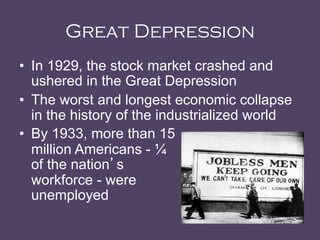
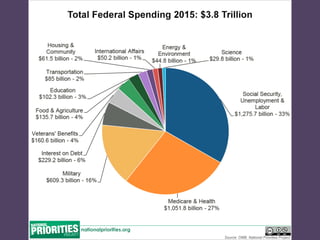
The document discusses different economic policies and theories throughout history, including laissez-faire capitalism prior to the Great Depression, John Maynard Keynes' interventionist views, Reaganomics, and modern fiscal and monetary policy approaches. It provides an overview of the key economic challenges faced during the Great Depression and recession periods, and the different solutions proposed and enacted by governments.