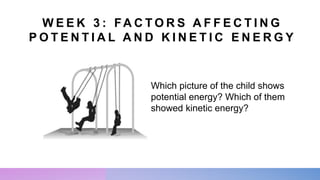
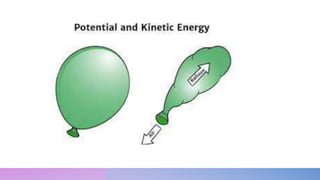
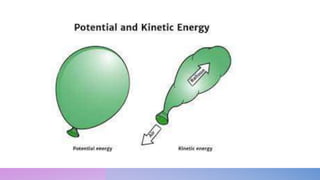
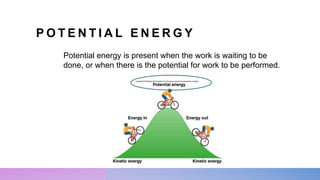
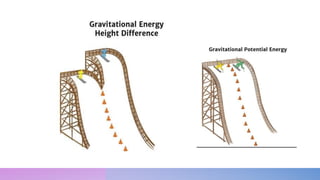
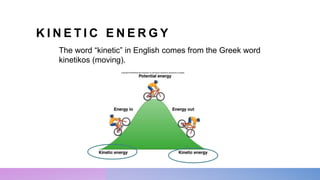
The document discusses potential and kinetic energy. It defines potential energy as stored energy due to position or deformation, including elastic potential energy from compression or stretching. Potential energy depends on mass and height according to the gravitational potential energy formula. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Examples calculate potential energy using the formula and find the height corresponding to a given potential energy.