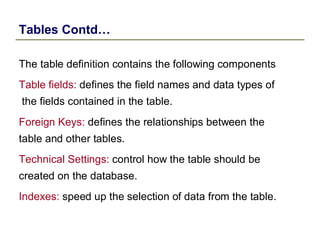
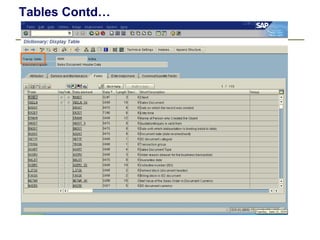
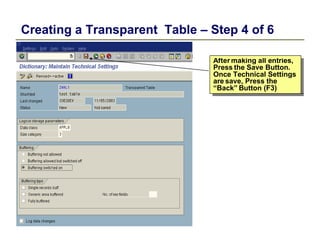
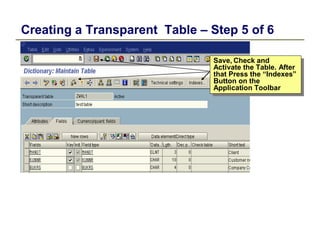
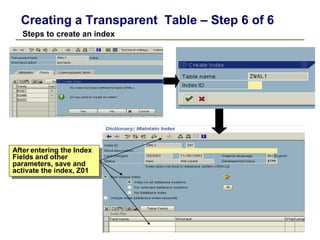
1) The data dictionary is a virtual database that contains metadata (data about data) such as the definition of tables, fields, domains and other database objects. It provides information for data manipulation and processing.
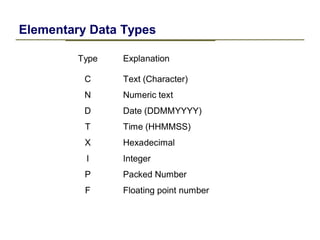
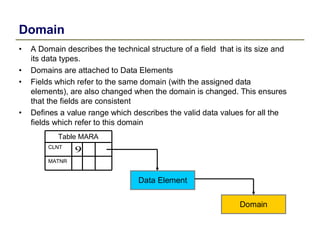
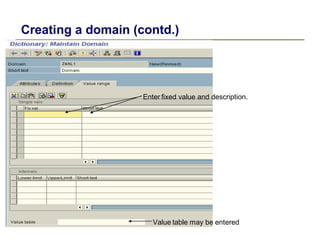
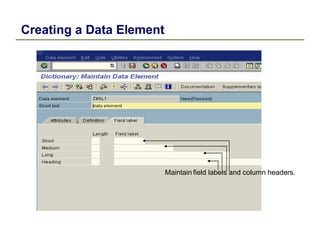
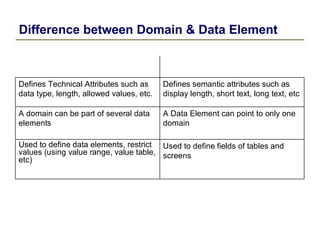
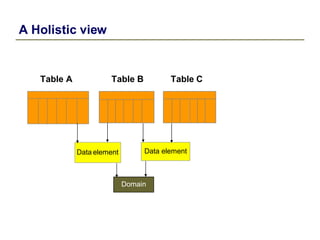
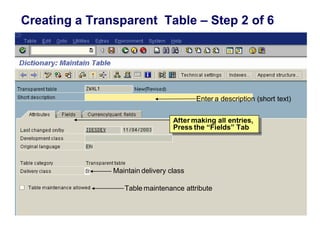
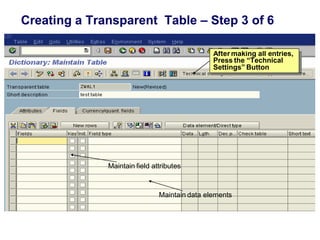
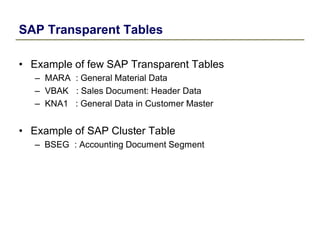
2) Key data dictionary objects include domains, which define field attributes like type and length; data elements, which define field semantics; and tables, which store records of data. Transparent tables can be created to store custom tables.
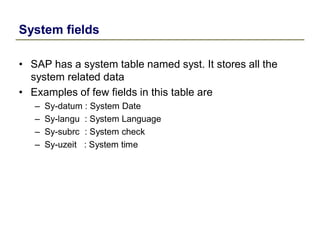
3) System fields store system-related data like date and time, while structures store temporary data during runtime and views combine data from multiple tables.