1) Gregor Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments with pea plants and established the concept of discrete inheritance units called genes.
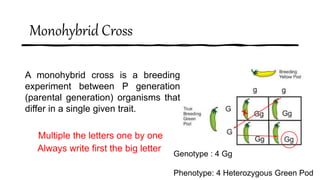
2) A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between organisms that differ in a single trait, and Punnett squares can be used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring.
3) Terms like homozygous, heterozygous, dominant and recessive traits describe genetic inheritance patterns and how alleles interact to influence observable traits.