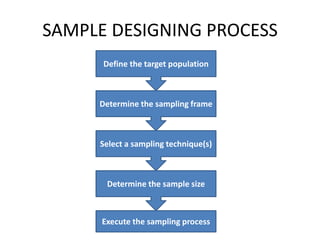
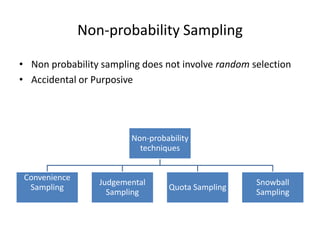
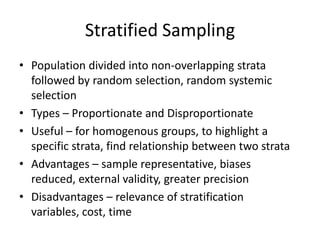
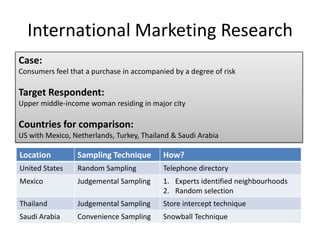
This document discusses key concepts related to sampling design and procedures. It defines important terms like population, census, and sample. It then outlines the 5 main steps in the sample design process: 1) defining the target population, 2) determining the sampling frame, 3) selecting a sampling technique, 4) determining the sample size, and 5) executing the sampling process. It also discusses probability and non-probability sampling techniques and when each is most appropriate to use.