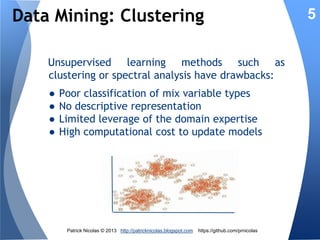
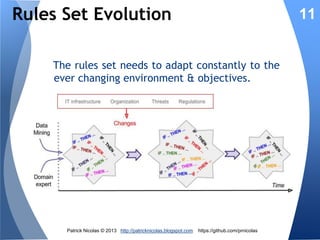
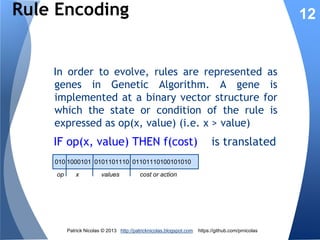
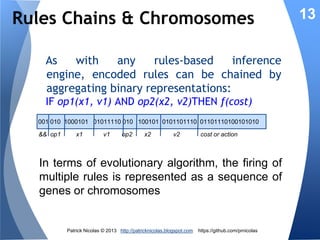
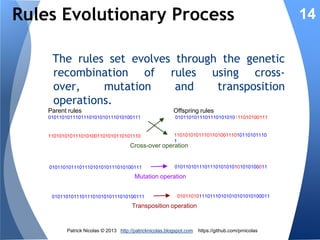
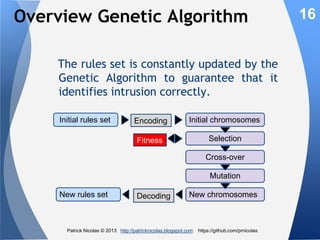
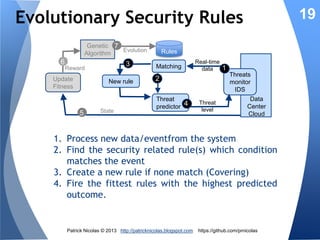
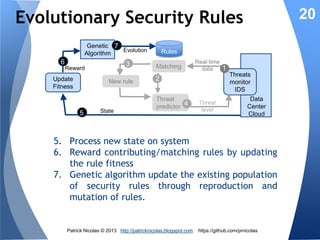
The document discusses using learning classifiers and genetic algorithms to implement an adaptive intrusion detection system. Traditional data mining techniques are limited in their ability to adapt to changing environments, but learning classifiers systems combine genetic algorithms and reinforcement learning to discover and evolve security policies and rules from real-time data. The rules are represented as genes and evolved over time through processes of crossover, mutation, and selection to accurately identify threats.