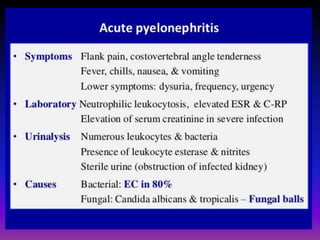
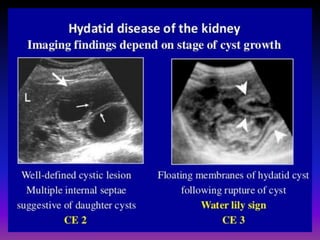
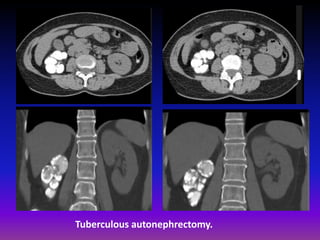
This document discusses various renal and urinary tract conditions that can be imaged and diagnosed using medical imaging techniques. It provides examples of imaging findings for conditions such as pyelonephritis, renal cysts, renal cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, renal tuberculosis, renal lymphoma and renal metastases. The document emphasizes that CT and CT intravenous pyelography are effective imaging modalities for evaluating many renal conditions and defining abnormalities.