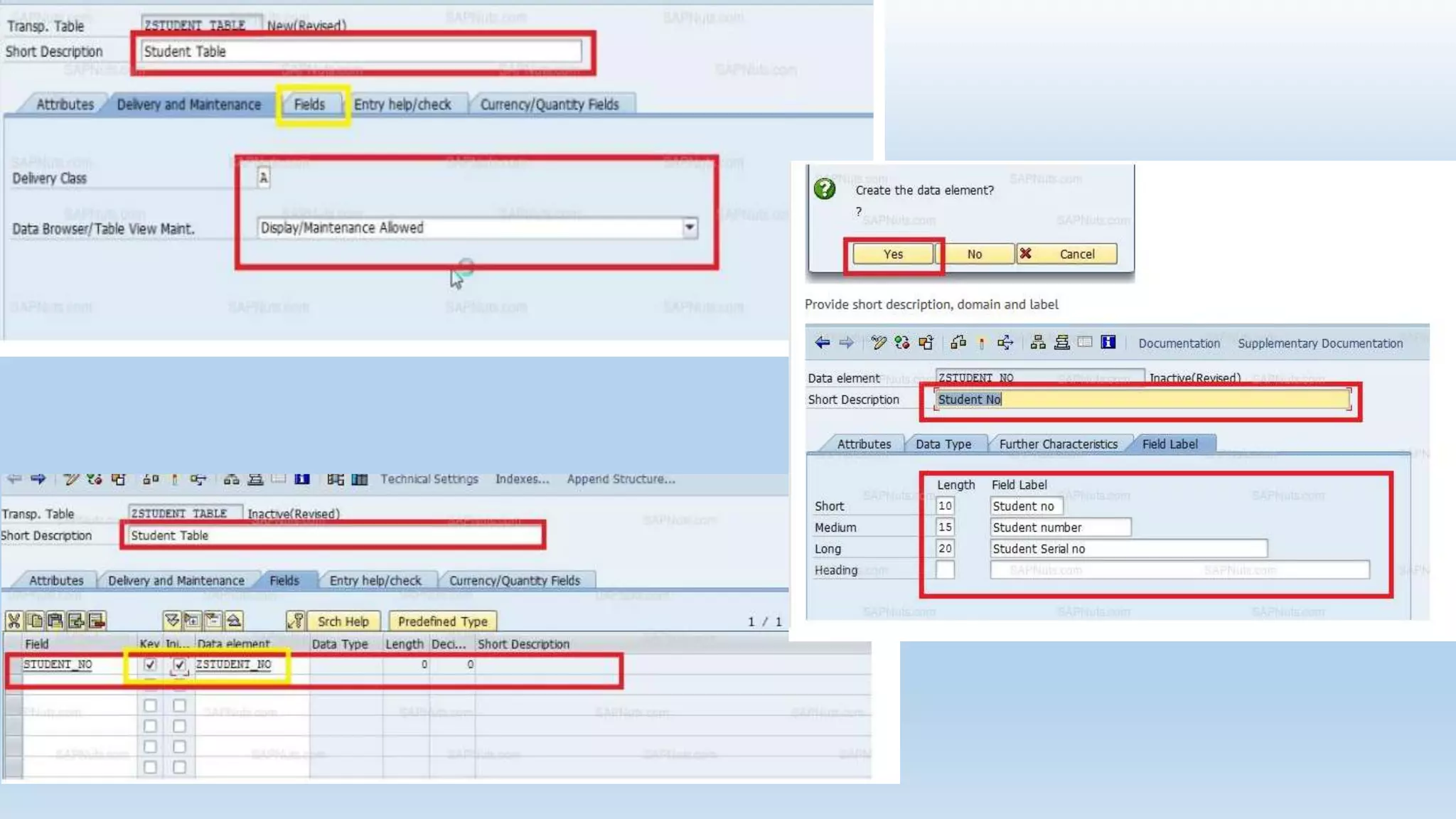
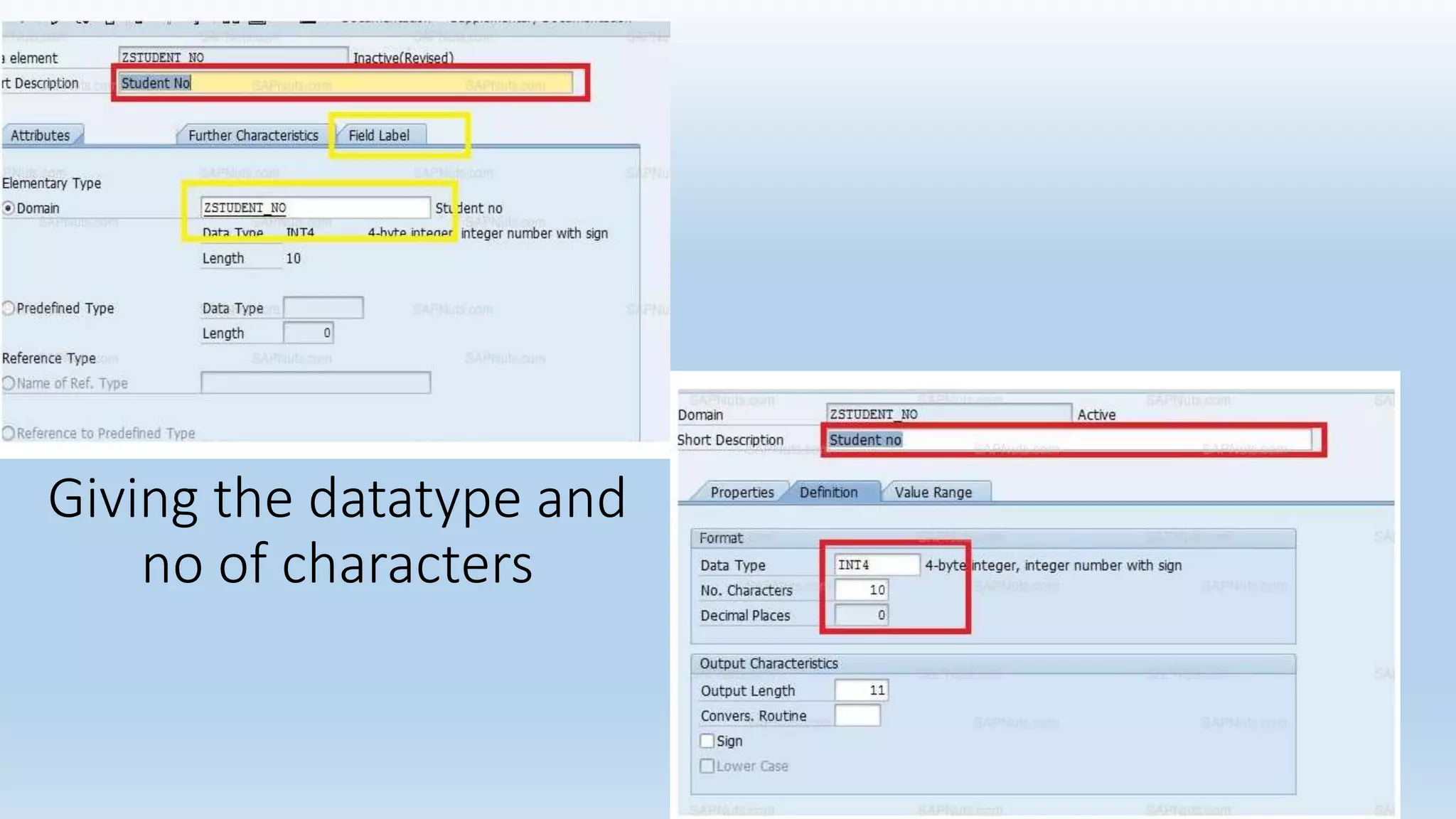
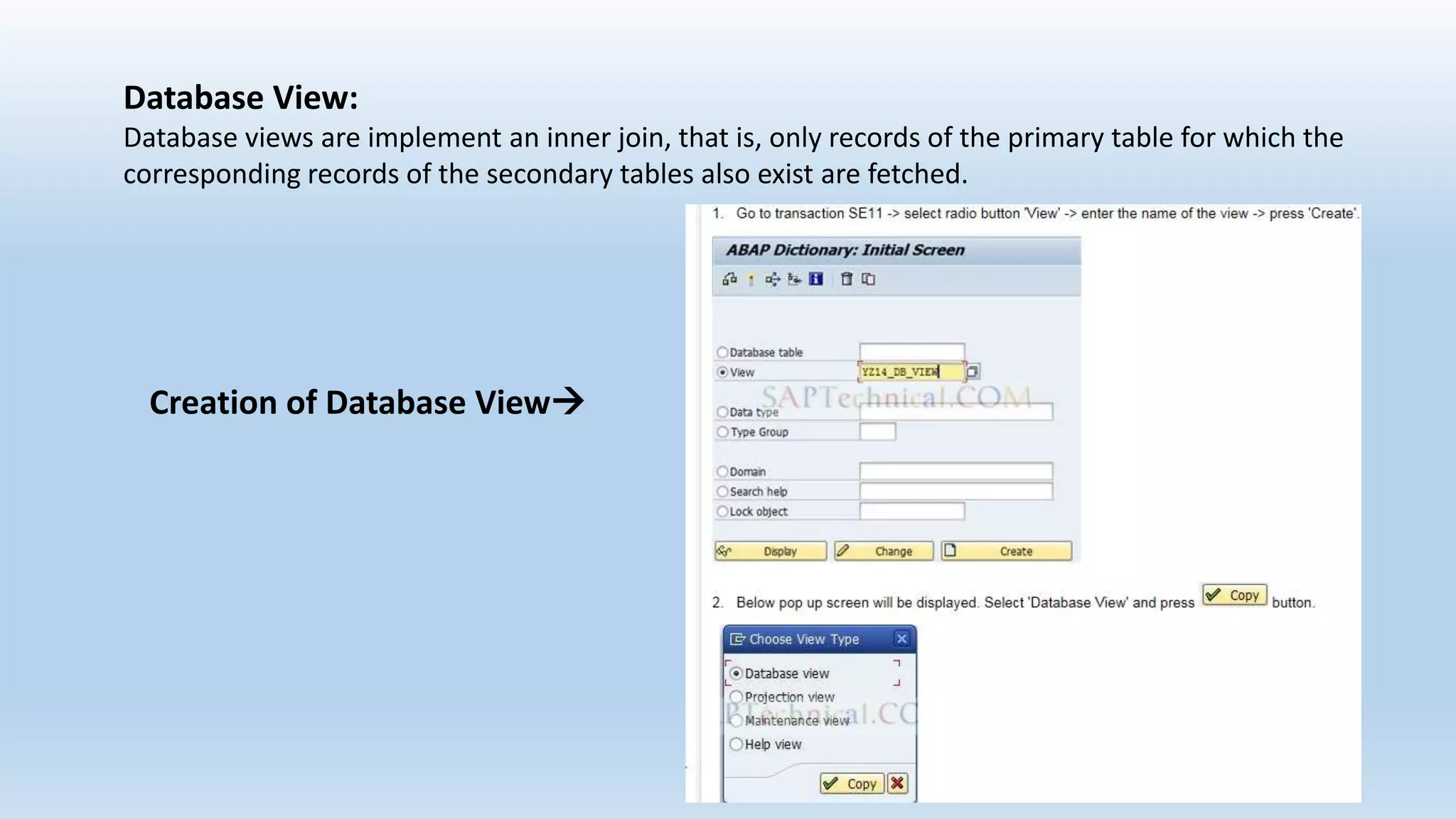
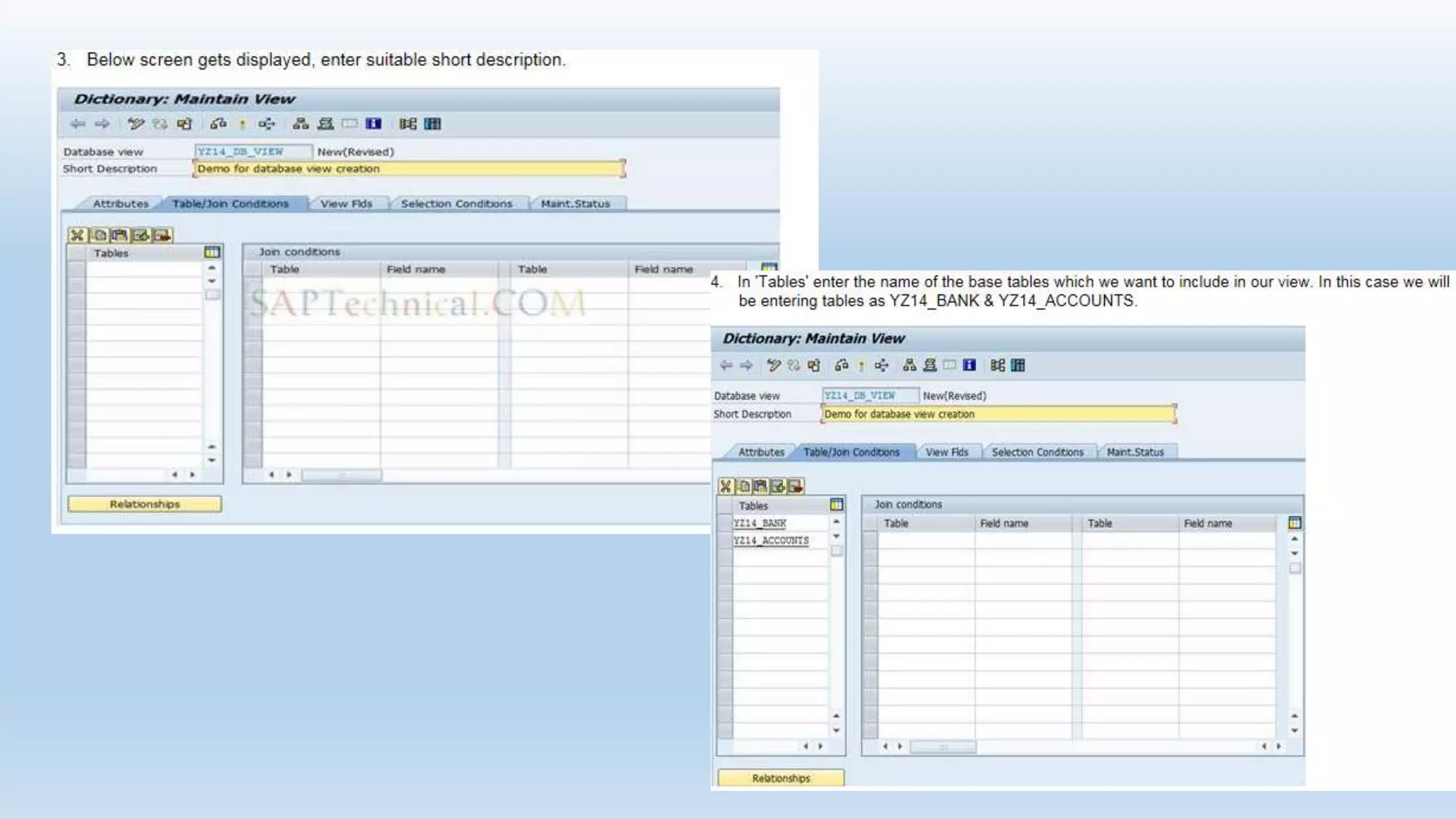
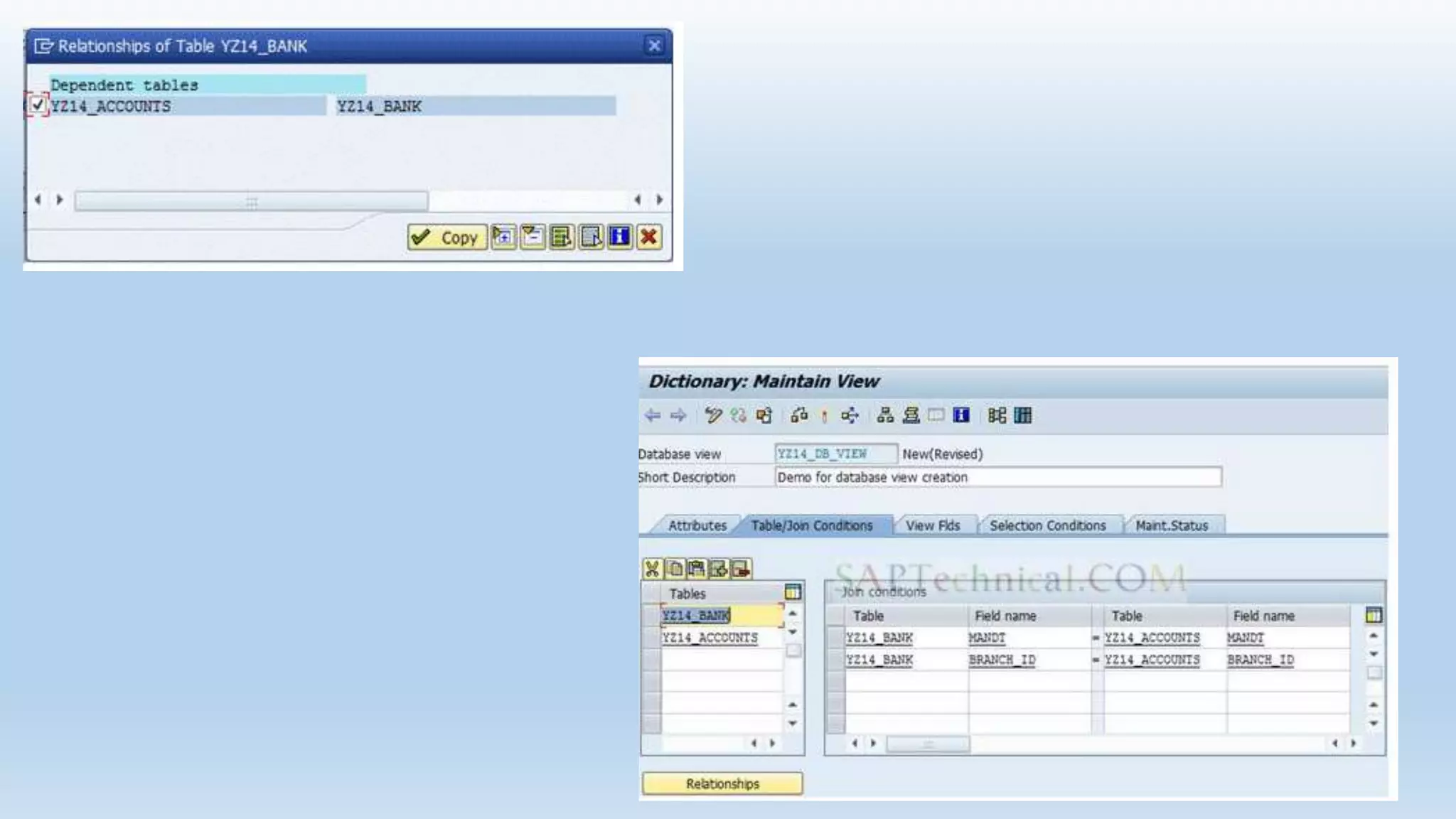
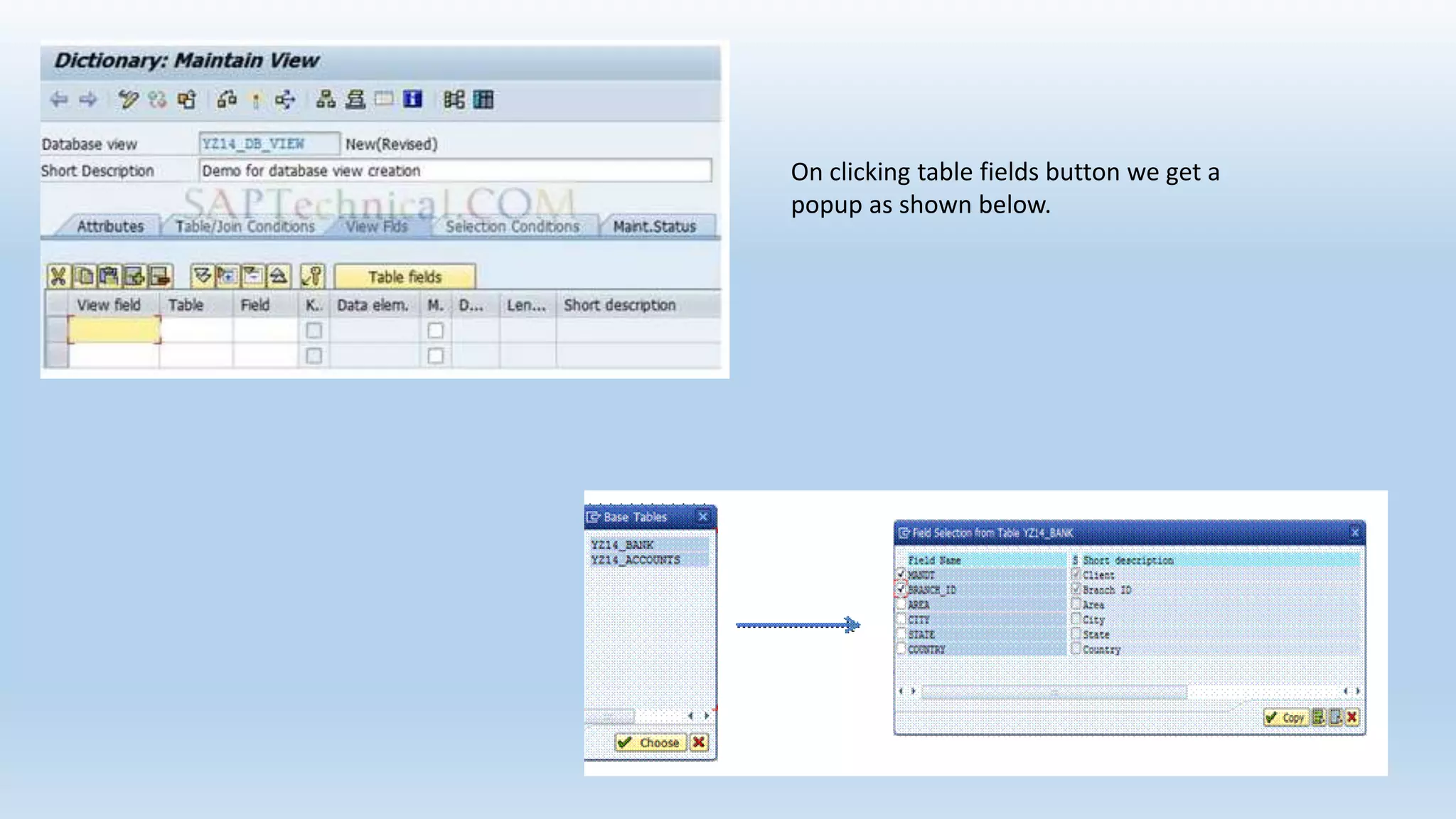
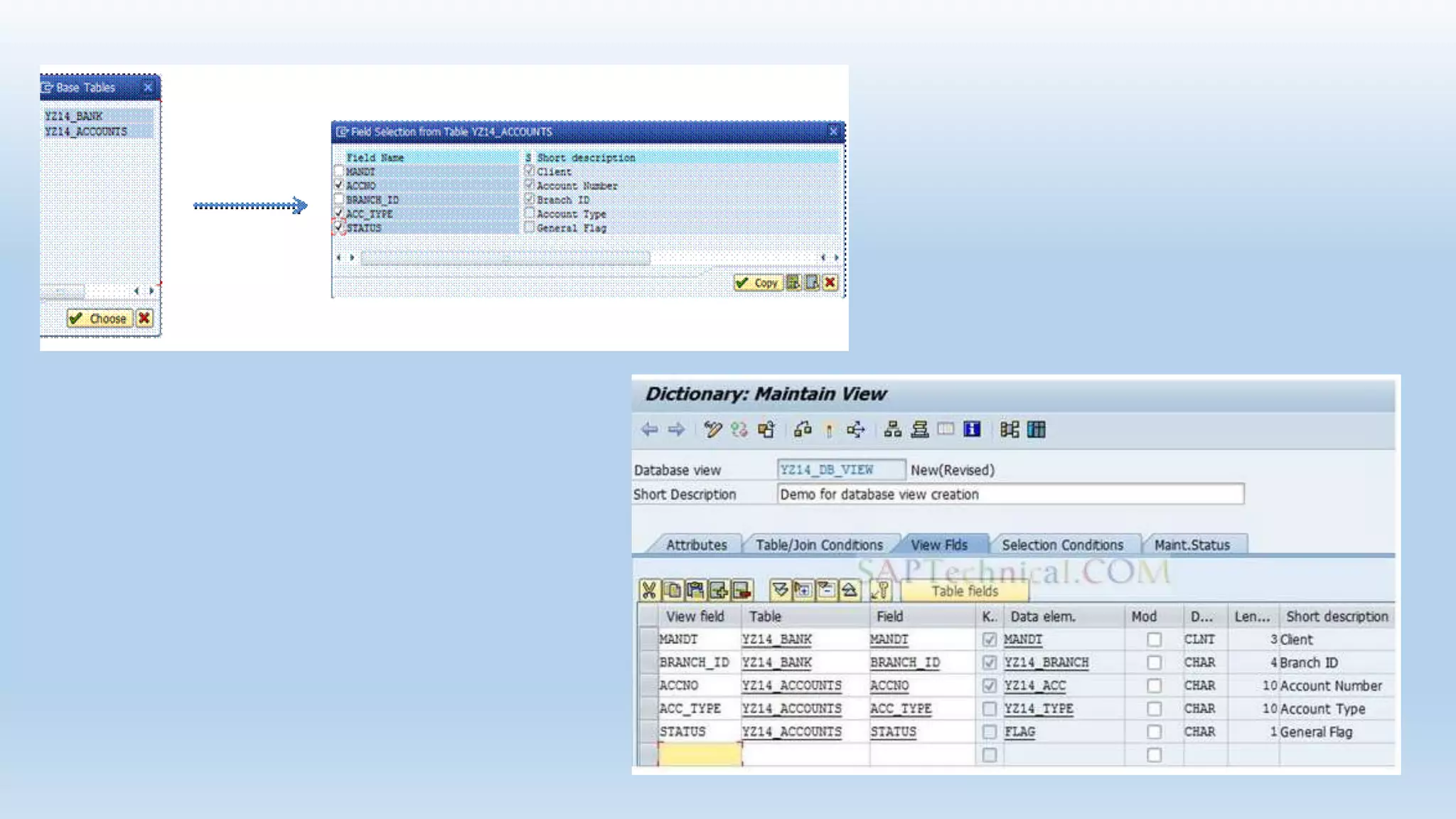
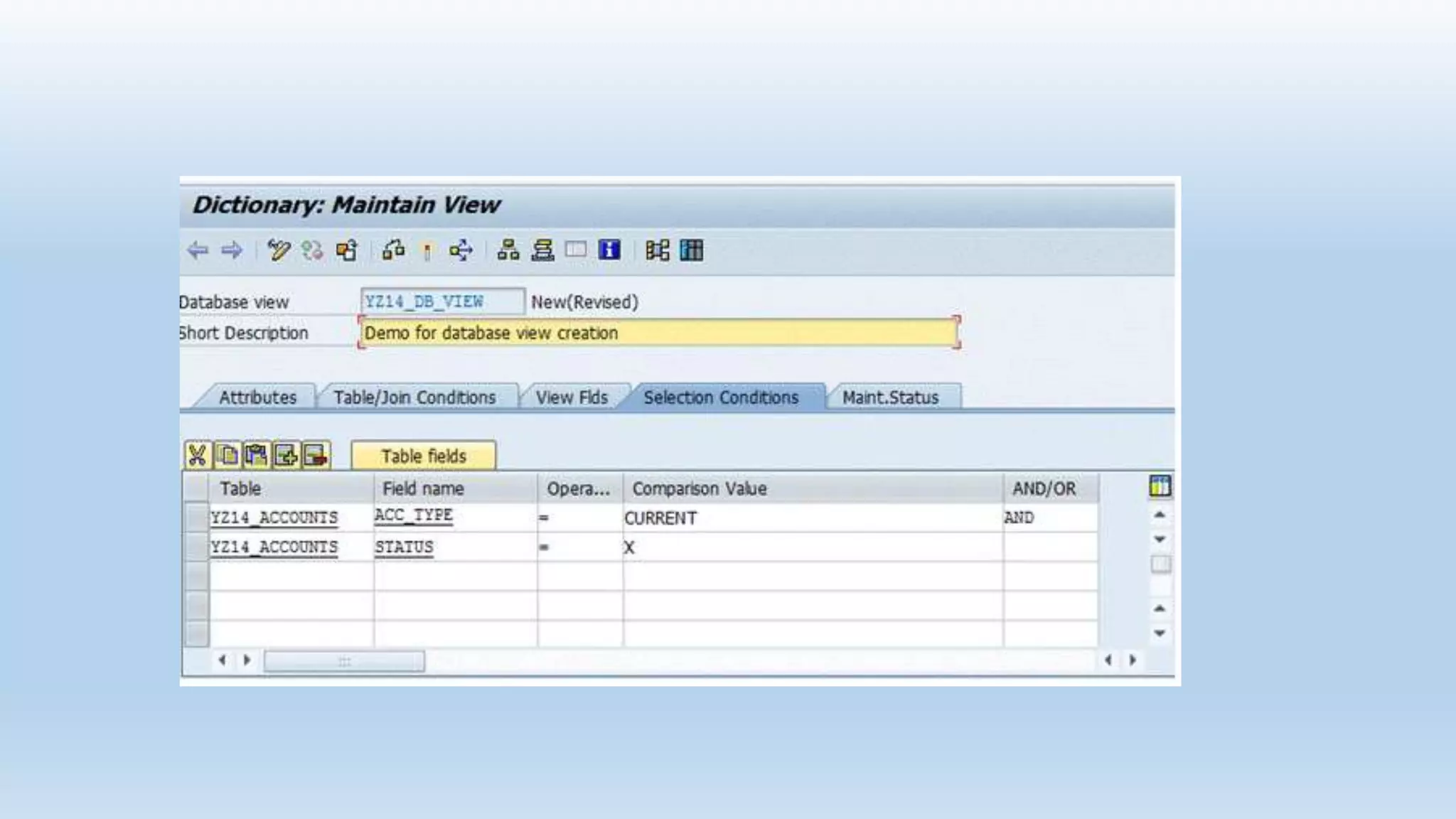
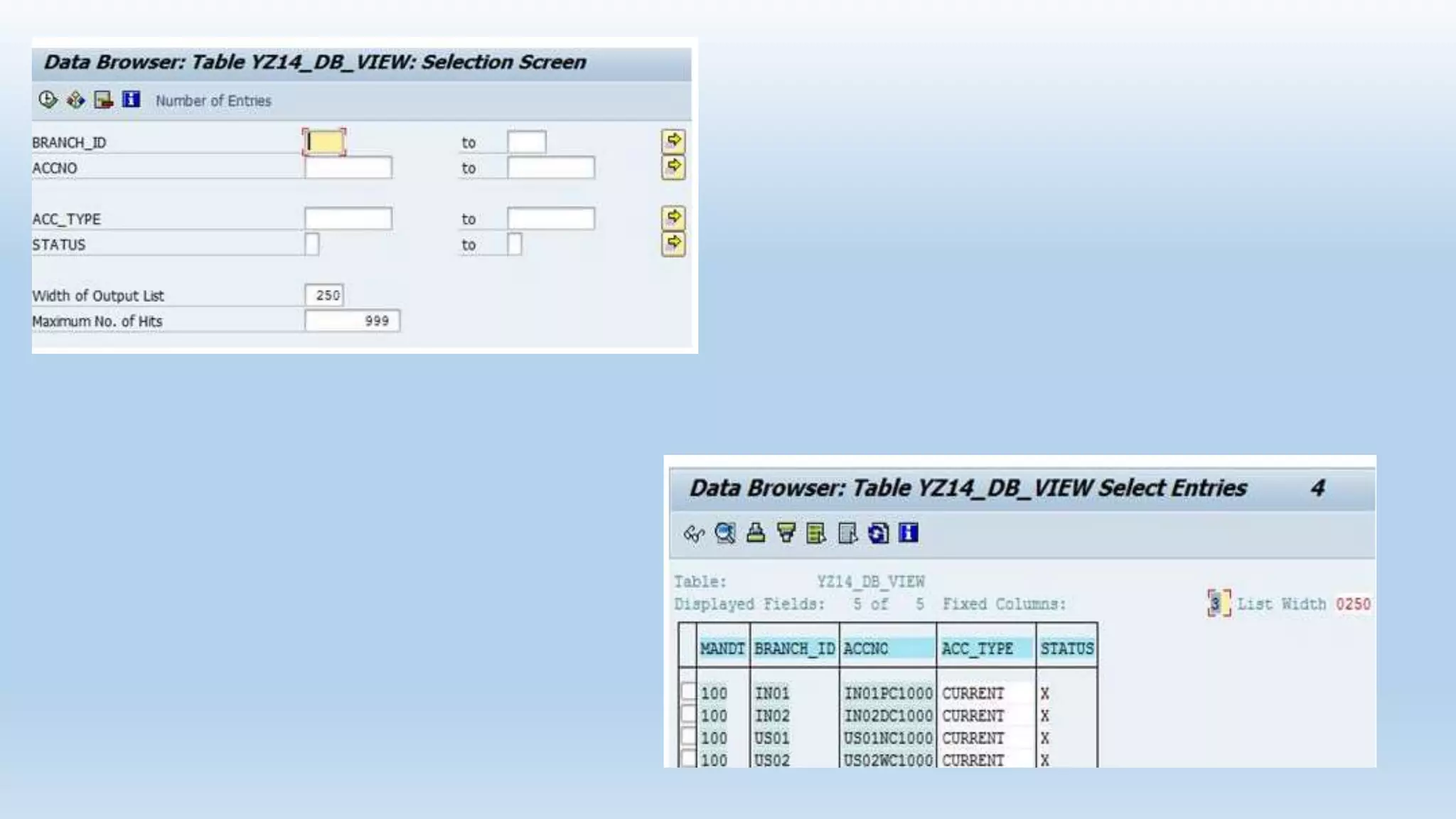
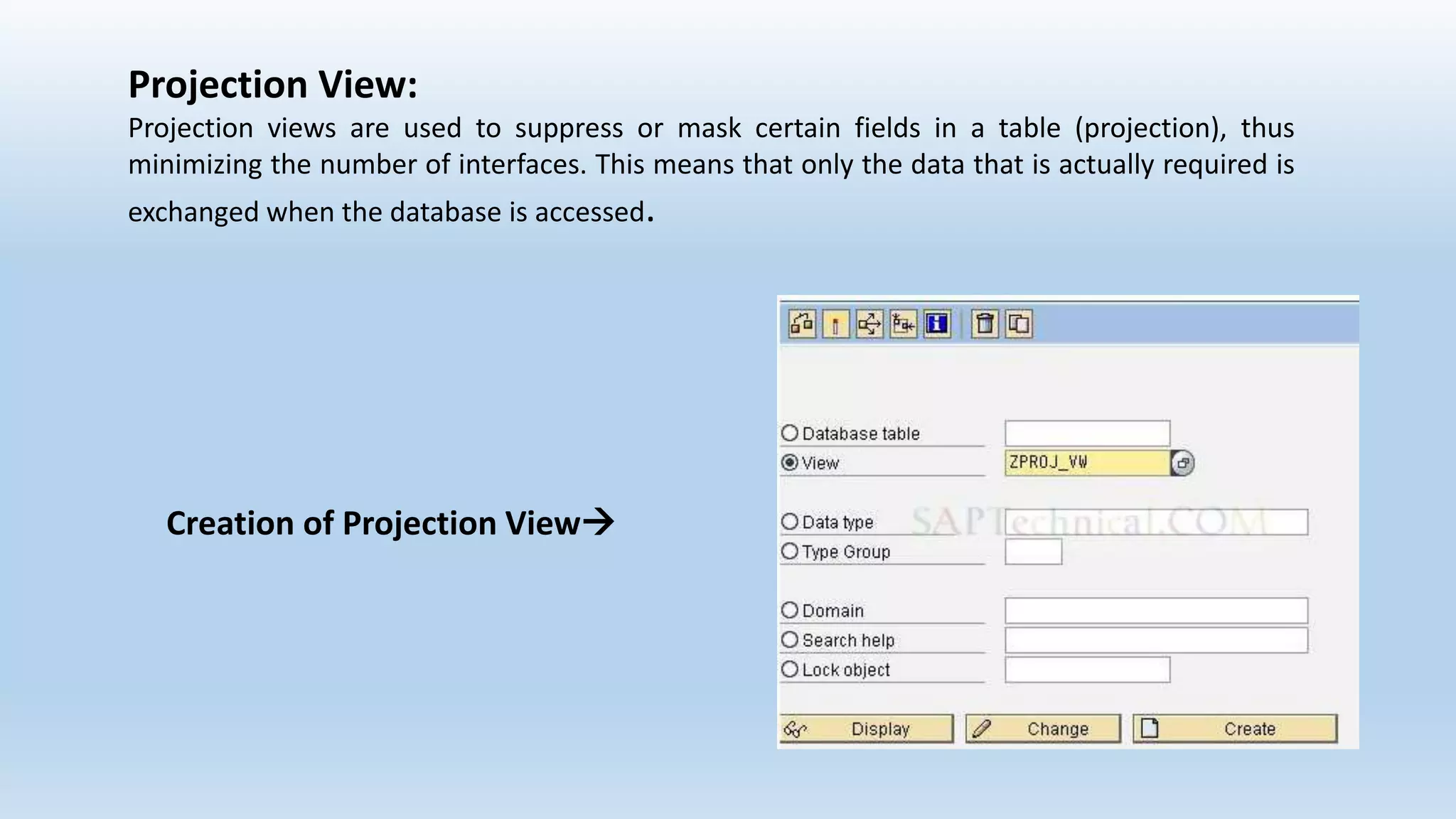
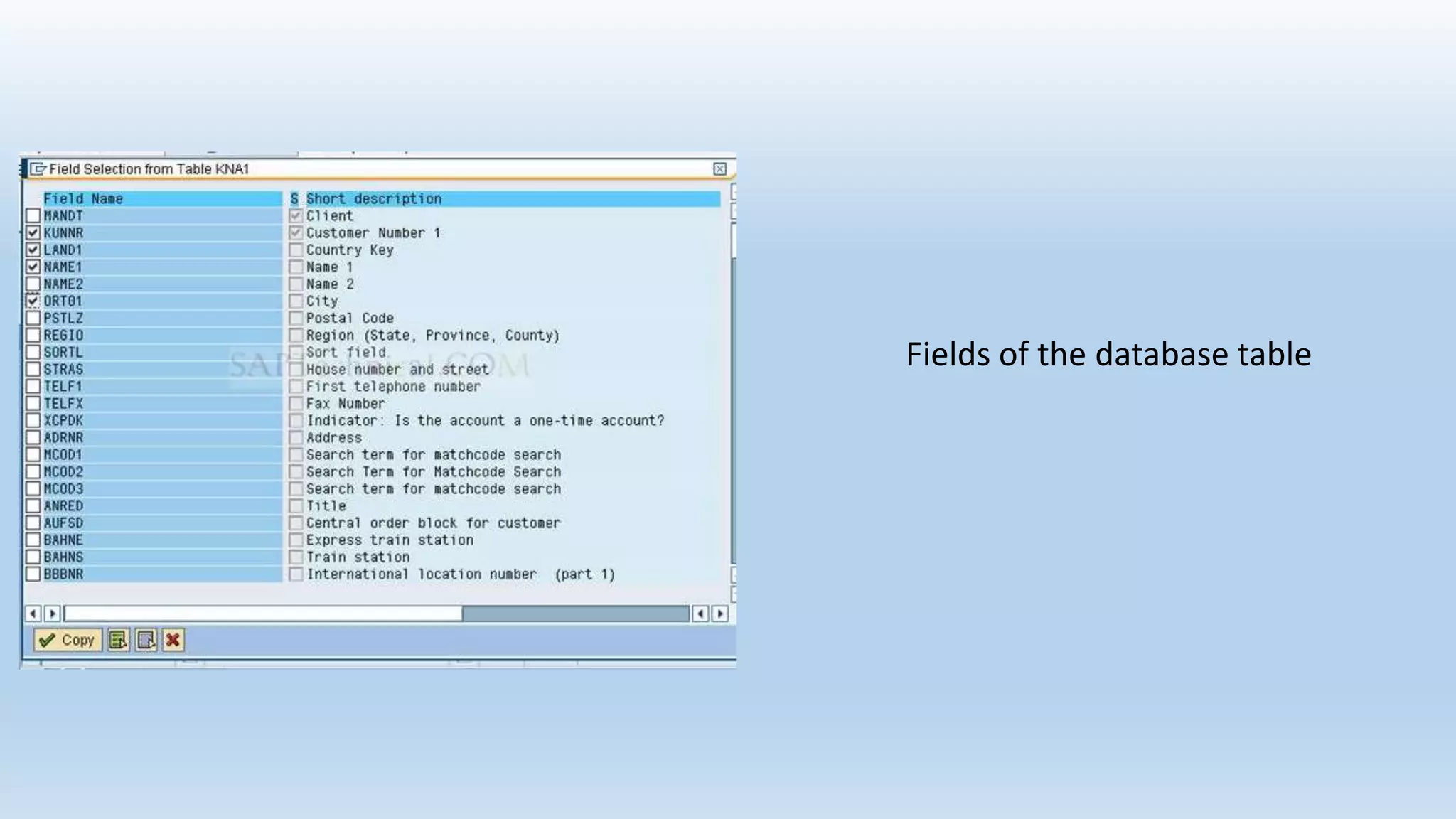
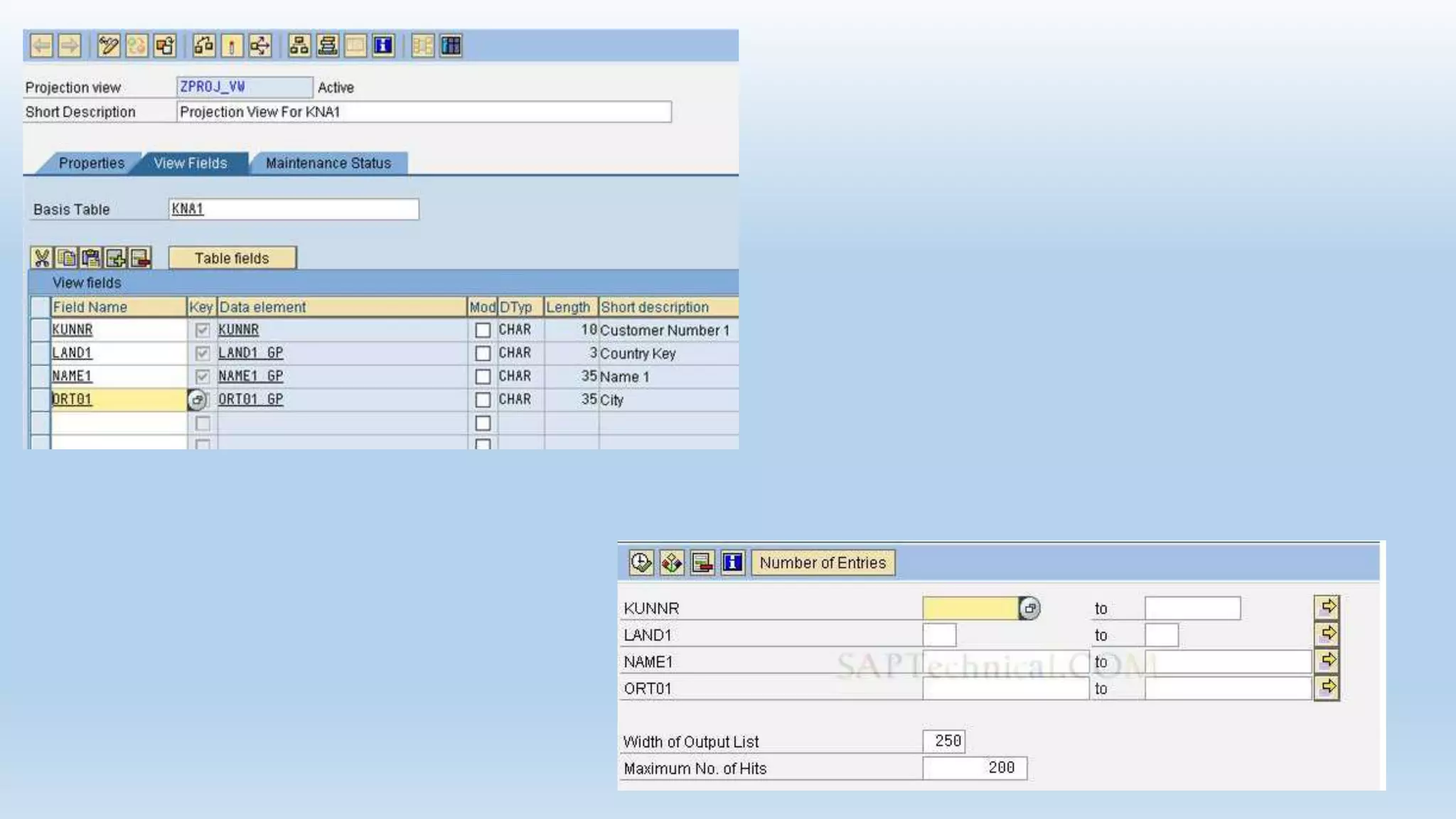
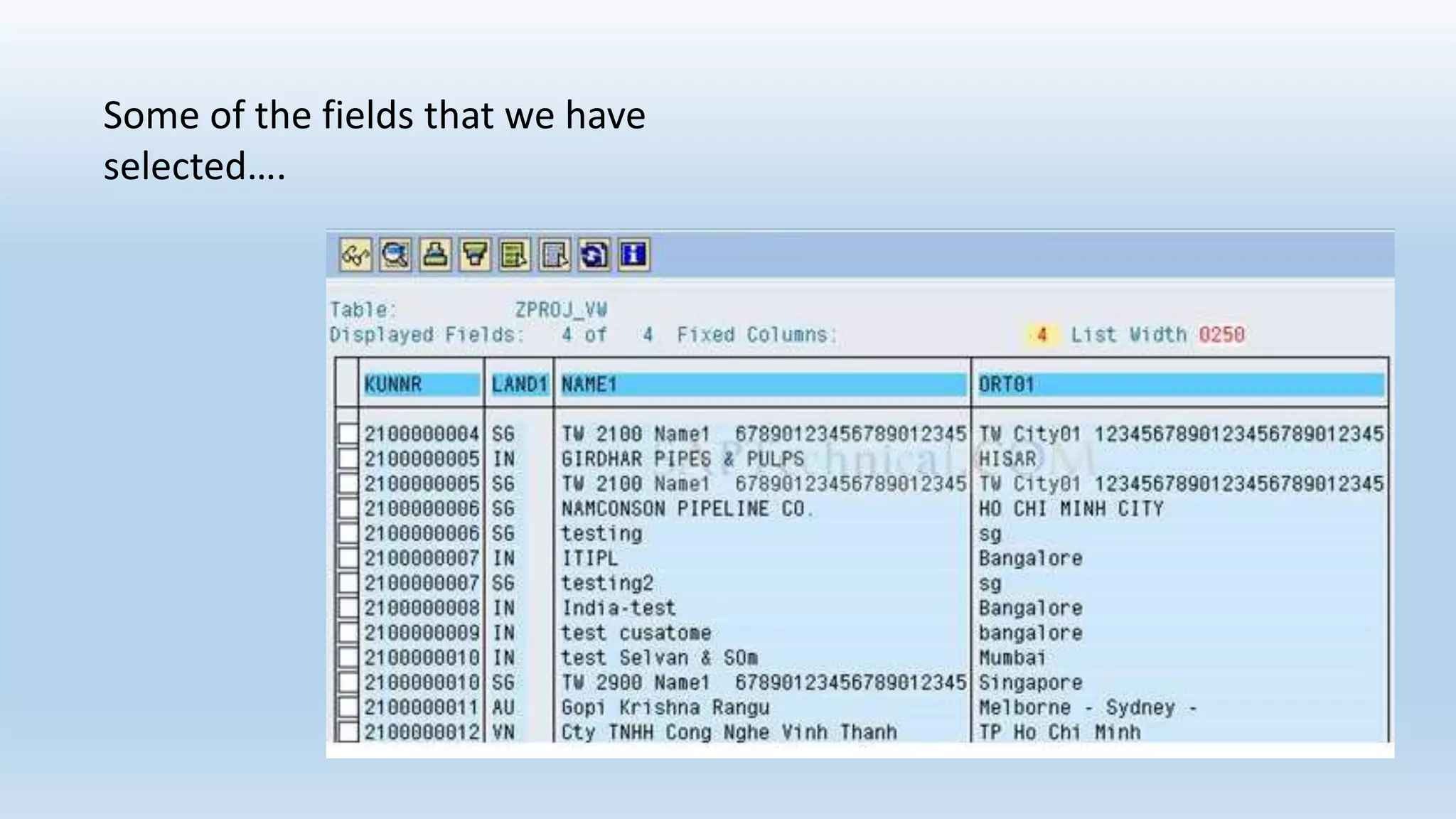
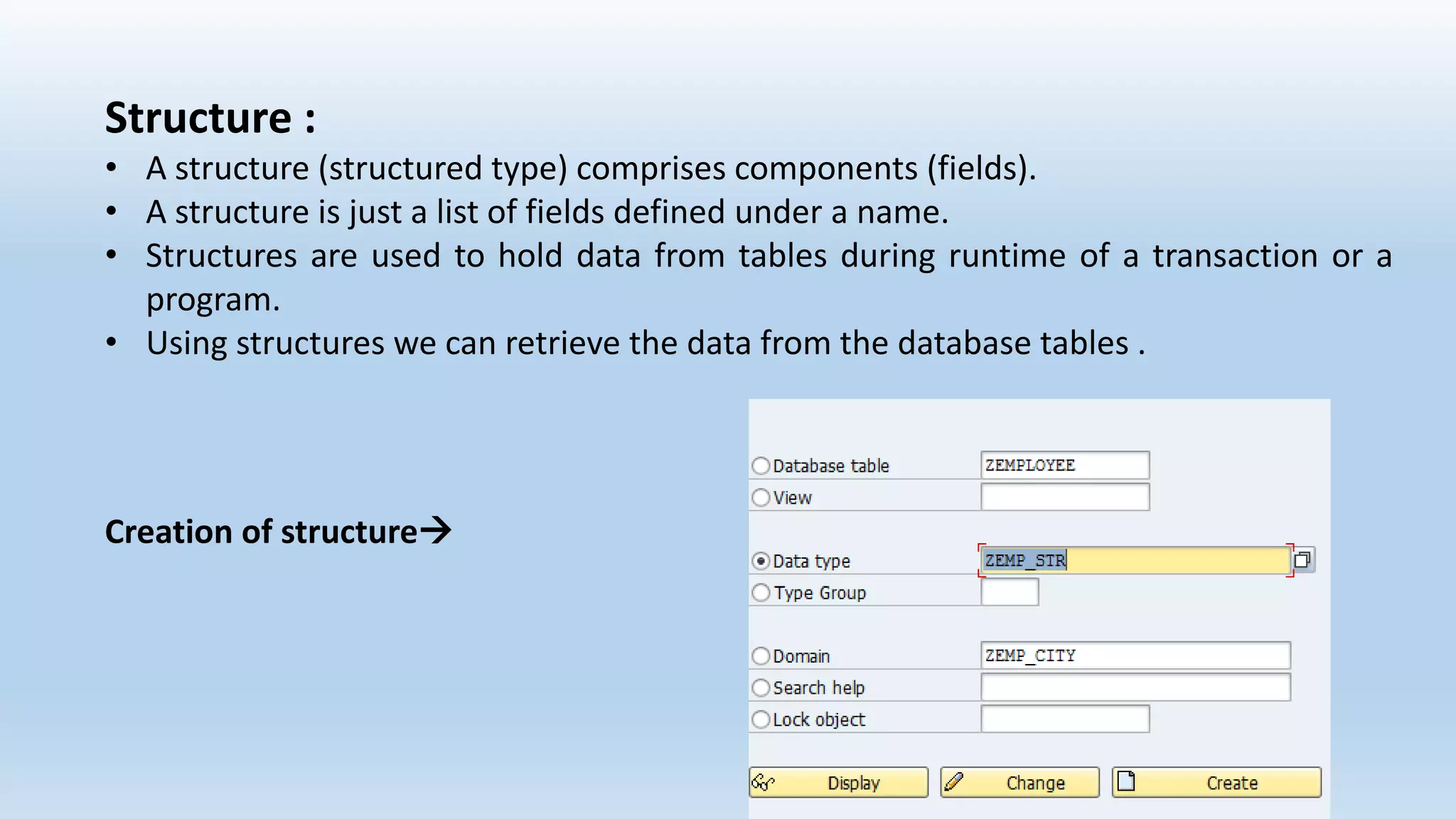
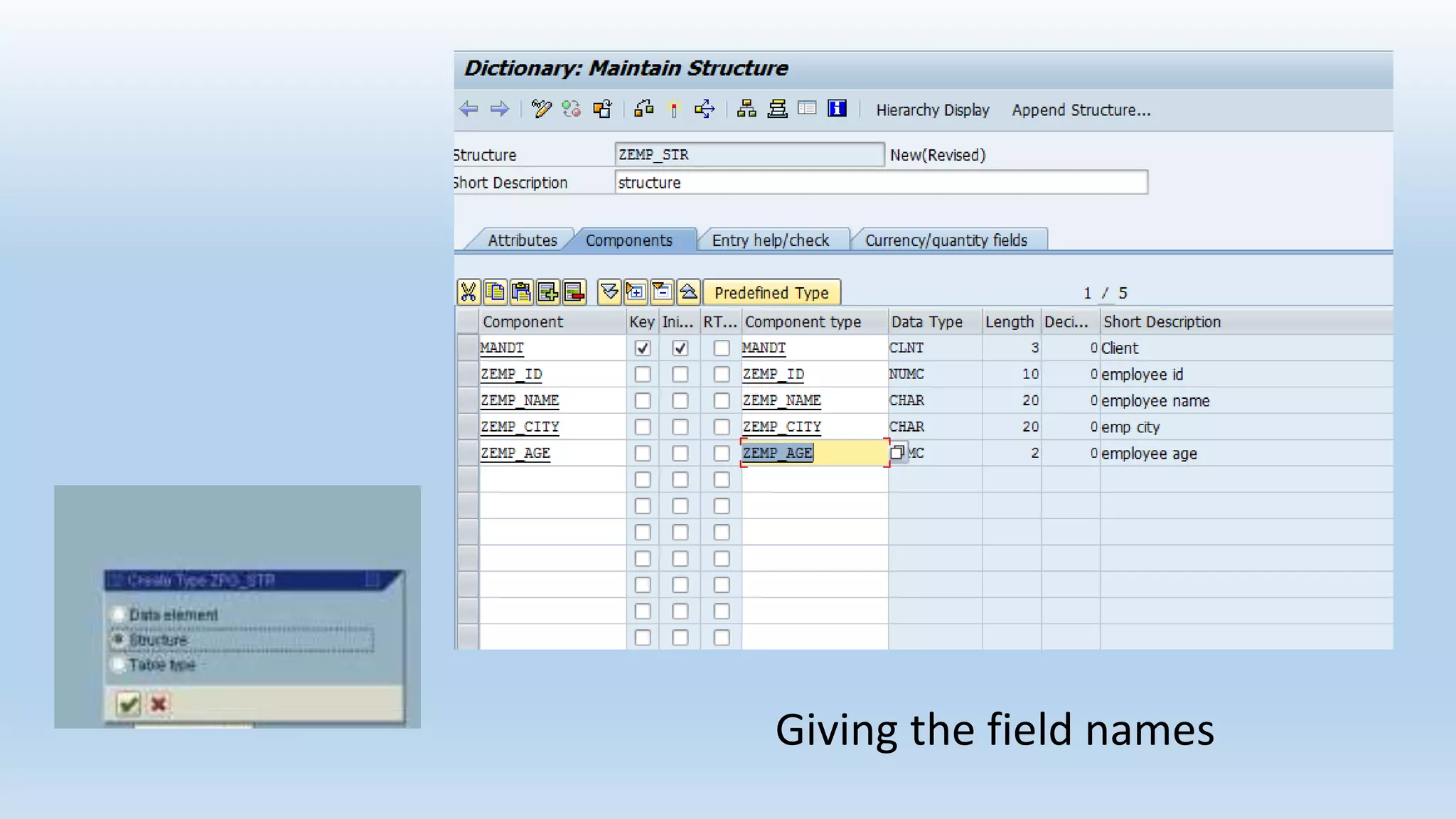
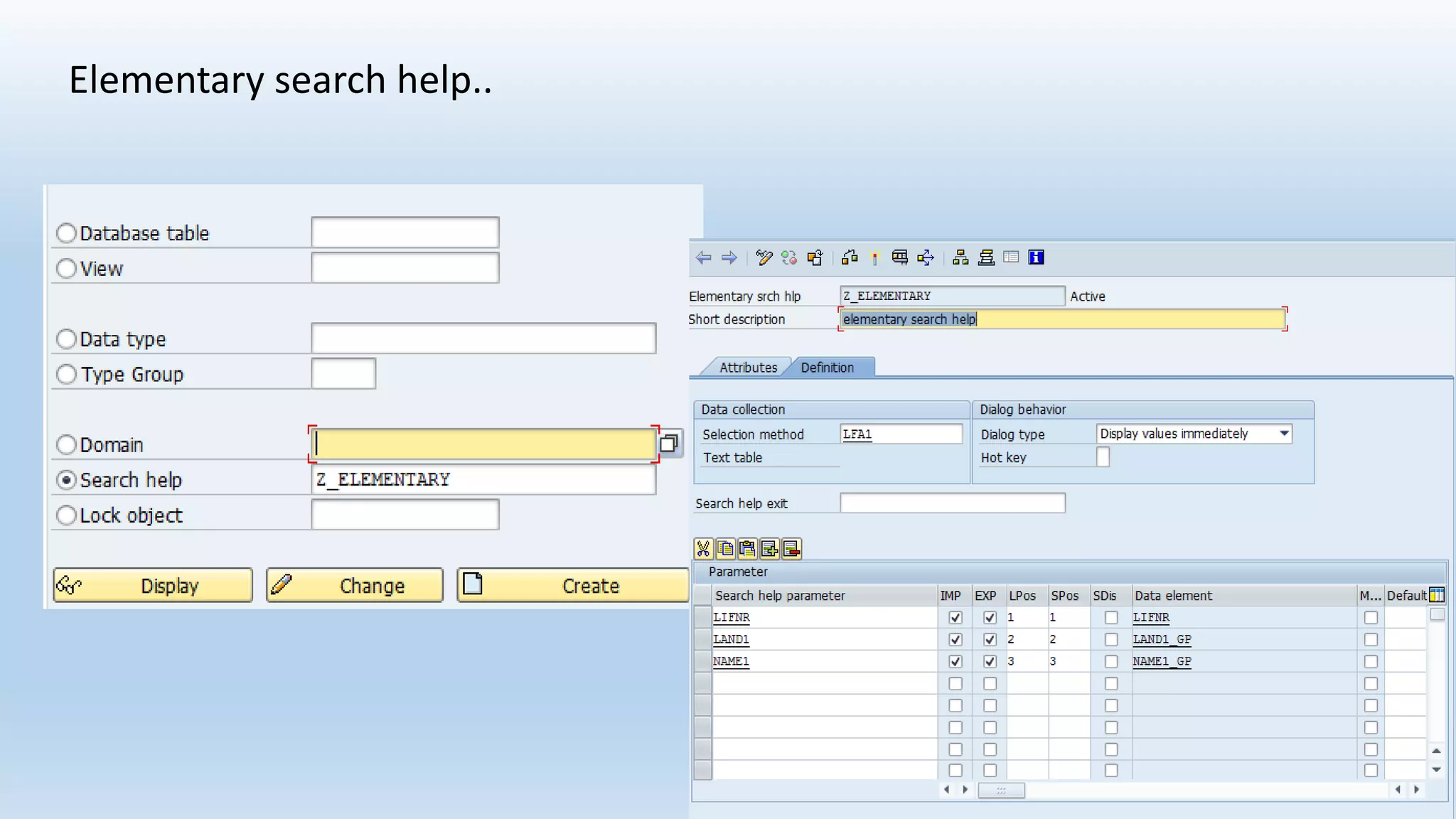
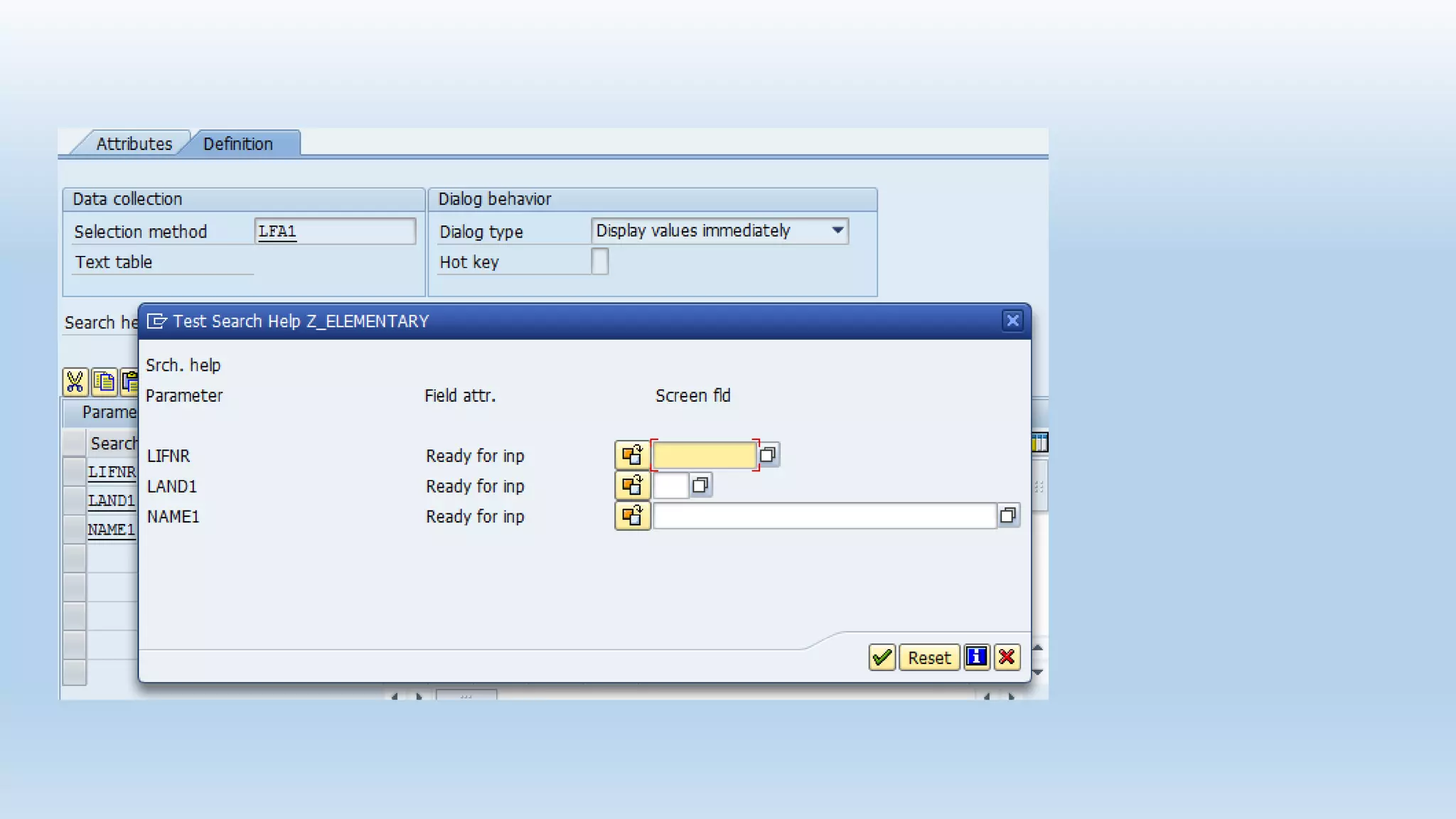
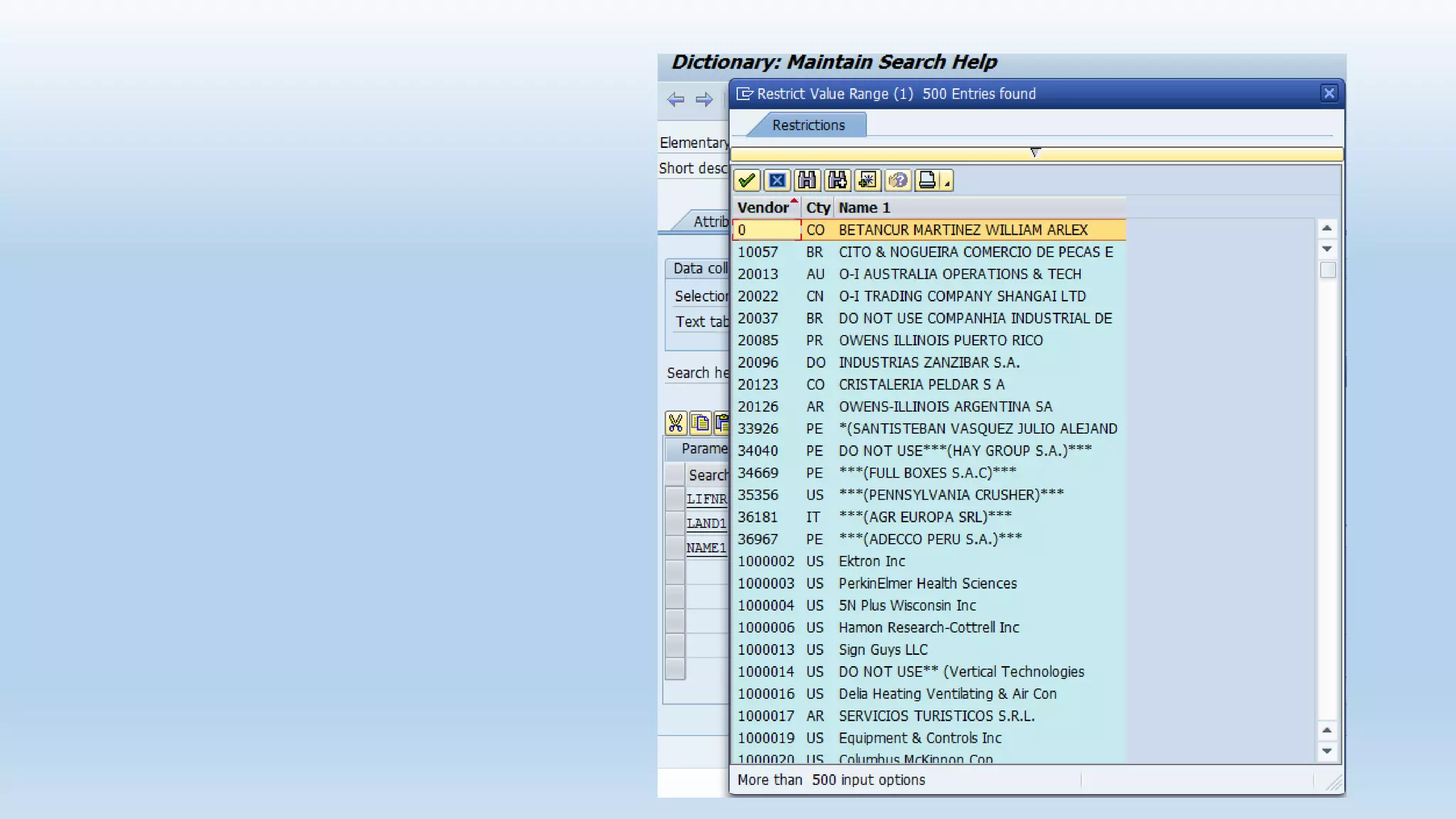
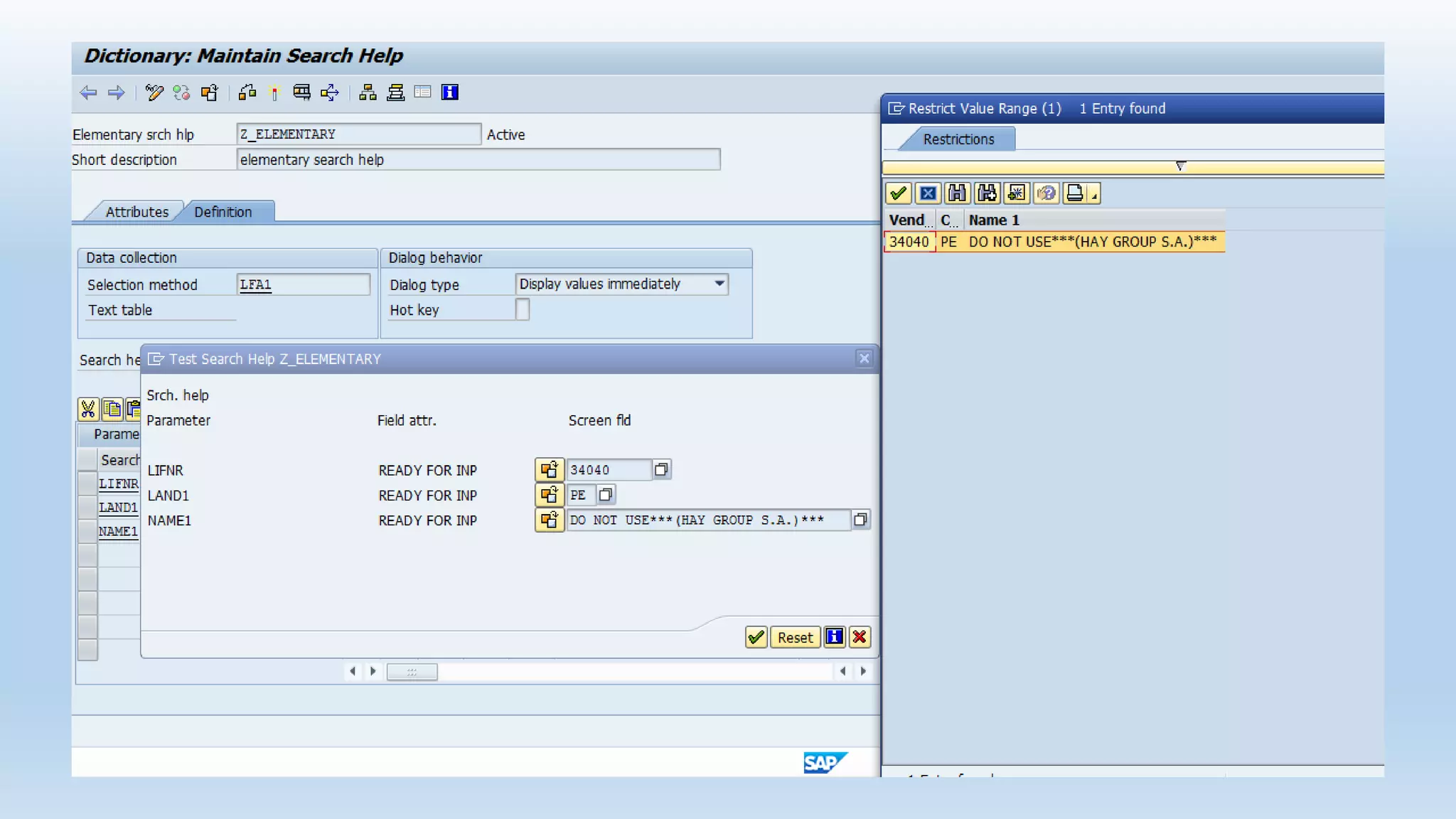
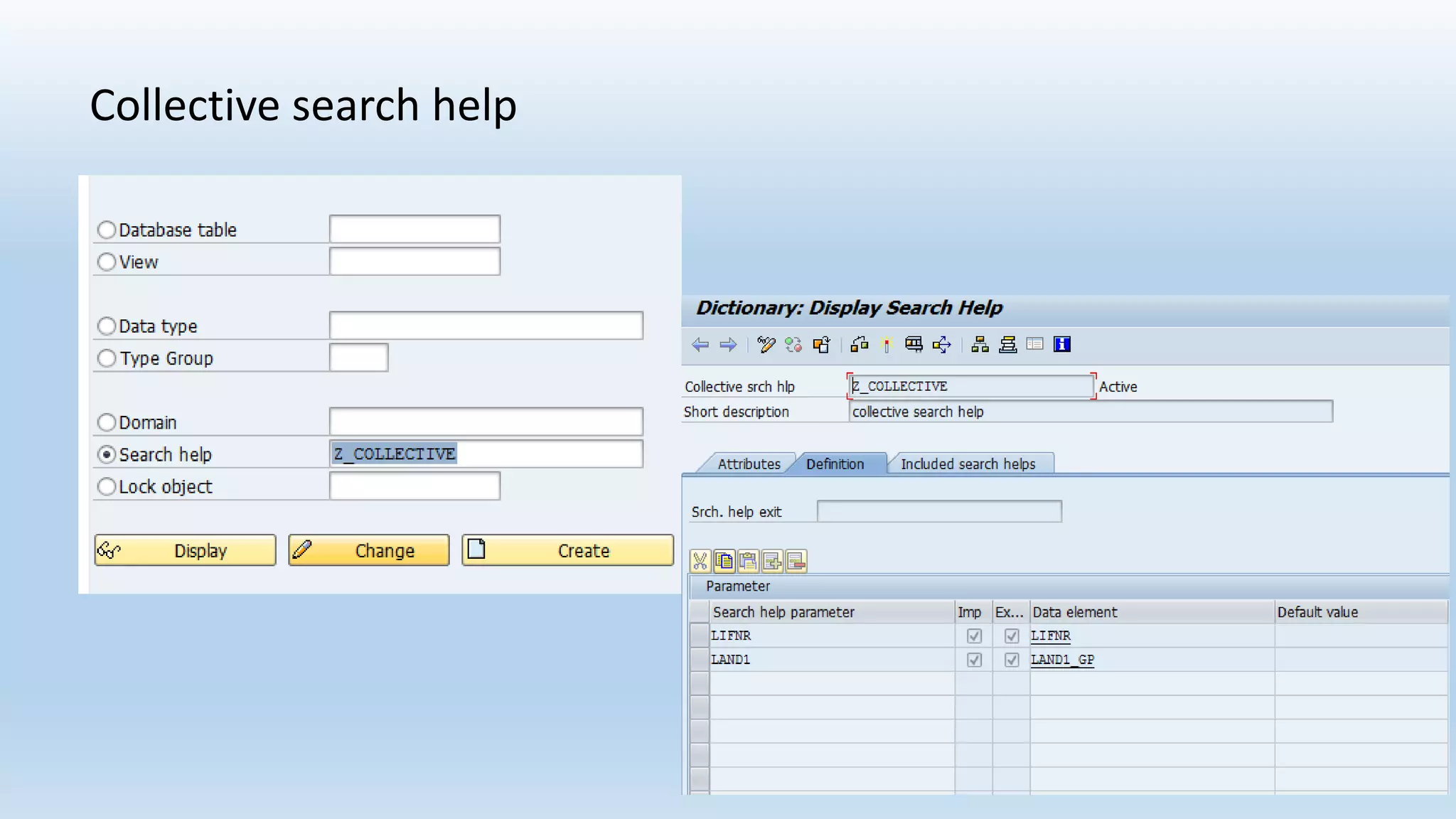
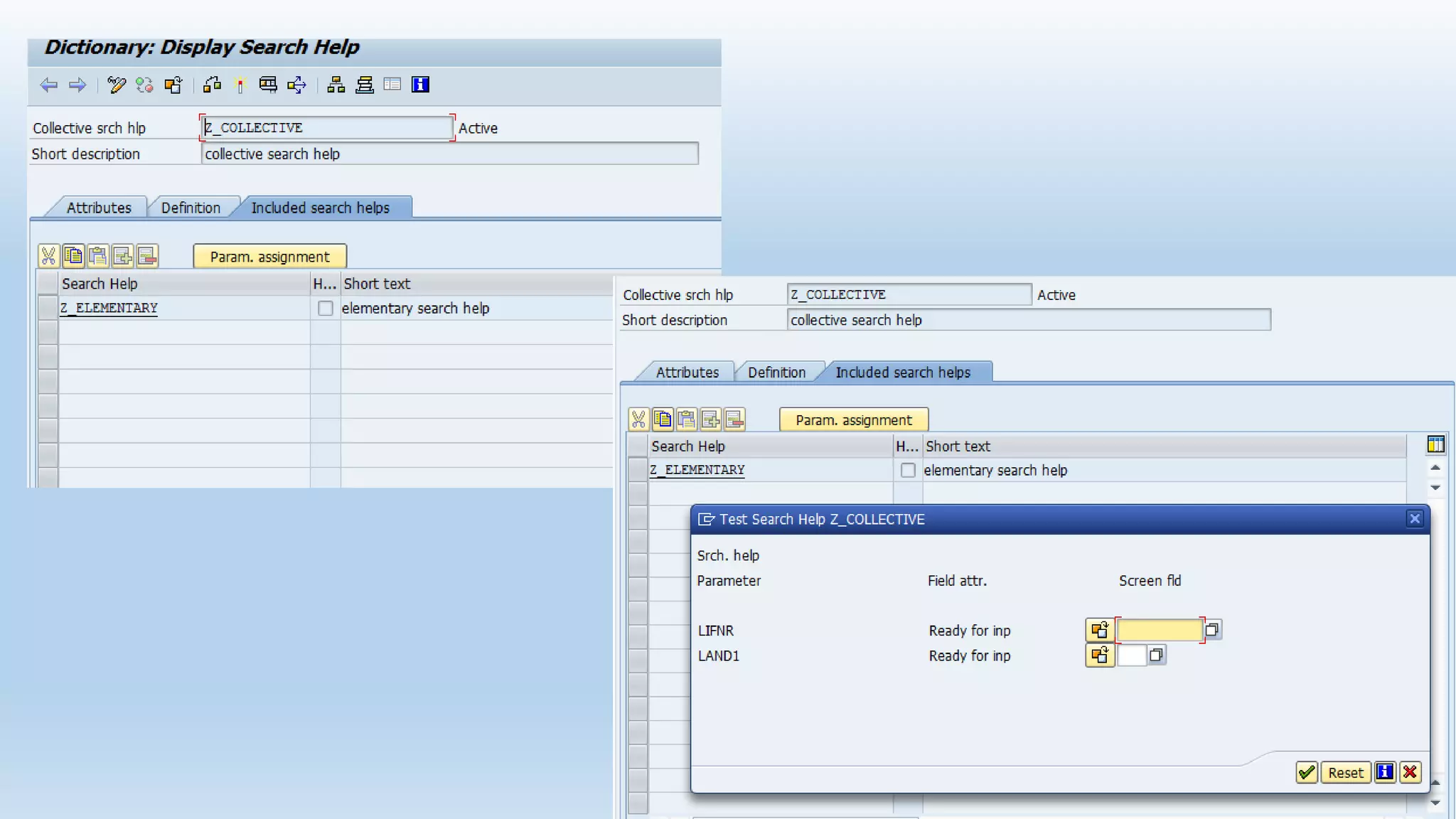
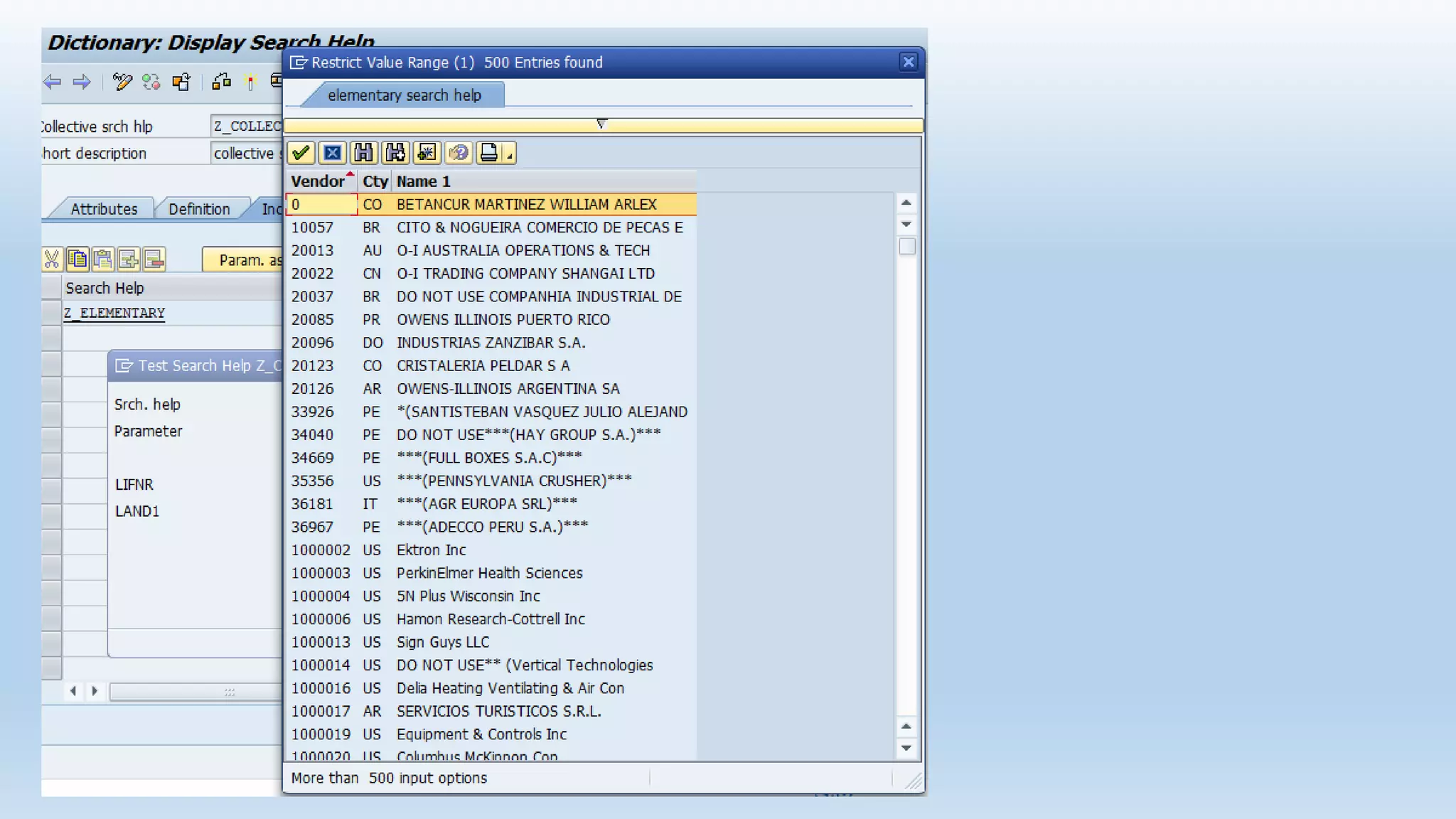
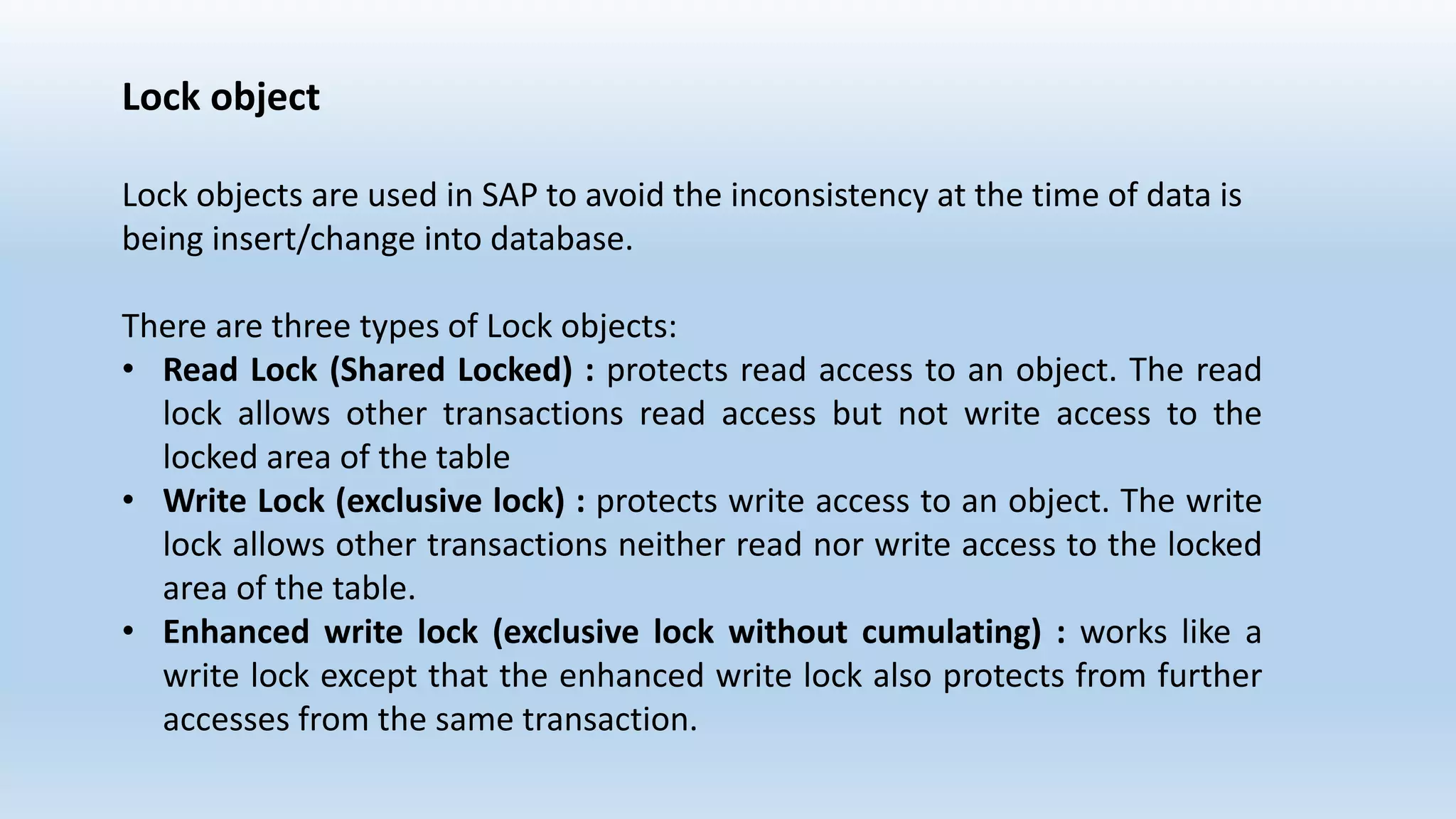
1. The data dictionary is a central repository that stores metadata like tables, fields, domains and views. It is used to create and maintain these database objects.
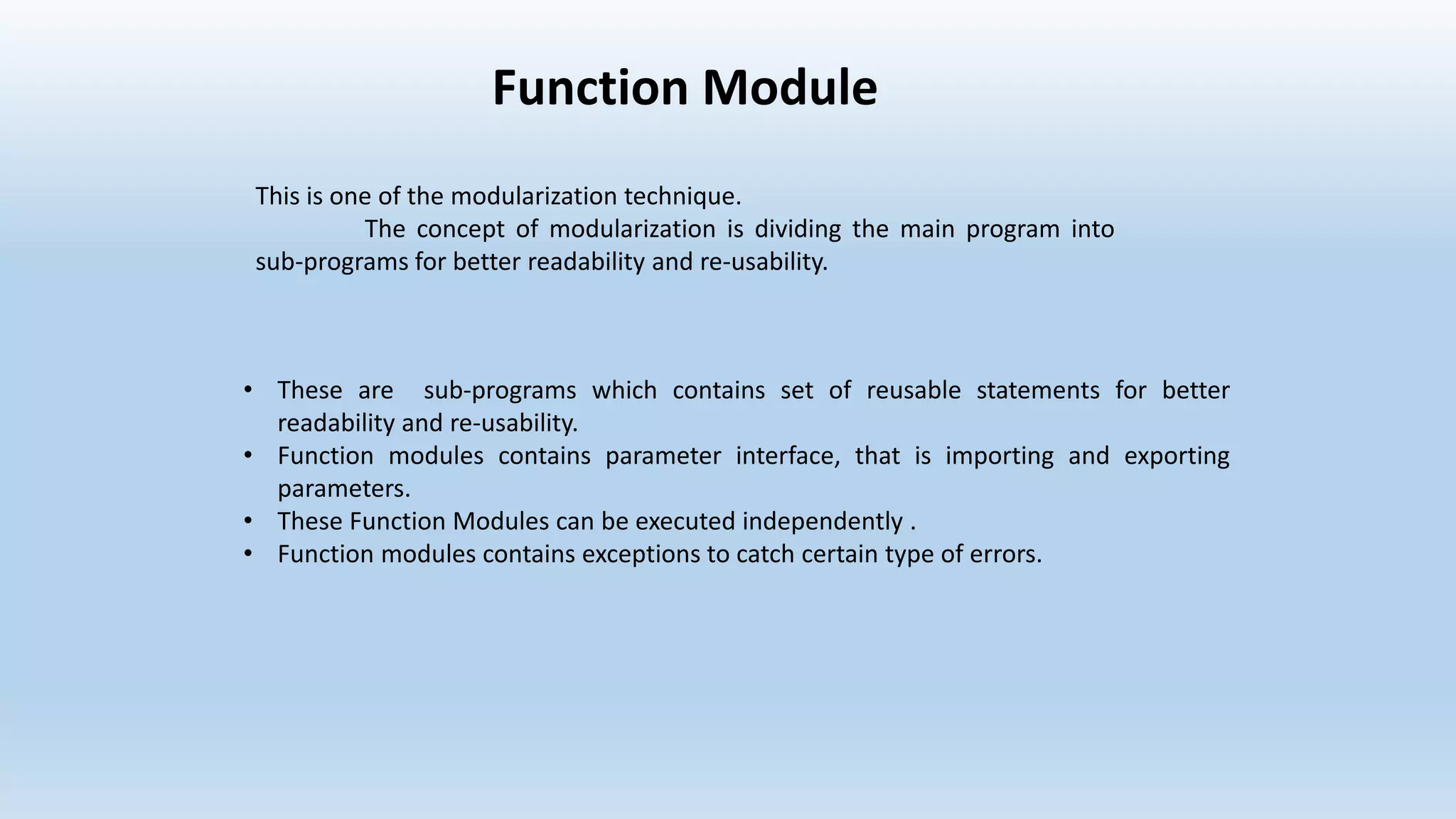
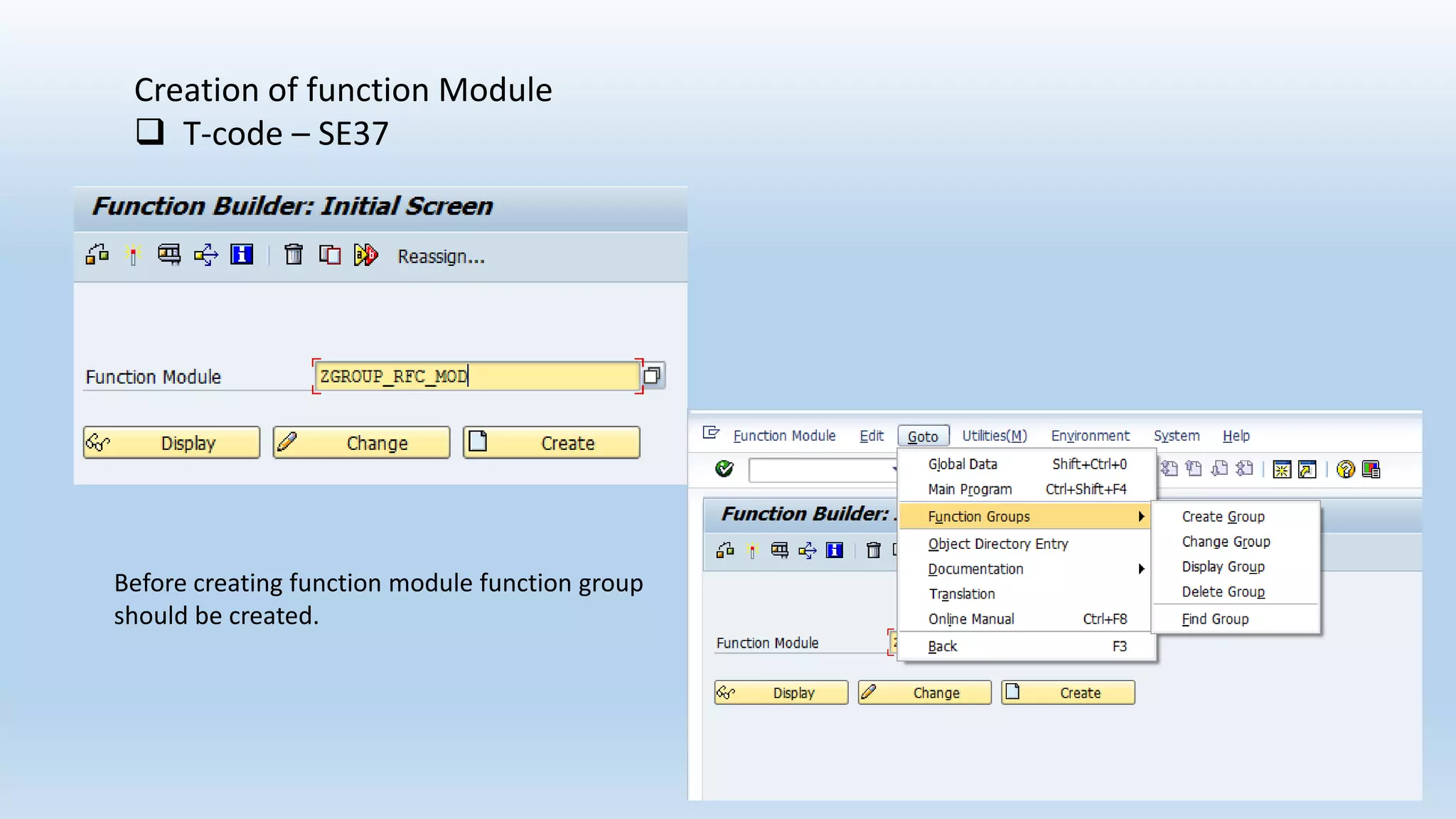
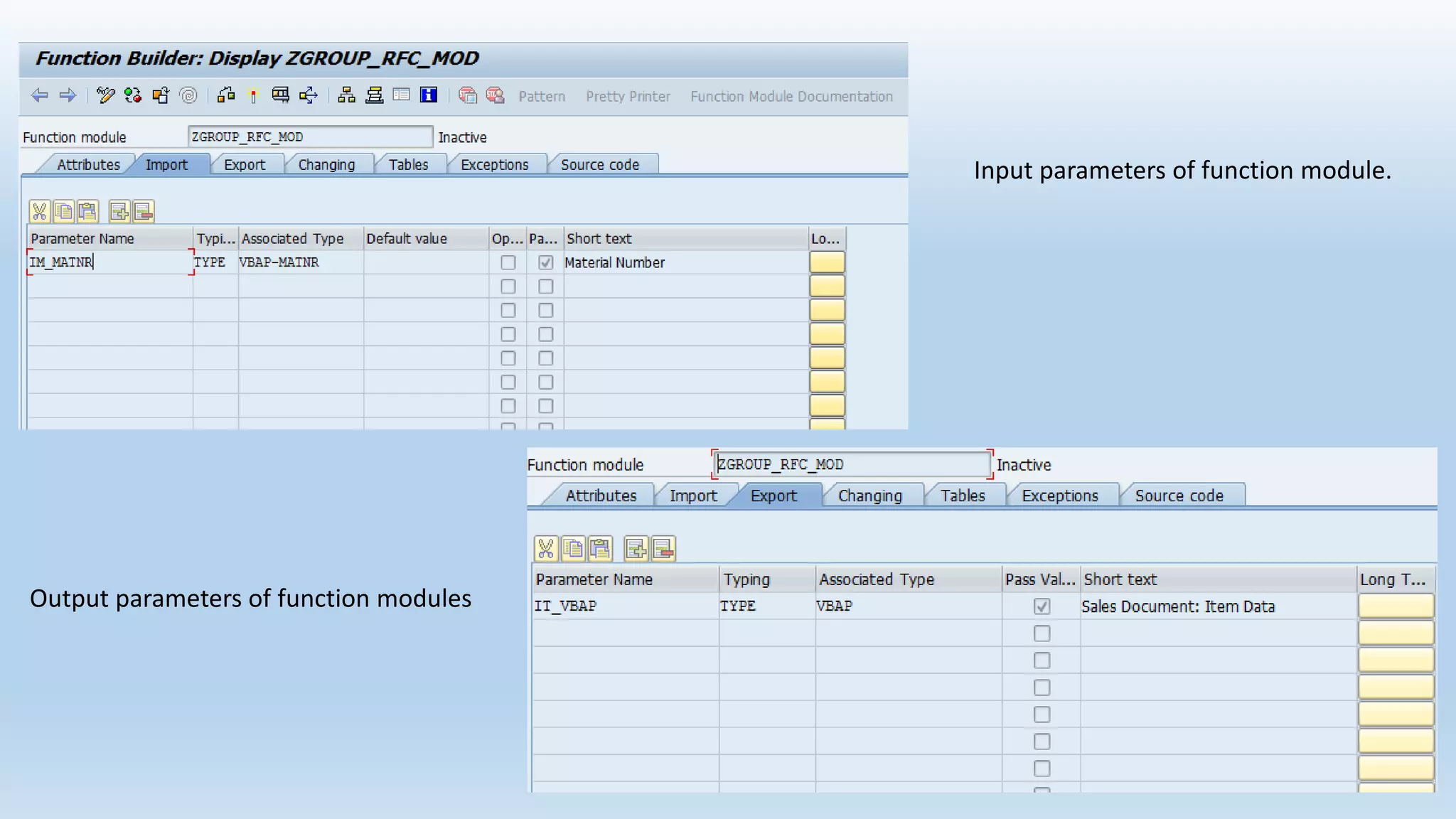
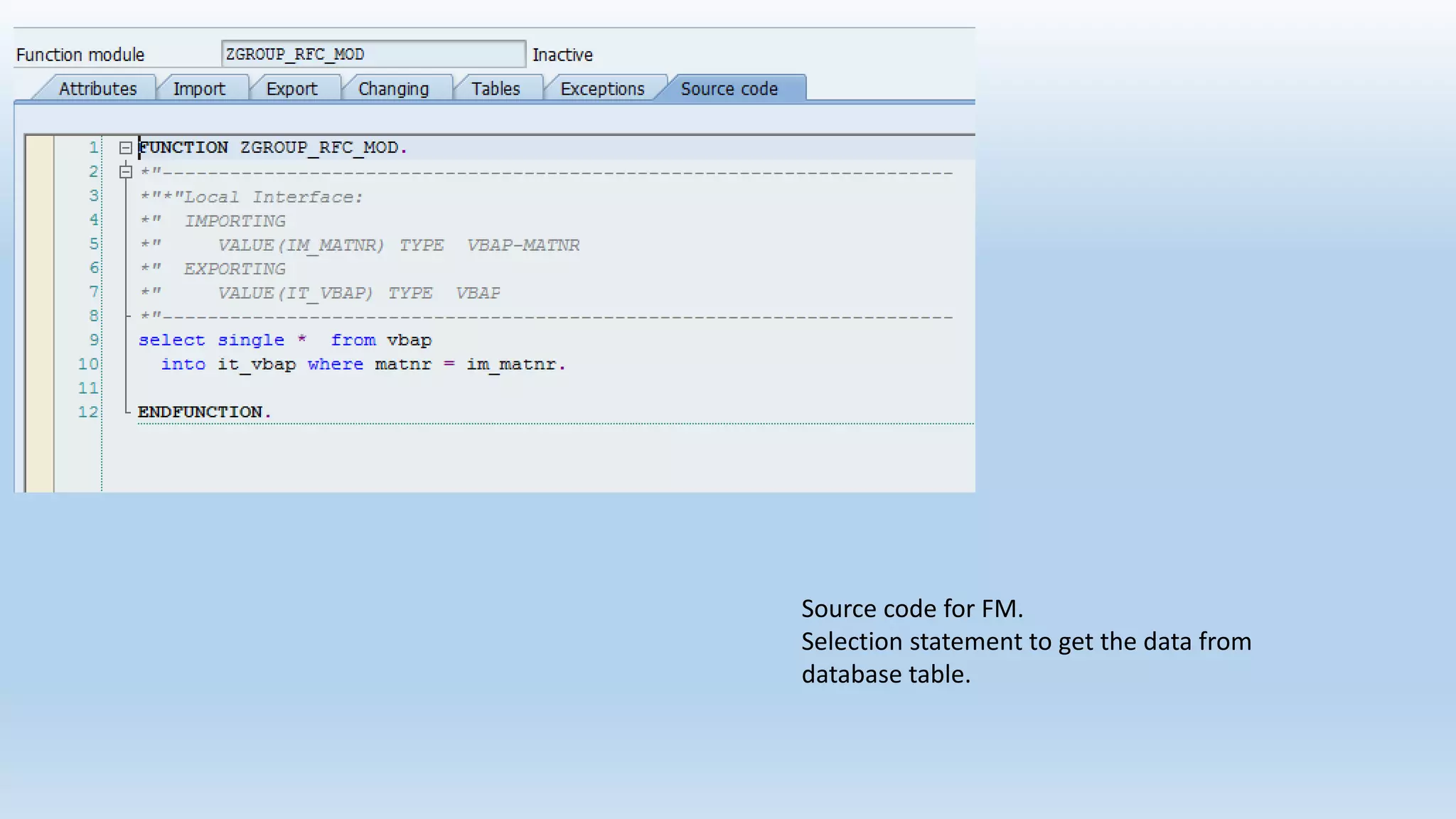
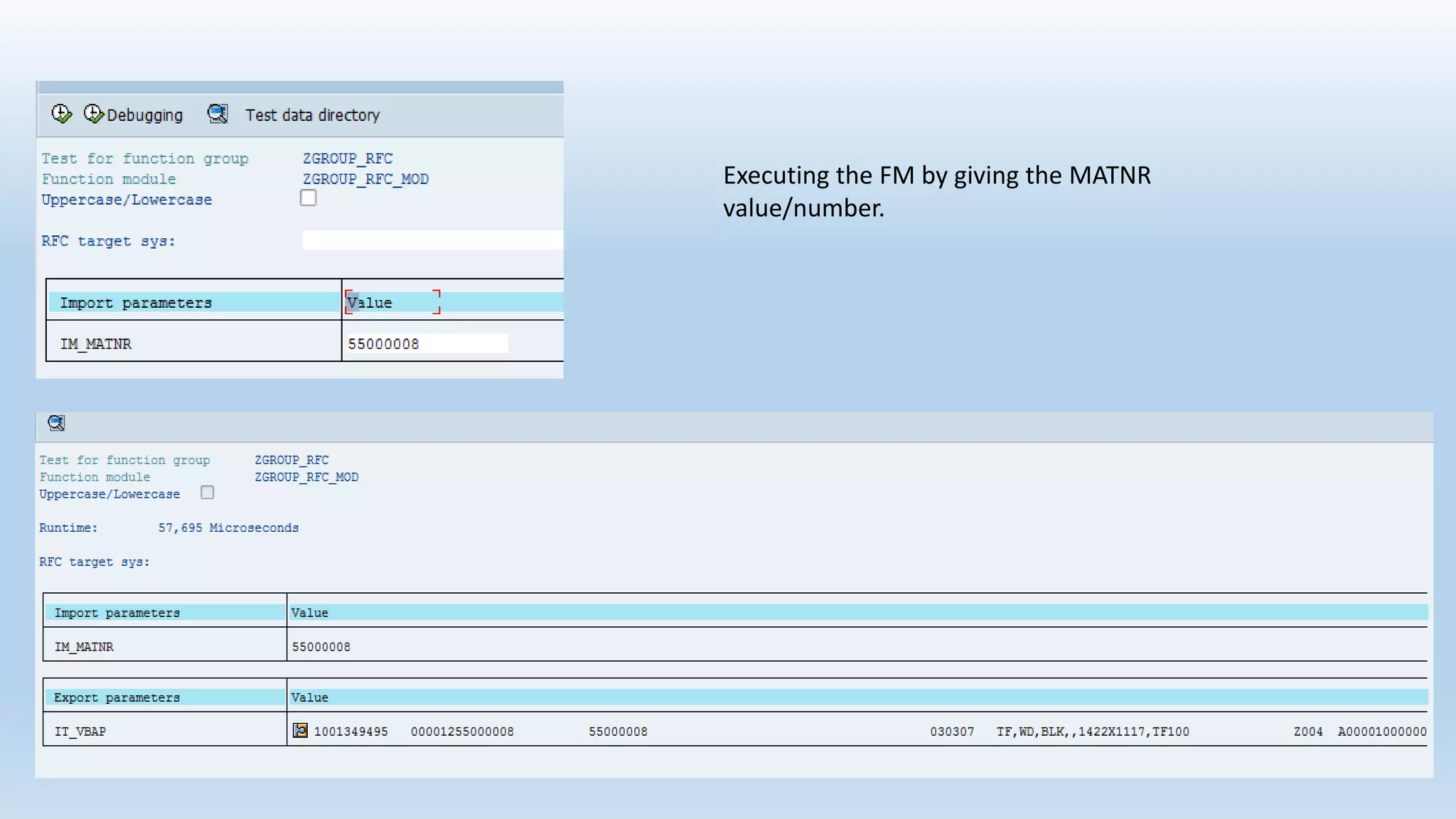
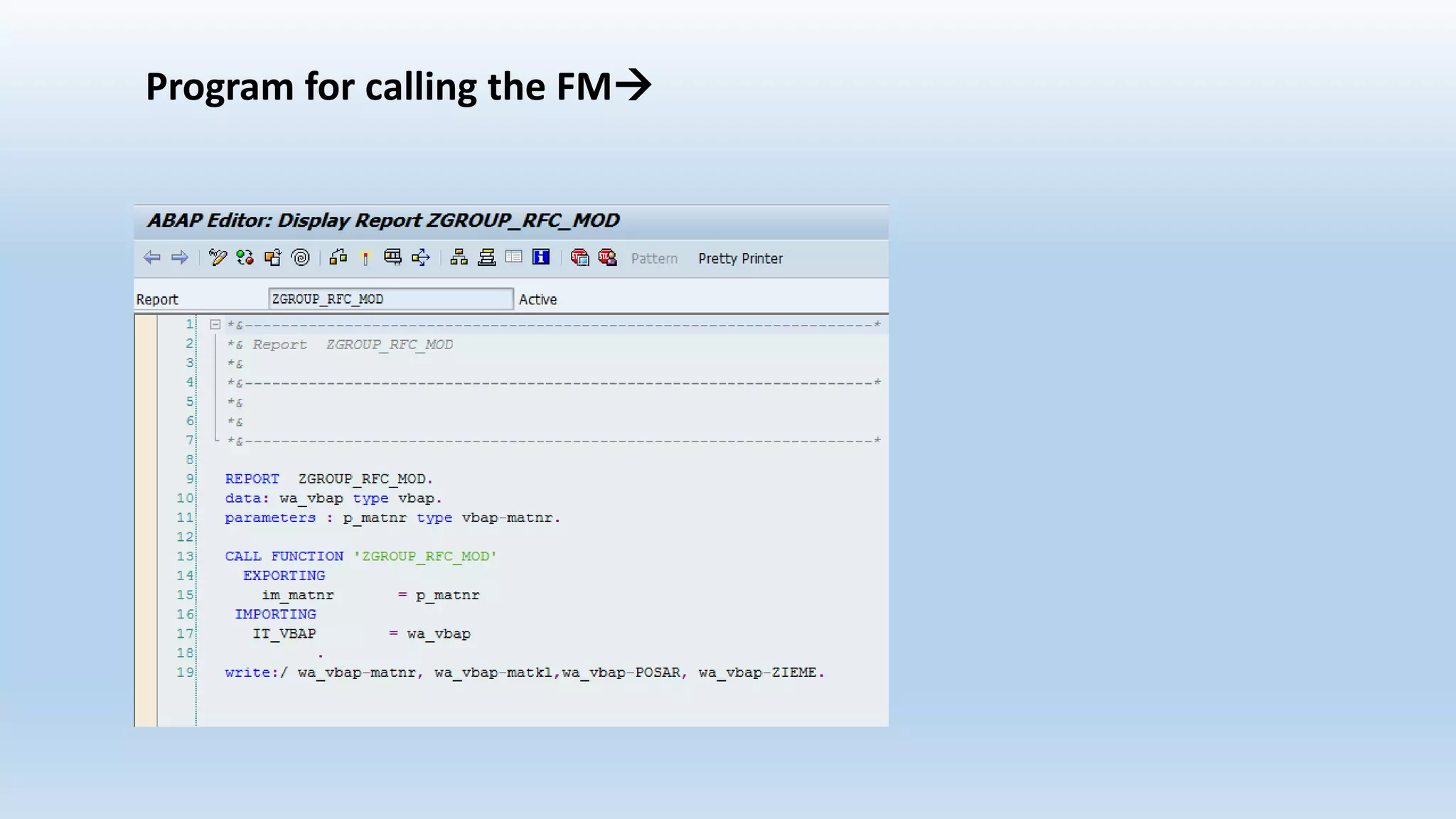
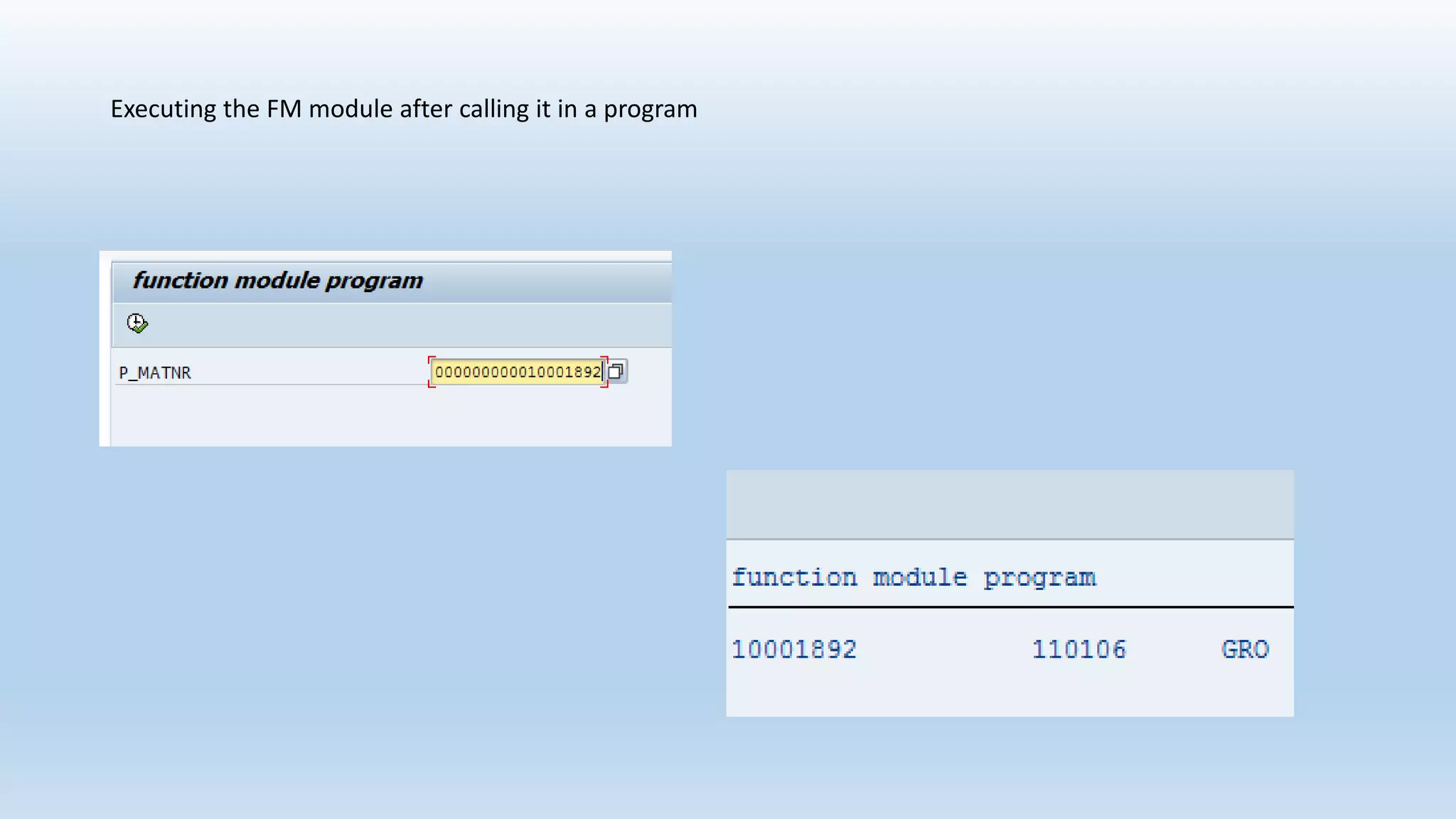
2. Function modules are reusable subprograms that contain importing and exporting parameters. They are used to modularize programs for improved readability and reusability.
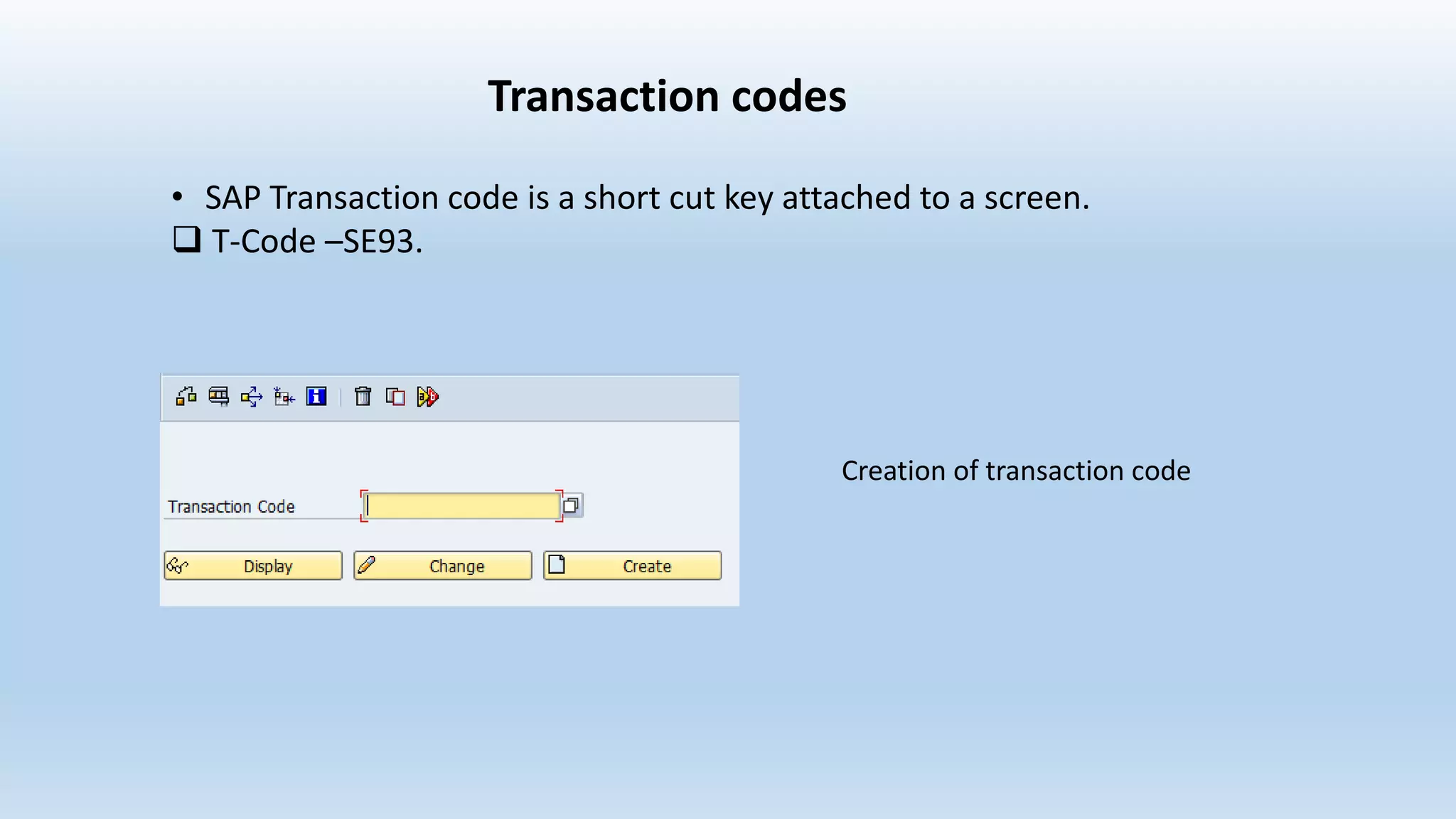
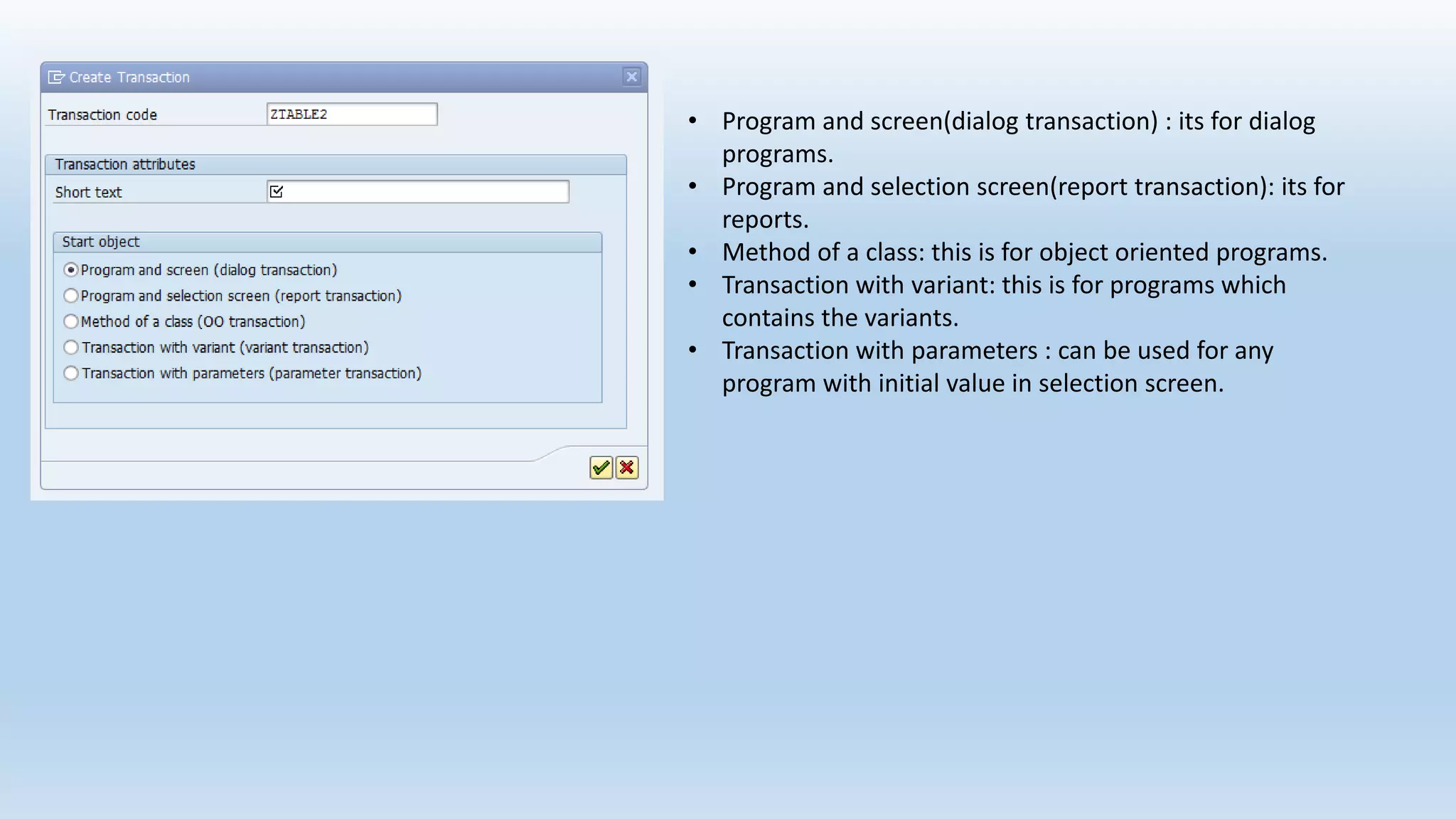
3. Transaction codes provide shortcuts to programs and screens in SAP. They are created using transaction SE93 and can link to dialog, report, class or parameterized programs.