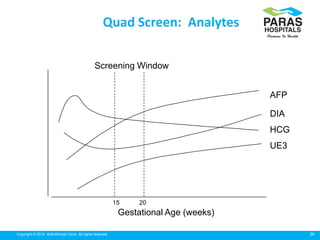
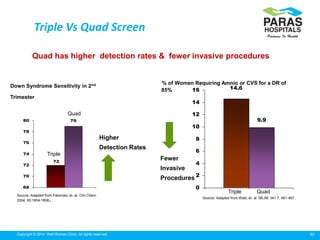
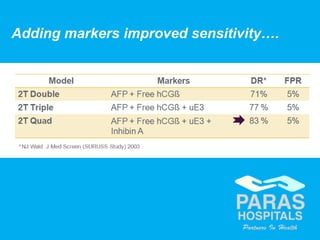
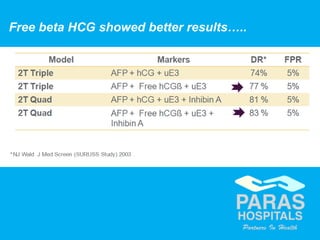
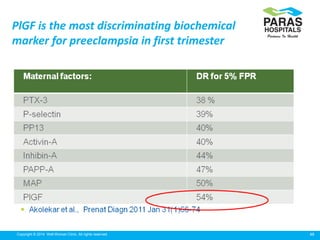
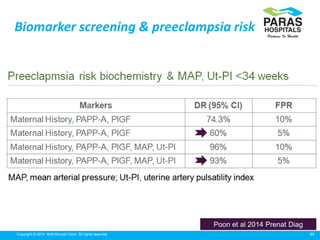
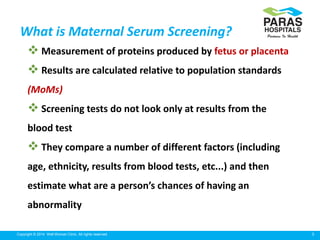
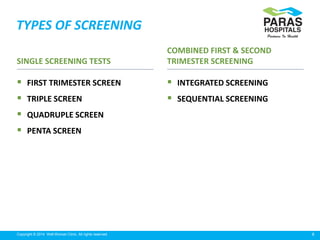
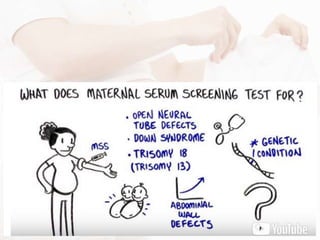
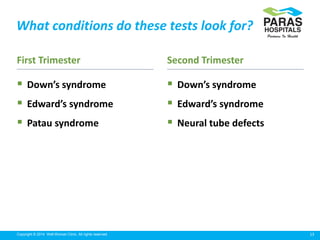
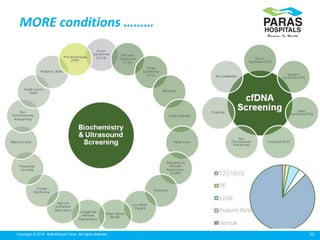
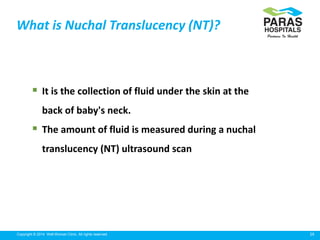
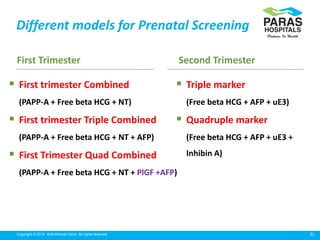
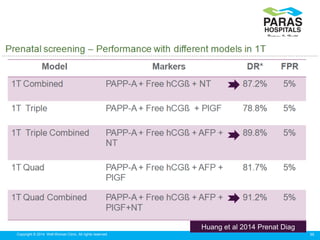
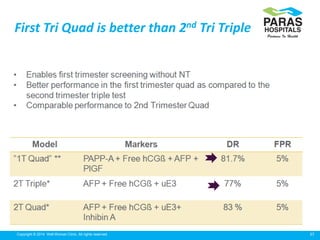
Maternal serum screening tests measure levels of proteins in a pregnant woman's blood to screen for fetal abnormalities. Screening tests are not diagnostic but provide risk estimates to determine if further testing is needed. Advances now allow for screening in the first and second trimesters. First trimester screening combines measurements of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, human chorionic gonadotropin, and nuchal translucency to screen for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, neural tube defects, and preeclampsia risk. Second trimester screening measures alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin-A to screen for similar conditions. While not definitive



















![38Copyright © 2014 Well Woman Clinic. All rights reserved.
Started in the 1970’s when it was found that fetal neural tube
defects were associated with increase in maternal MSAFP
Such measurements were offered to pregnant woman for
screening purposes
It was also noted that MSAFP tended to be low in fetal down’s
syndrome.
With a cut off of 2.0 multiples of median[MOM] 85% of NTD’s
would be screened in & with a threshold of 0.5 MOM approx
33% of DS fetus would be screened
Second trimester biochemical screening](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maternalscreenscreening-170916064750/85/Maternal-screening-in-Pregnancy-Double-quadruple-marker-38-320.jpg)