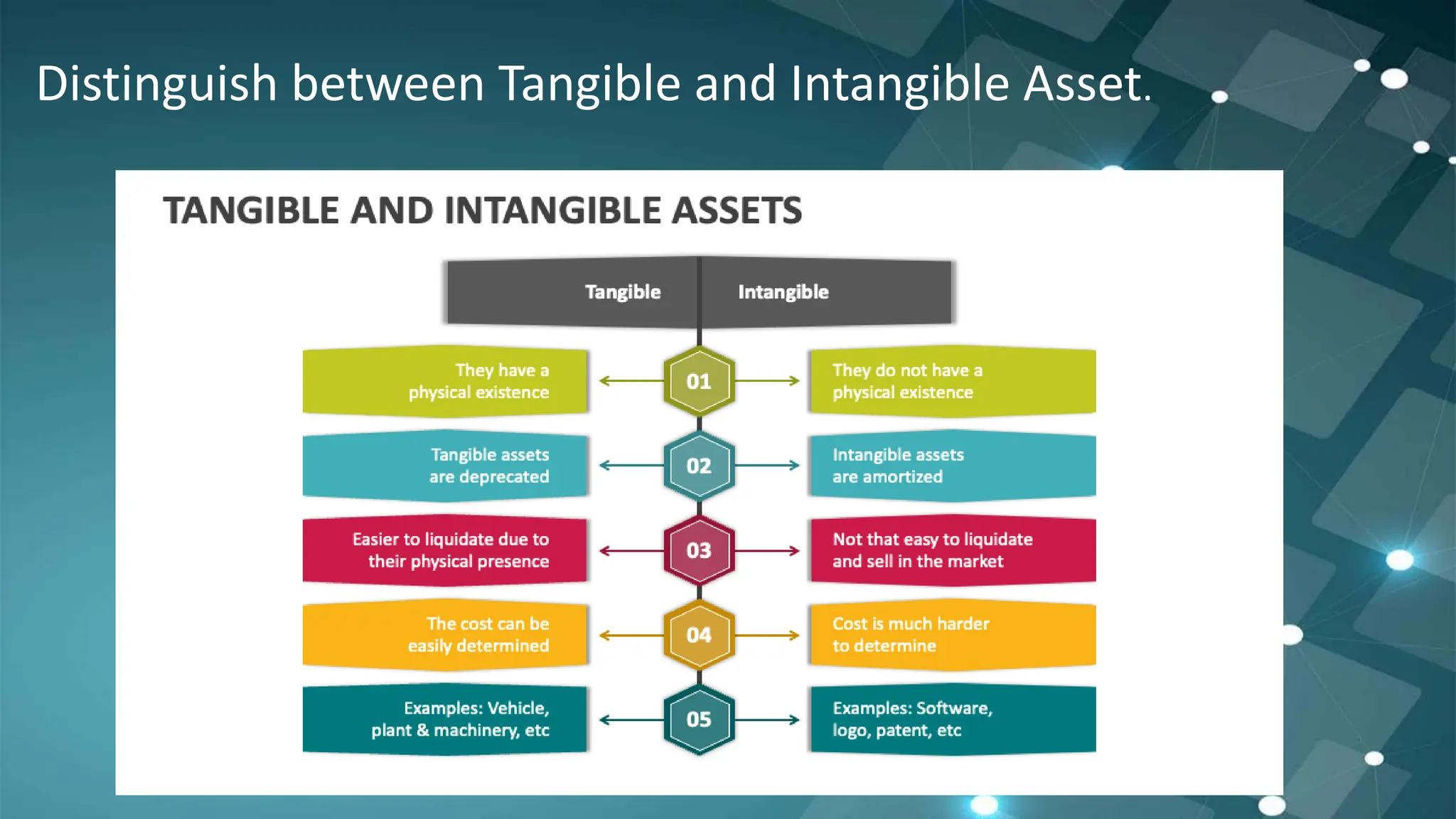
This document summarizes Accounting Standard 26 regarding intangible assets. It defines intangible assets as non-physical assets that provide future economic benefits and are controlled by an entity. Examples include goodwill, patents, trademarks, and software. Intangible assets must be recognized initially at cost and amortized over their useful lives, generally using the straight-line method over 10 years. When intangible assets are impaired, an impairment loss is recognized to reduce the carrying amount. The document also distinguishes research and development phases for self-generated intangible assets and outlines accounting for disposals of intangible assets.





![Recognition Of Intangible Assets
[1] Purchased INTANGIBLE ASSET should
be recorded at:
Cost Price Paid
ADD: Taxes Paid
ADD: Expenses To Obtain Title](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptas26-240107154550-869fa3e3/75/PPT-AS-26-pptx-powerpoint-presentation-adv-acc-6-2048.jpg)
![[2] Exchanged INTANGIBLE ASSET
Should be Recorded at
Fair Value Of Asset Surrendered
Whichever is more clearly evident
Fair Value Of Asset Obtained](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptas26-240107154550-869fa3e3/75/PPT-AS-26-pptx-powerpoint-presentation-adv-acc-7-2048.jpg)
![[3] Self Generated INTANGIBLE ASSETS are
those assets which are generated by the
entity at it own
Goodwill , Brand , Trade marks , Copyrights , should
be recorded as INTANGIBLE ASSET.
Remaining INTANGIBLE ASSETS Software ,
Website , Trademark , Knowhow are recorded as
follows:
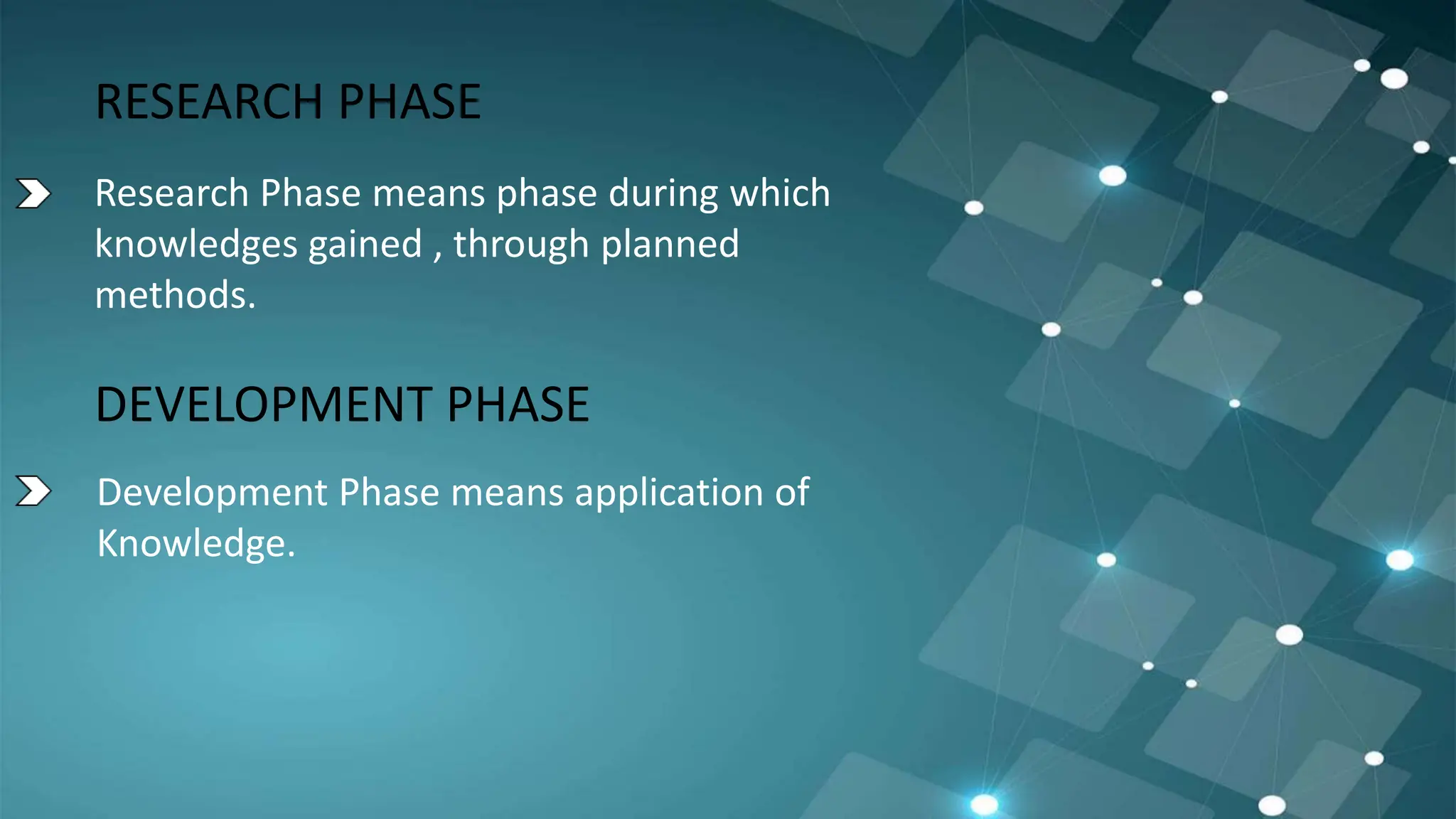
Expenditure during RESEARCH PHASE will
be transferred to P&L A/C
Expenditure during DEVELOPMENT PHASE
will be capitalized with value of asset](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptas26-240107154550-869fa3e3/75/PPT-AS-26-pptx-powerpoint-presentation-adv-acc-8-2048.jpg)