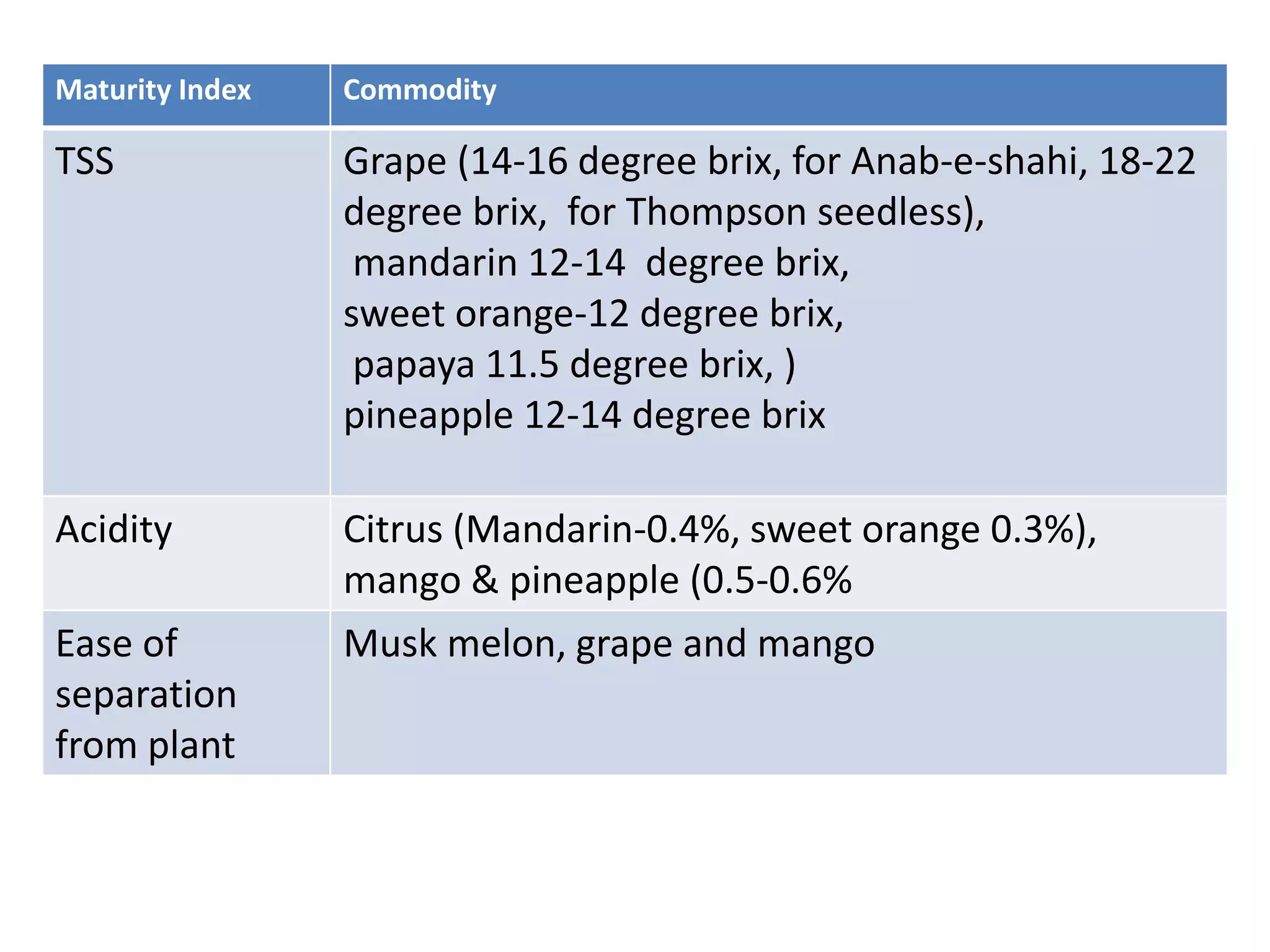
This document discusses maturity and ripening of horticultural crops. It defines maturity as the stage of full development when fruit can normally ripen. Maturity includes horticultural, physiological and commercial stages. Physiological maturity occurs when fruit can ripen after detaching from the plant. Various methods to determine maturity are described, including color, size, shape, aroma, sugars and acidity. Ripening is a genetically programmed process involving physiological and biochemical changes, and it is classified as climacteric or non-climacteric. Changes during ripening include cell wall breakdown, starch hydrolysis, organic acid and pigment changes, flavor and nutrient development.