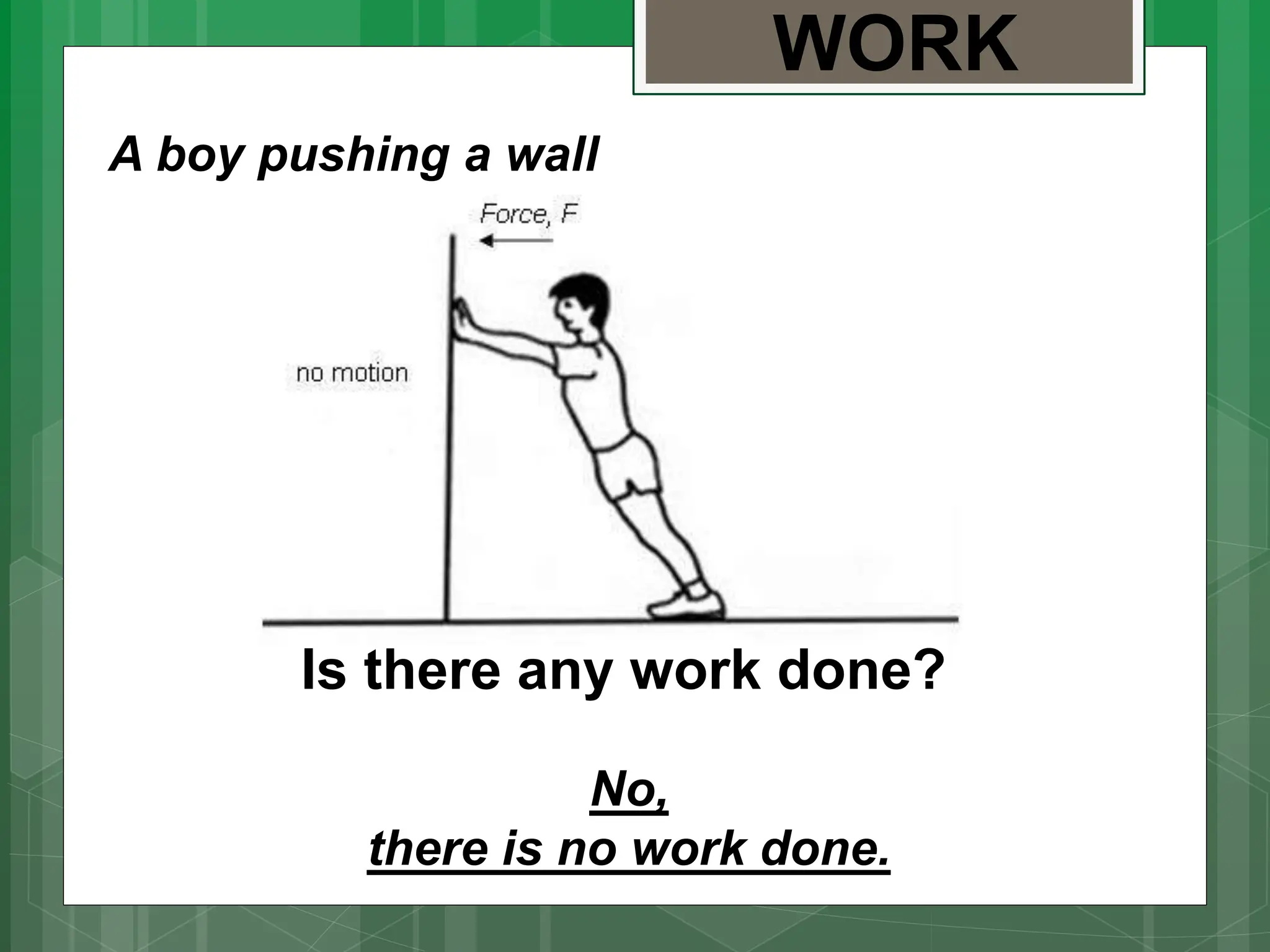
The document is a lesson on energy for an 8th grade science class. It defines energy as the ability to do work and discusses two main types of energy: kinetic energy, which is energy of motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy. It provides examples of objects possessing kinetic or potential energy. Formulas are given for calculating kinetic energy based on mass and velocity and potential energy based on mass, gravity, and height. Students are asked to identify types of energy and solve computational problems involving kinetic and potential energy calculations.