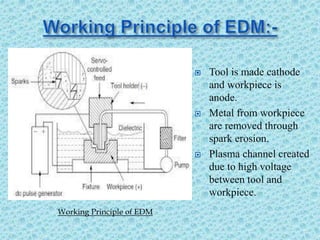
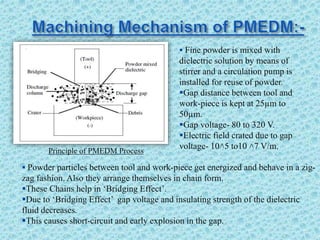
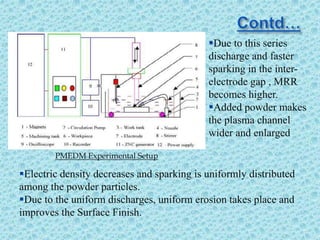
1. The document discusses powder mixed electro discharge machining (PMEDM), a variant of electro discharge machining (EDM) that improves surface finish, material removal rate, and reduces tool wear.
2. In PMEDM, fine conductive powder is mixed with the dielectric fluid, allowing for more uniform sparking between the tool and workpiece.
3. Key benefits of PMEDM include the ability to machine any conductive material regardless of hardness and the ability to produce complex, stress-free geometries with a fine surface finish.