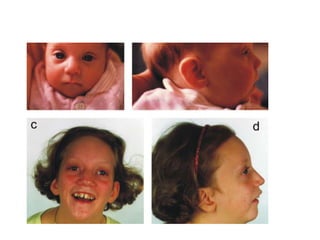
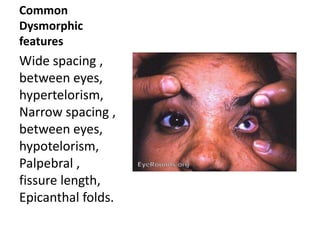
Dysmorphism refers to abnormalities in morphological development where structures can appear in different forms. Dysmorphism can be facial or structural and is seen in dysmorphic features which are differences in body structure that can be isolated or related to genetic disorders. Common dysmorphic features include variations in eye spacing, philtrum length, and nose shape. The causes of dysmorphism include chromosomal abnormalities, single gene mutations, teratogen exposure, and environmental factors during development.