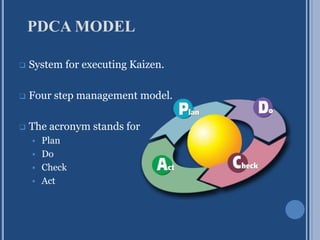
Kaizen is a Japanese term meaning continuous improvement. It originated from combining the Japanese words "Kai" meaning change and "Zen" meaning improvement. Kaizen focuses on continuously improving manufacturing, engineering, and business management processes by involving all employees. The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) model is used as the system for executing Kaizen in a four step approach. Some key advantages of Kaizen include reducing waste, improving employee utilization and production, and reducing completion cycle times.