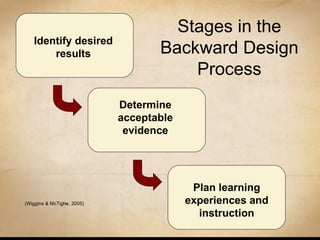
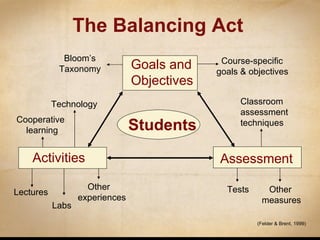
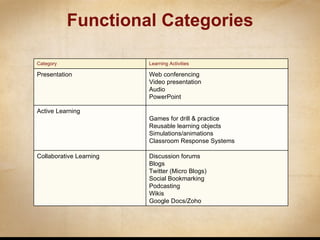
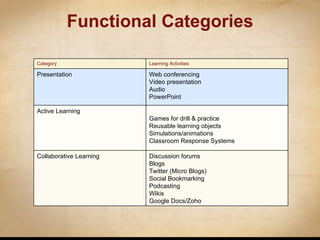
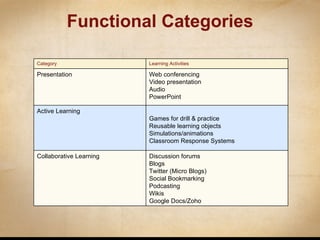
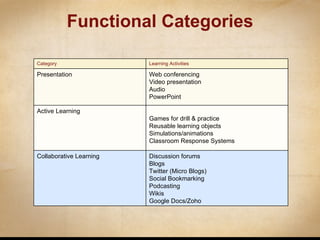
This document discusses various ways that instructional technology can be used to enhance teaching and learning. It is organized by functional categories of learning activities including presentation tools, active learning tools, collaborative learning tools, and more. Specific examples are provided for tools like video conferencing, simulations, discussion forums, blogs and wikis. Key principles of instructional design are also reviewed, such as backward design and establishing learning goals and objectives. Overall, the document serves as a guide for instructors to thoughtfully integrate different technologies into their teaching.