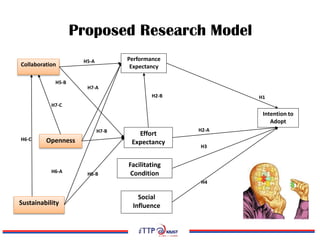
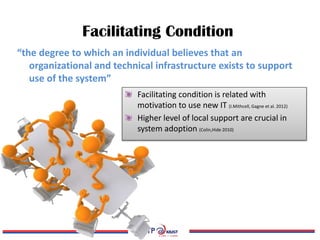
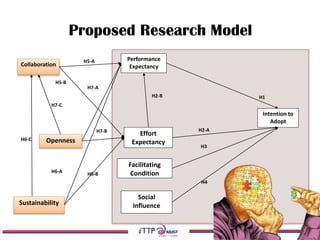
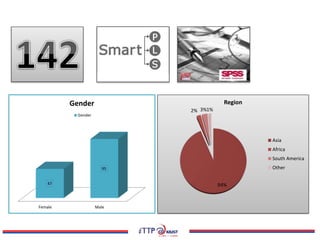
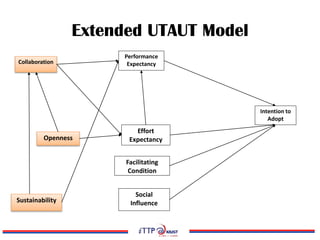
The document discusses the exploration of collaboration, openness, and sustainability in the context of e-research adoption, utilizing the extended UTAUT model to empirically test these effects. It highlights key findings that collaboration significantly influences performance expectancy, while sustainability and openness also play vital roles in fostering effective e-research practices. Moreover, the research identifies limitations and offers recommendations for future studies in the field.