The document discusses the effects of various economic events and policies on inflation and unemployment:
- Consumer expectations of an economic downturn could raise unemployment and lower inflation.
- Higher business expectations from a new president could lower unemployment and raise inflation.
- Lower electricity prices from solar energy adoption could lower inflation and have varying effects on unemployment.
- Raising the gasoline tax to balance the budget could raise both inflation and unemployment.
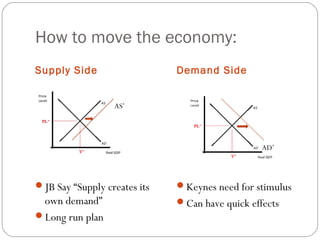
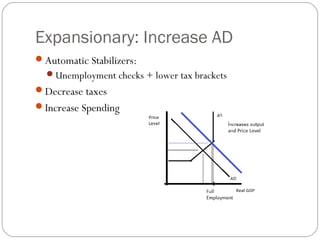
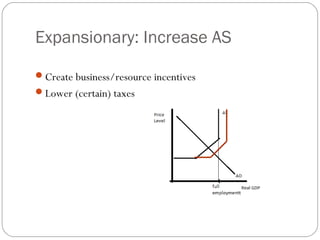
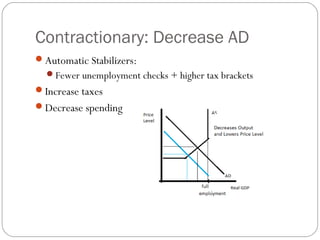
The document then analyzes different types of fiscal policy and their goals, including providing public goods, stabilizing the economy, and promoting cultural values through spending and taxation. Expansionary and contractionary policies are discussed as tools to influence aggregate demand and supply.