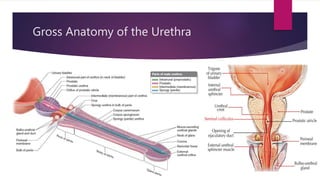
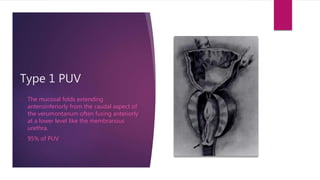
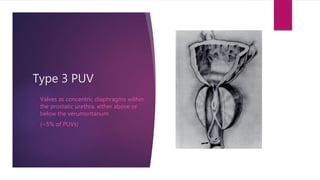
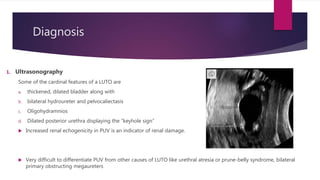
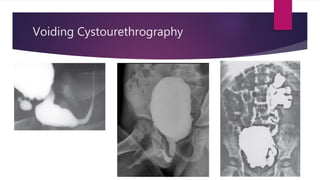
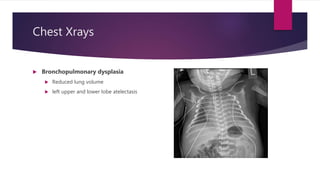
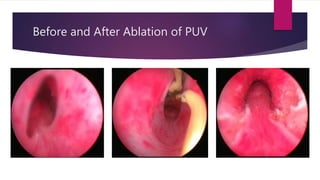
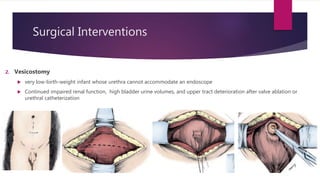
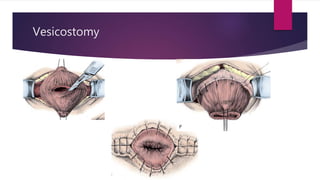
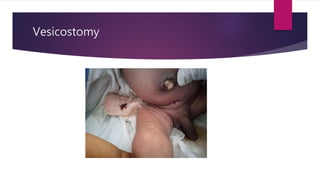
Posterior urethral valves is a congenital condition caused by abnormal membranes in the proximal urethra that obstruct the flow of urine. It most commonly presents in infancy with failure to pass urine and is diagnosed using imaging like ultrasound and voiding cystourethrography. Treatment involves surgical ablation of the valves via cystoscopy to restore urinary flow and halt renal damage. Prognosis depends on factors like age at diagnosis and degree of renal dysfunction, as patients may develop lifelong complications due to the original renal insults.