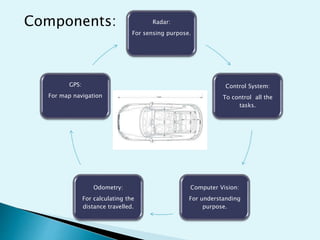
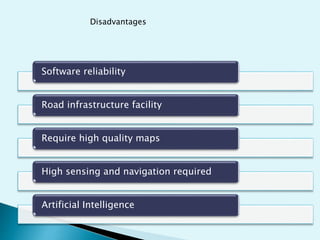
This document discusses driverless cars, including their components, functions, working, advantages and disadvantages. Driverless cars use sensors like radar, lidar, computer vision and GPS to detect their surroundings and navigate roads autonomously. They have control systems that analyze sensor data to identify other vehicles. Key components are sensors, a control unit and actuators that allow the computer to safely operate the vehicle. While driverless cars could solve traffic issues and reduce labor costs, challenges include relying on accurate high-quality maps and requiring sophisticated AI and sensing technologies.