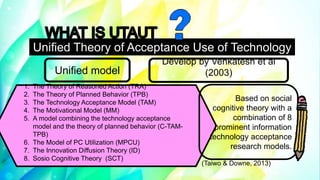
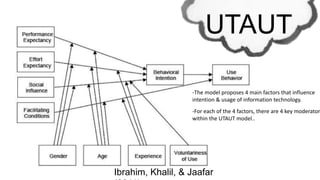
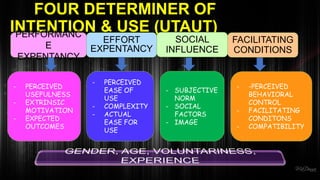
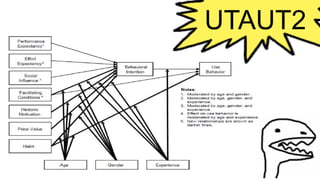
The document discusses the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), which aims to explain user intentions and behaviors towards information systems. Developed by Venkatesh et al. in 2003, it integrates eight existing models to predict technology acceptance, focusing on four main factors: performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions. The document also highlights the extension to UTAUT2, which includes additional factors such as experience and habit, and discusses its application in educational settings, along with associated strengths and weaknesses.