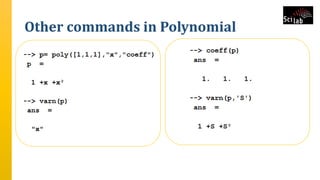
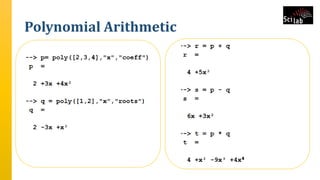
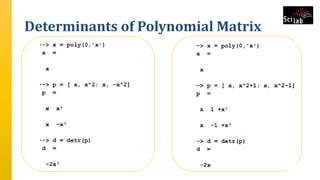
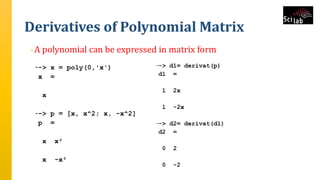
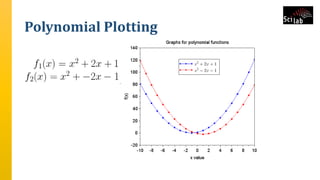
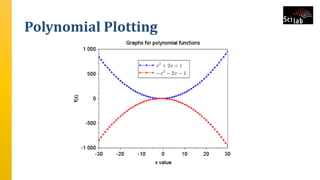
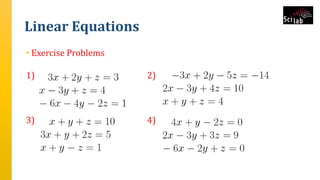
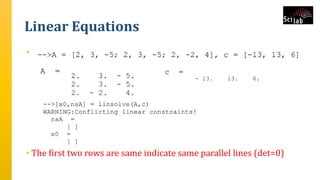
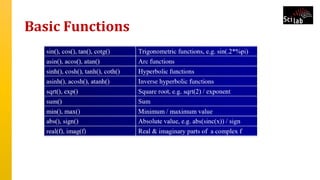
The document provides an overview of signal analysis in MATLAB, focusing on polynomials and their manipulation in Scilab. It discusses the creation, determinants, and derivatives of polynomials, as well as solutions to linear equations represented as matrix equations. Additionally, it covers definite integration in Scilab, demonstrating the evaluation of definite integrals using various functions.




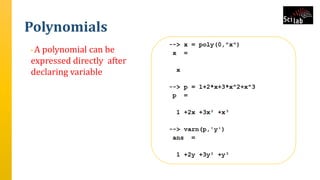
![Polynomials
• Examples in SCILAB
• 1] 3]
• 2] 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polynomialsinscilab-201016043459/85/Polynomials-in-scilab-6-320.jpg)