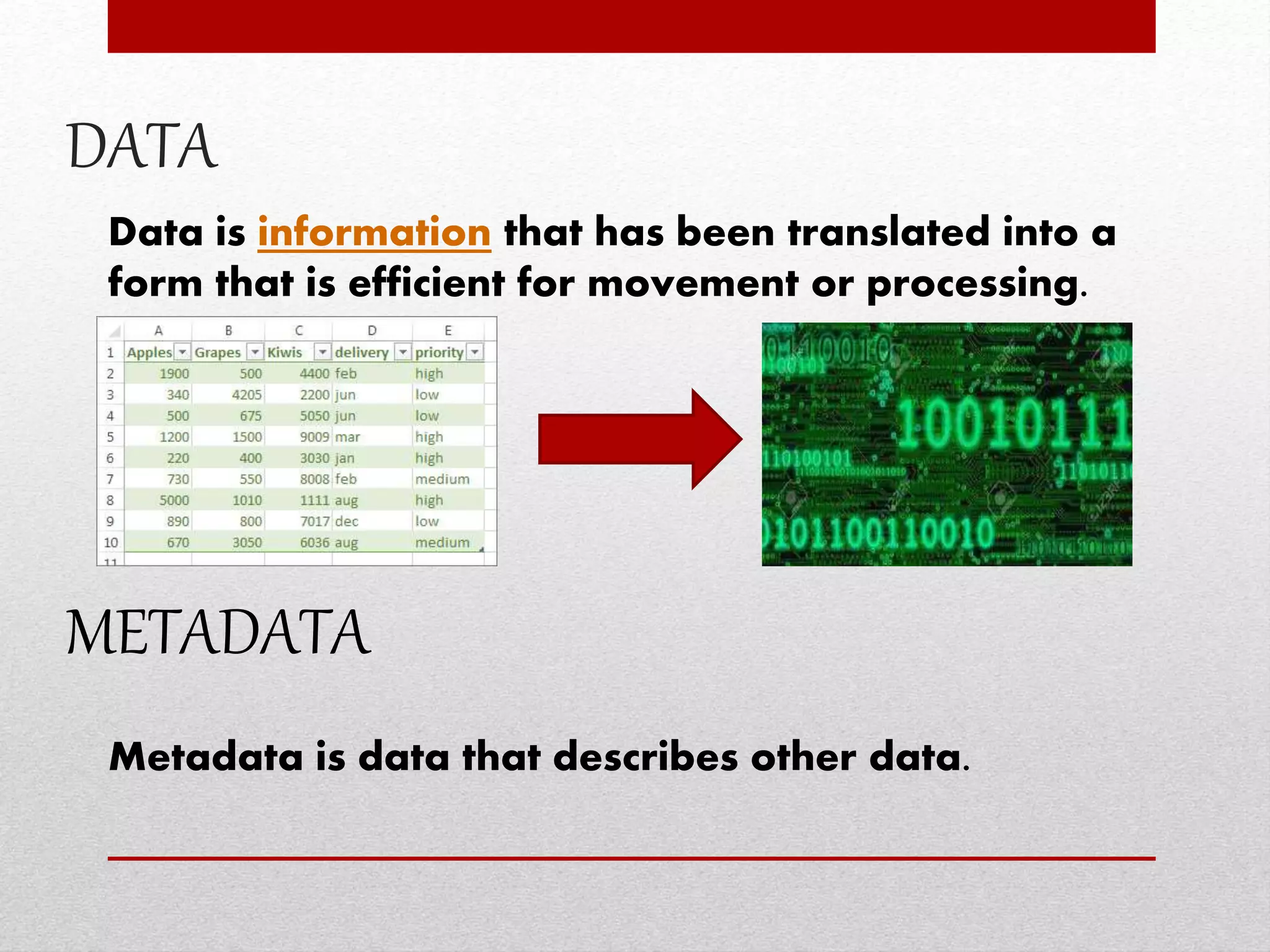
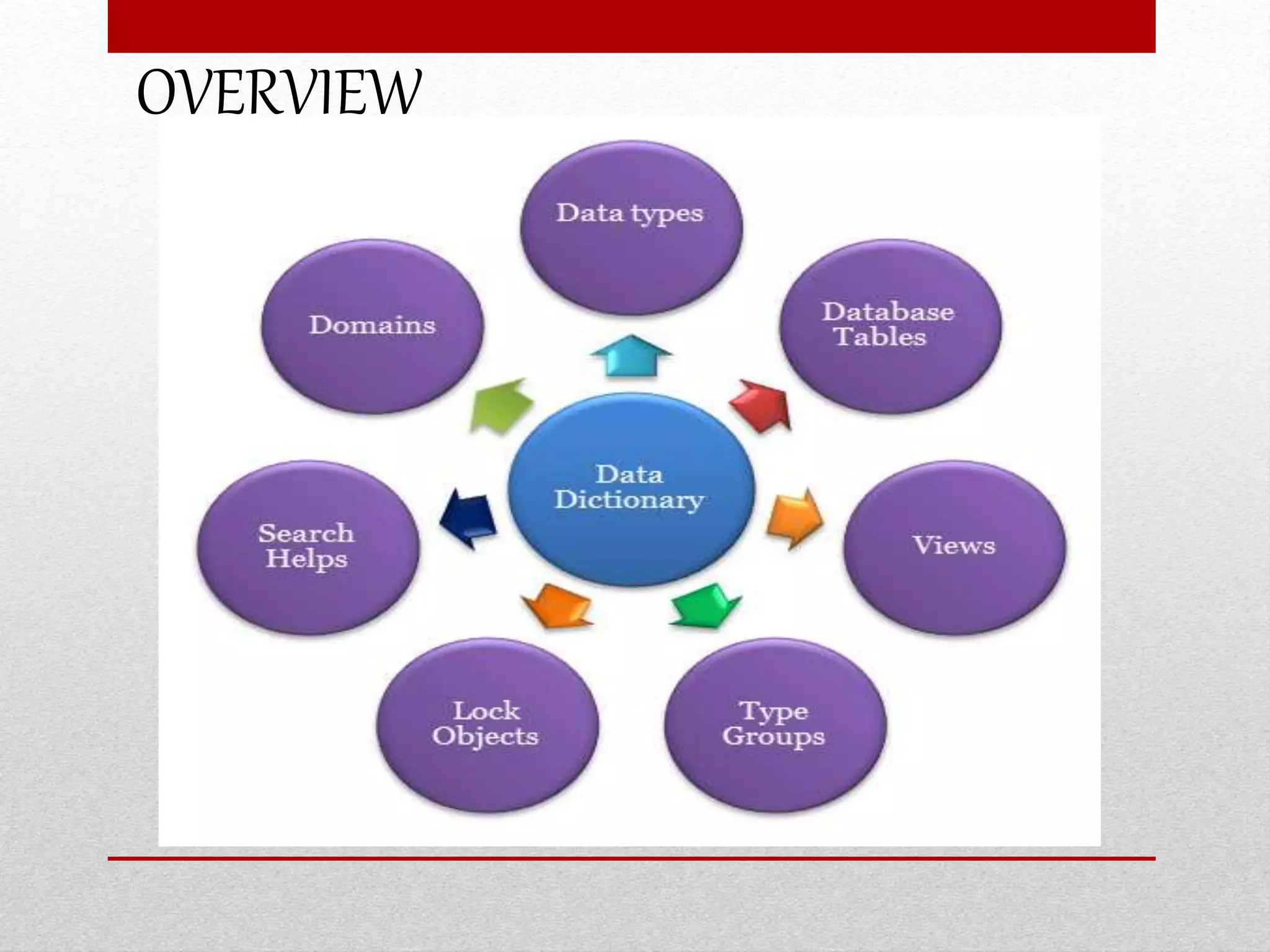
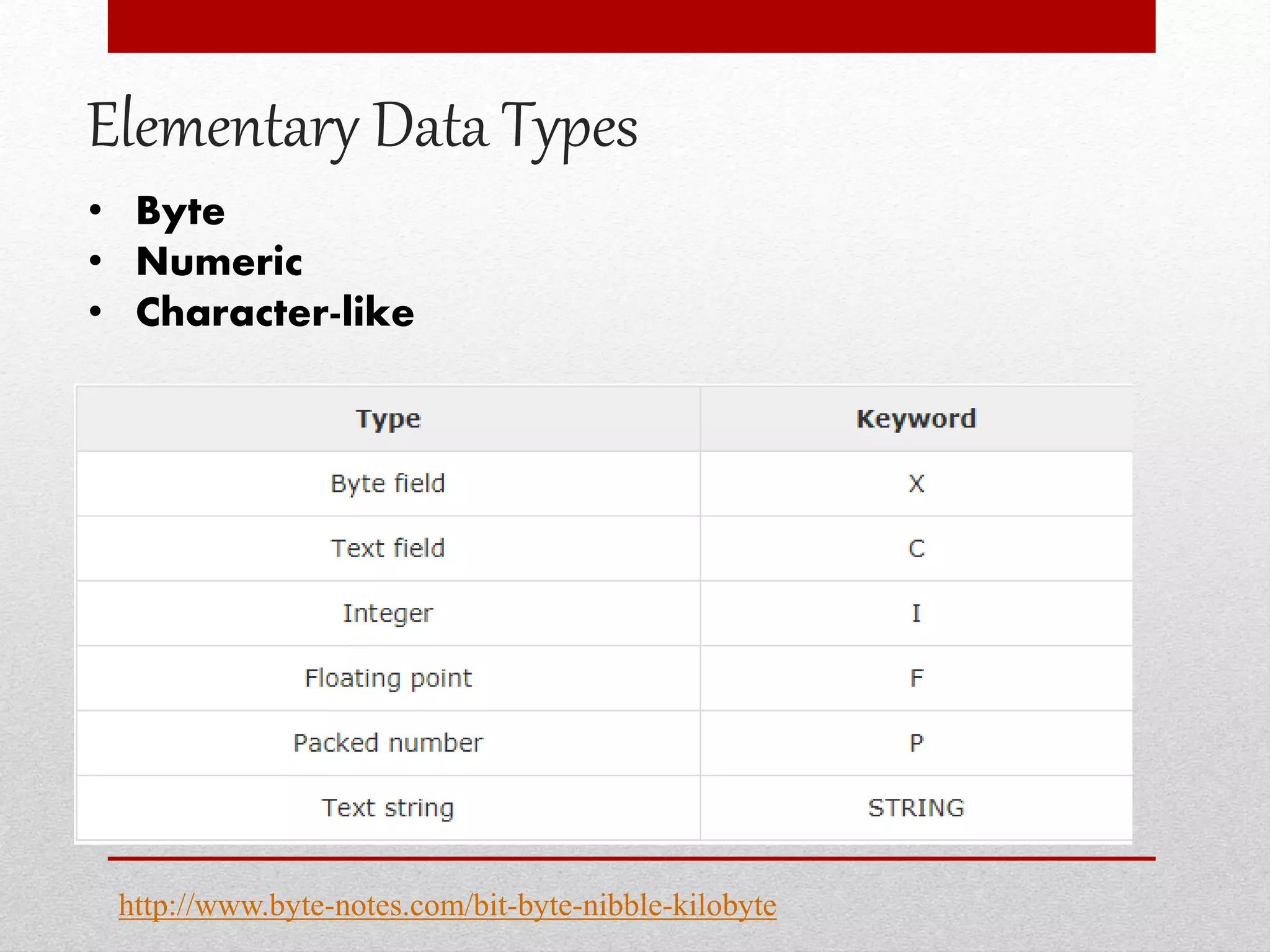
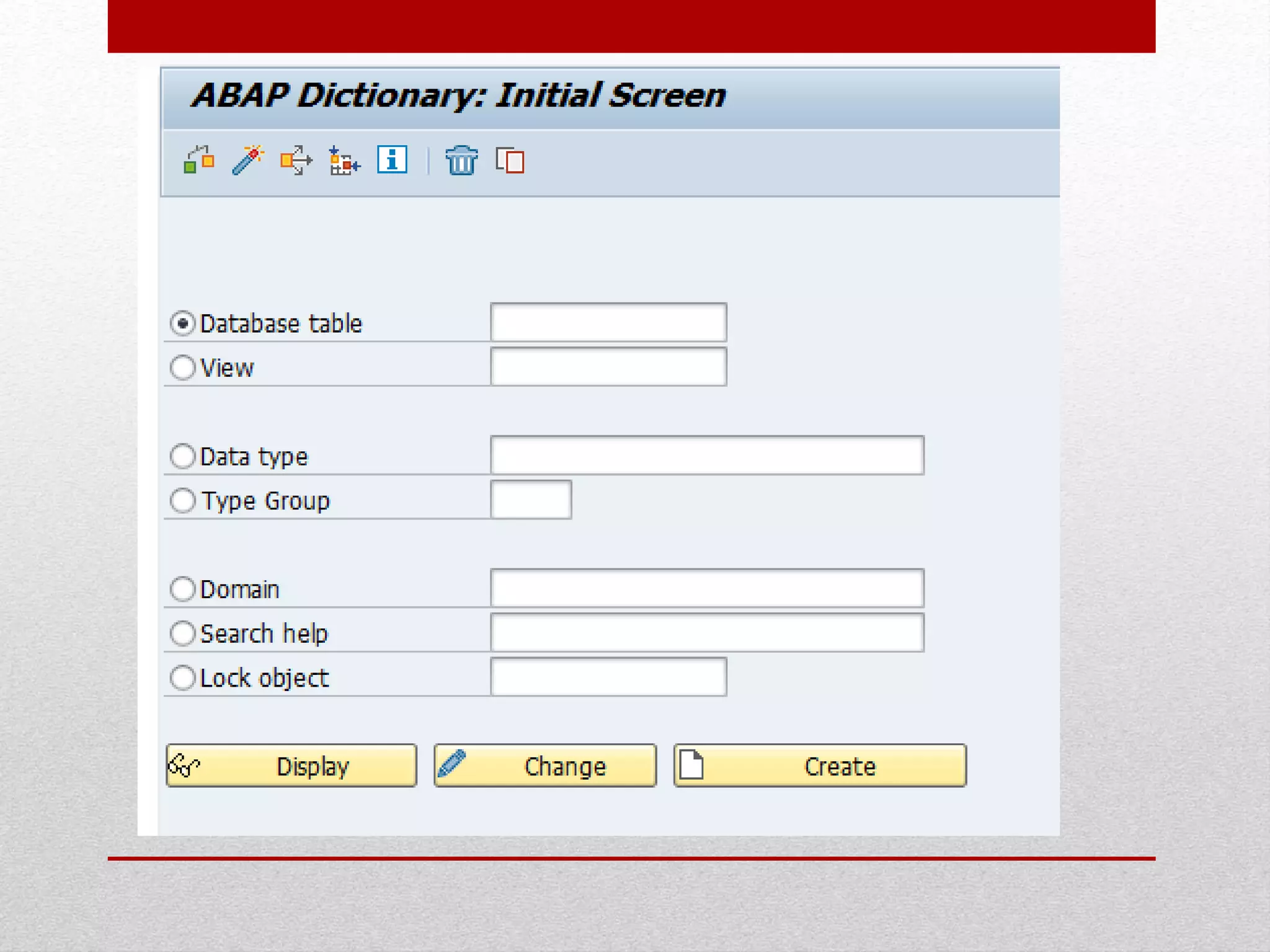
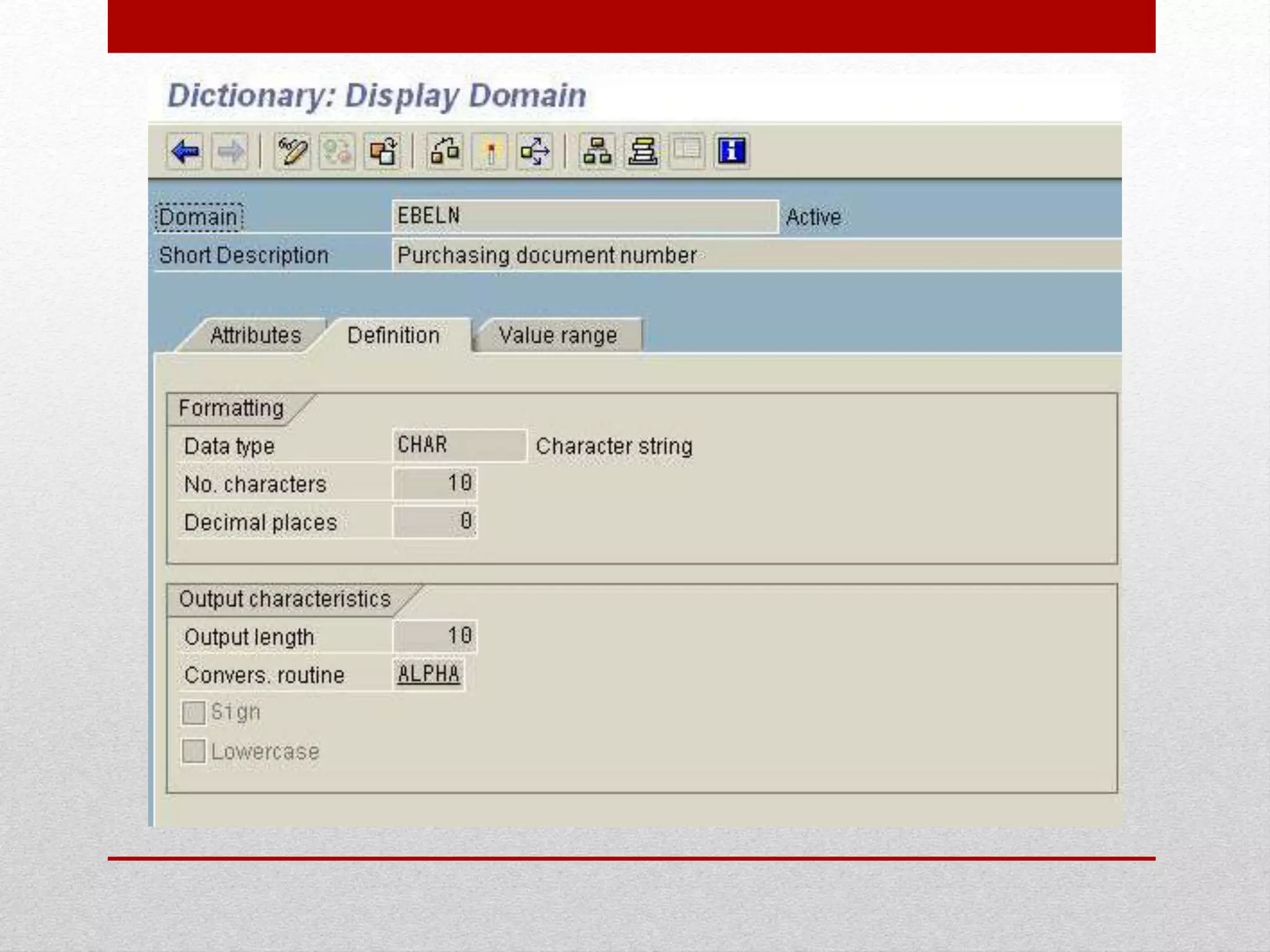
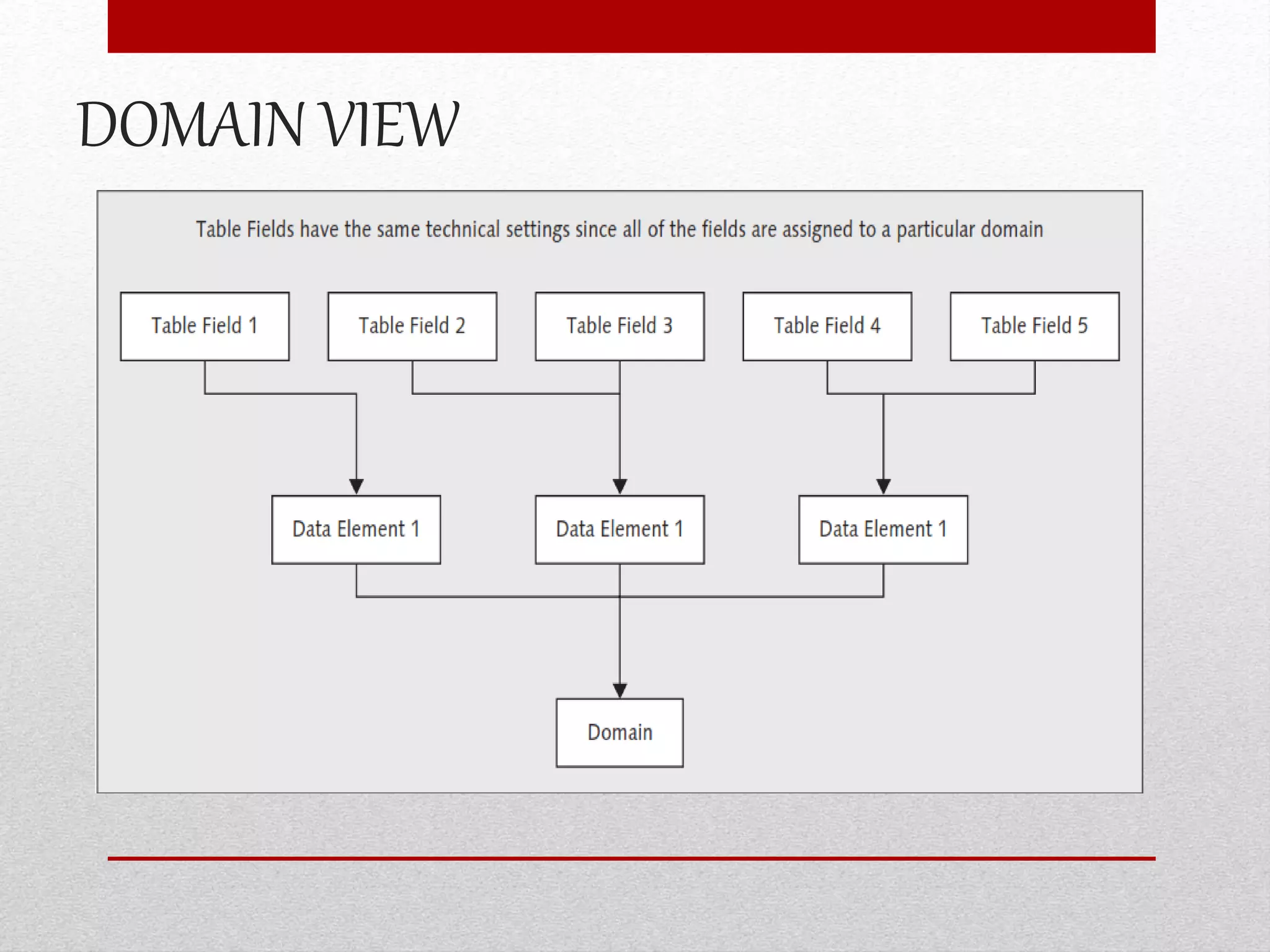
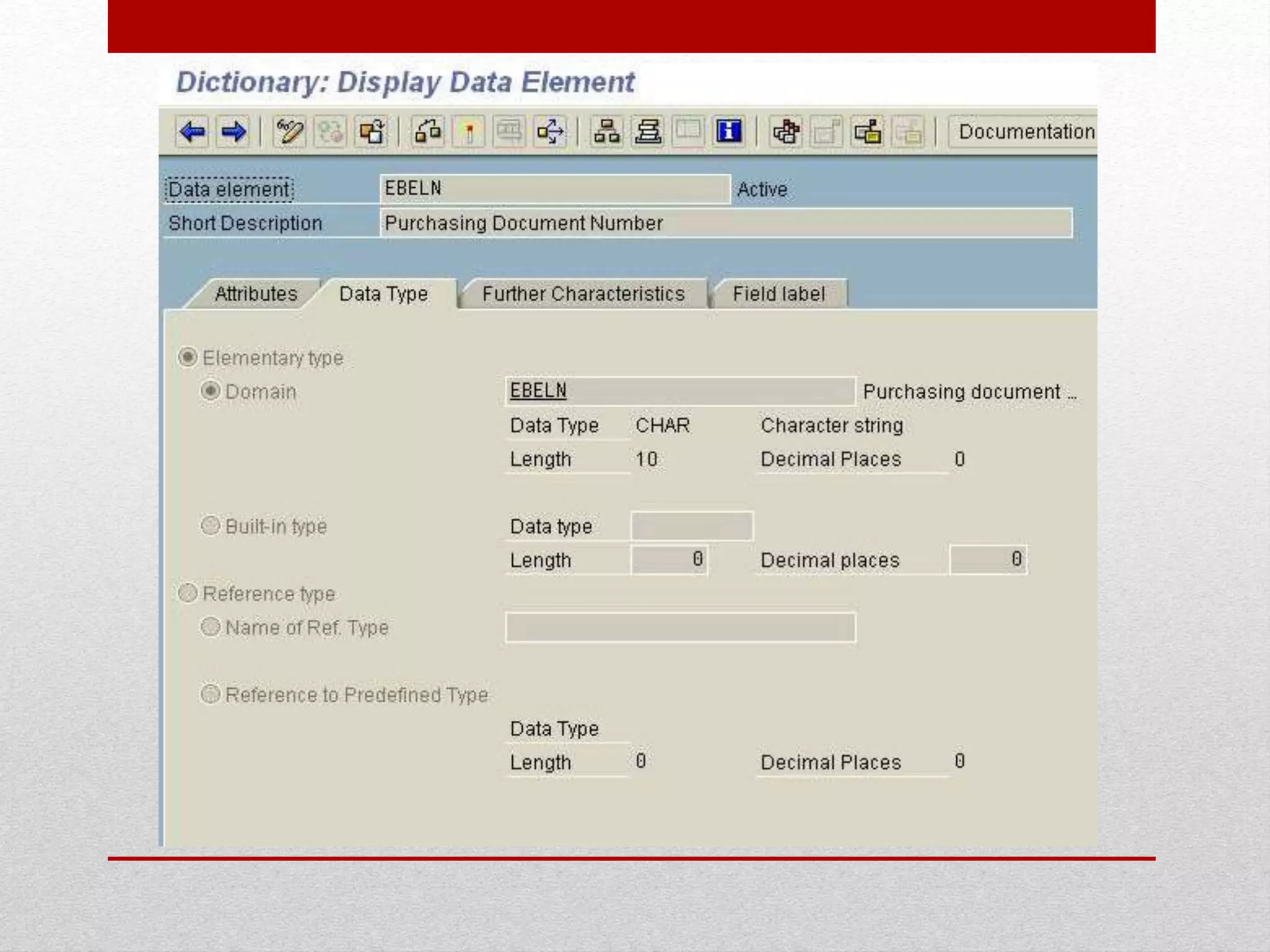
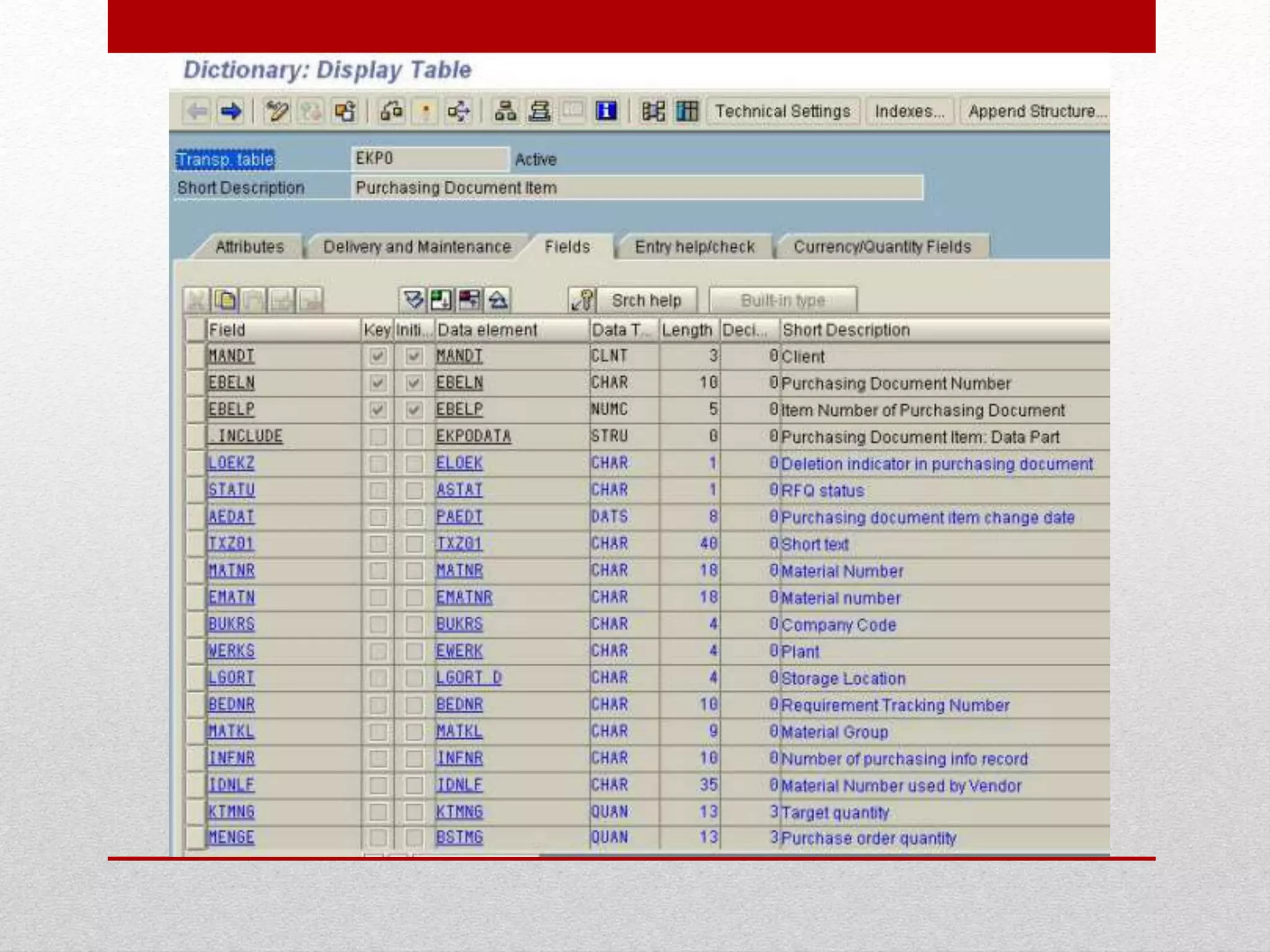
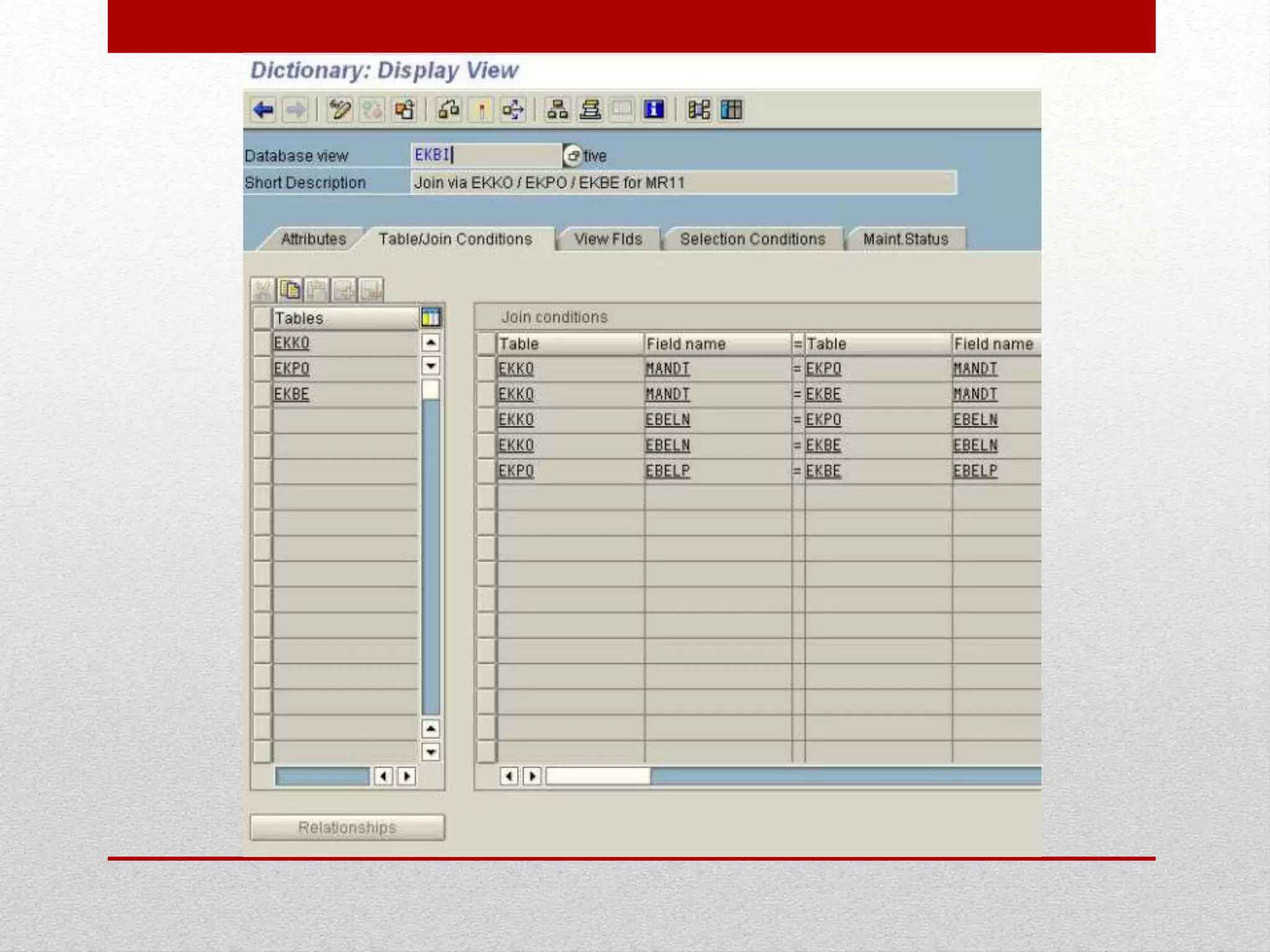
This document provides an overview of data dictionaries and data modeling in ABAP. It discusses key concepts like data types, domains, data elements, tables, structures, and aggregated objects. Data dictionaries are described as central sources of information that define and manage metadata. Domains specify value ranges for fields, while data elements describe field roles and semantics. Tables represent database tables, structures are like user-defined types, and views summarize distributed data. Search helps assist with searching and locks synchronize simultaneous data access. Common ABAP dictionary transactions and syntax for declaring variables and structures are also included.