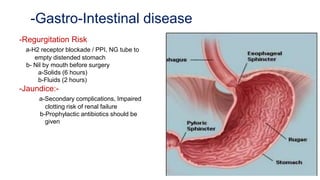
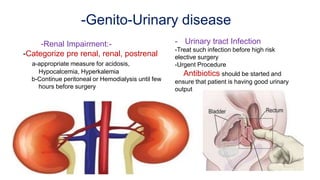
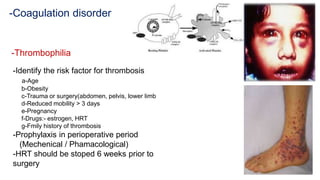
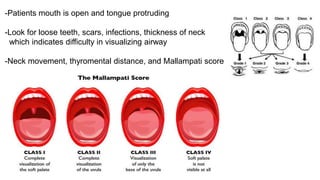
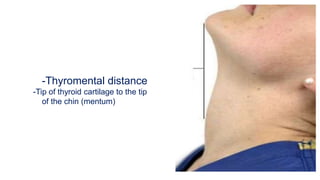
The document discusses preoperative preparation and assessment of patients. It outlines the key steps which include gathering relevant medical history, conducting a physical exam, ordering appropriate tests and labs, identifying and managing any medical conditions, developing a treatment plan, discussing risks and obtaining consent. The goals are to optimize the patient's condition, minimize risks and communicate effectively with the surgical team. Key aspects of the physical exam and specific considerations for various medical conditions are also described. Finally, the document discusses arranging the operating room schedule to ensure proper resources and prioritization of patients.