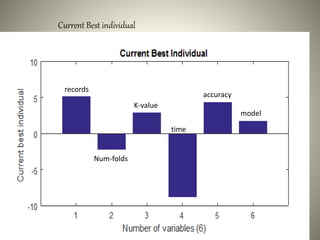
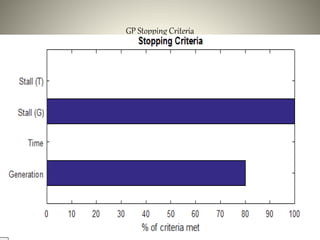
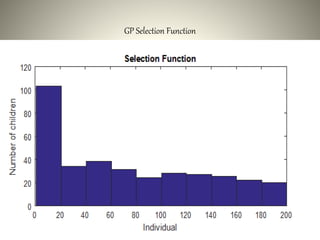
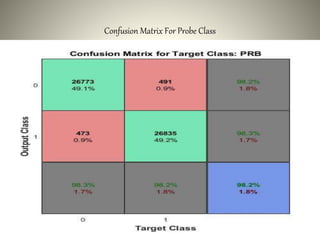
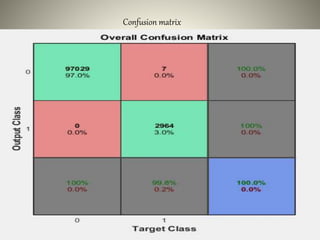
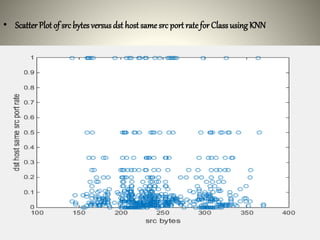
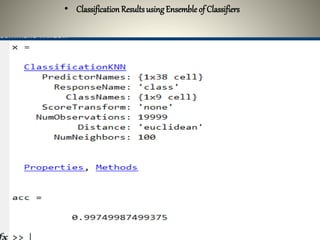
The document proposes using an ensemble of K-nearest neighbor classifiers optimized with genetic programming for intrusion detection. It trains multiple K-NN classifiers on subsets of the KDD Cup 1999 intrusion detection dataset and then uses genetic programming to combine the classifiers to improve performance. Results show the ensemble approach reduces error rates compared to individual classifiers and the genetic programming-based ensemble achieves an area under the ROC curve of 0.99976, outperforming the component classifiers.




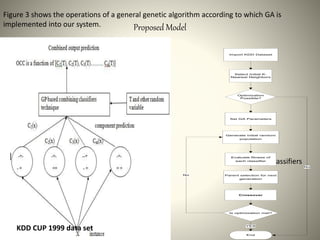
![GP Based Learning Algorithm
Training Pseudo Code
Stst , St represents the test and training data.
C(x): class of x instance
OCC: a composite classifier
Ck : kth component classifier
Ck (x): Prediction of Ck
Train-Composite Classifier (St ,OCC)
Step 1: All input data examples x ∈ St are given to K component
classifiers.
Step 2: Collect [C1 (x),C2 ( x), ,Ck (x)] for all x ∈ St to form a set of
prediction Class
Step 3: Start GP combining method, while using predictions as unary
function in GP tree. Threshold T is used as a variable to compute
ROC curve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00f37fa3-04da-4738-8b0b-bc21f0a378ae-160430071623/85/powerpoint-feb-6-320.jpg)
![GP Based Learning Algorithm………
Pseudo Code for Classification
1. Apply composite classifier (OCC, x )to data examples x
taken from Stst .
2. X= [C1 (x),C2 ( x), ,Ck (x)], stack the predictions to form new
derived data.
3. Compute OCC(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00f37fa3-04da-4738-8b0b-bc21f0a378ae-160430071623/85/powerpoint-feb-7-320.jpg)