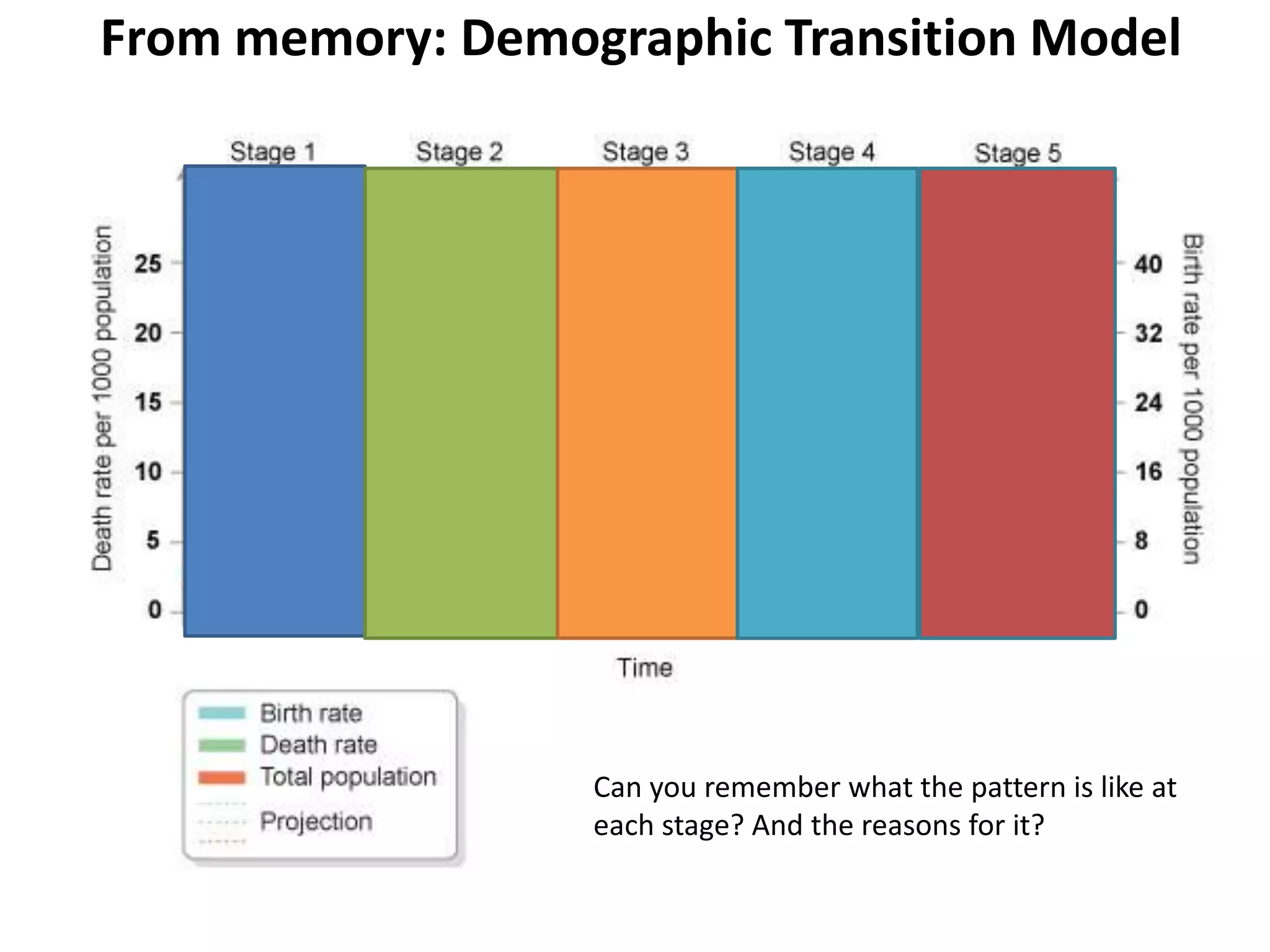
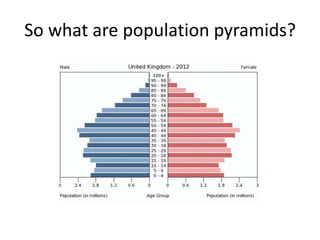
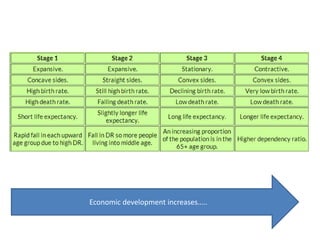
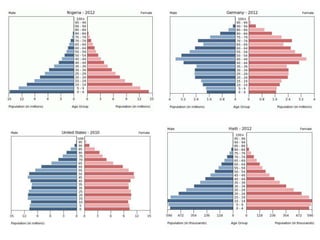
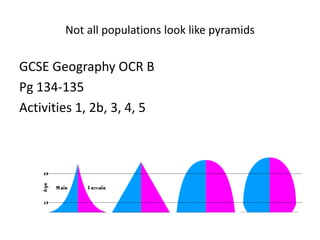
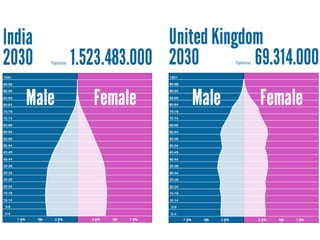
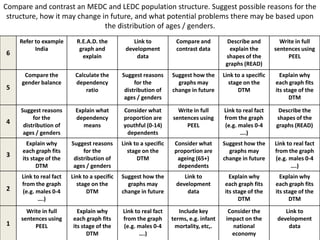
The document discusses the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) and population pyramids. It provides instructions to determine which stage of the DTM various population scenarios described in statements would fall under. It also discusses comparing population pyramids of less economically developed countries (LEDCs) and more economically developed countries (MEDC), how they vary in age and gender structure, and how this relates to development indicators and can change over time. Finally, it provides activities analyzing India's population structure through population pyramids and discussing overpopulation issues.