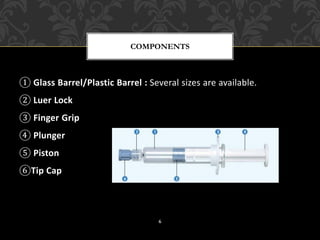
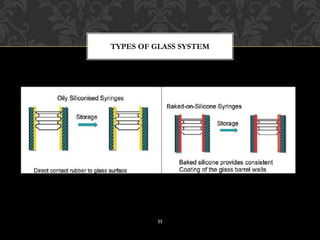
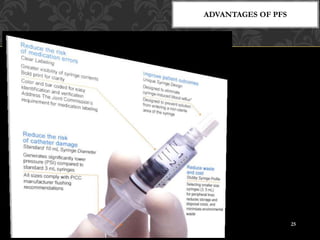
This document provides an overview of prefilled syringes, including what they are, their purpose, types, materials, filling and sterilization processes, advantages and disadvantages, and some examples of marketed products. Prefill syringes are single-dose packages containing a parental drug and fixed needle provided by the manufacturer. They serve the purposes of primary packaging and a delivery system to administer the correct dose to patients. The two main types are glass-based and plastic-based systems, with plastic gaining acceptance for benefits like break resistance and decreased reactivity. Proper filling and sterilization processes are important to ensure safety and efficacy.