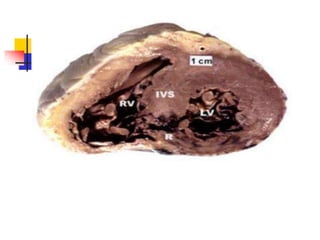
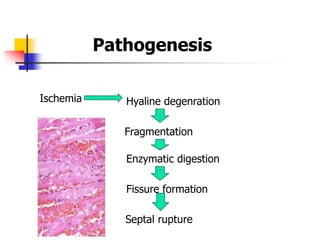
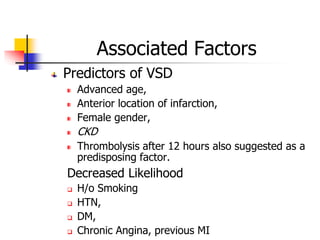
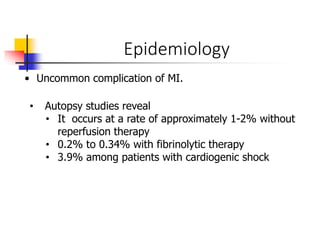
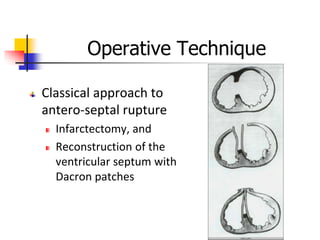
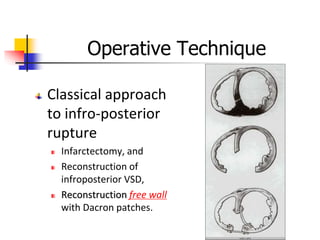
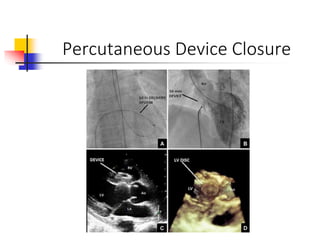
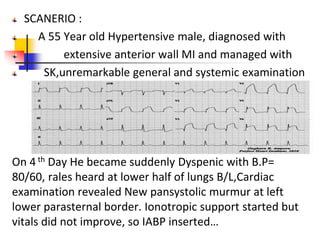
Ventricular septal rupture (VSR) is a rare but serious complication of myocardial infarction where a tear forms in the ventricular septum, creating a left-to-right shunt. It typically occurs 2-8 days after MI. Diagnosis is made through echocardiography which demonstrates the shunt. Urgent surgical repair is the treatment of choice to close the defect before hemodynamic deterioration, though supportive medical management may be used to stabilize the patient pre-operatively. Surgical techniques involve infarct removal and patch reconstruction of the septum. Prognosis depends on factors like presence of cardiogenic shock, with posterior defects associated with higher mortality.