Chapter 2: Polynomials – Summary Notes
A polynomial is an algebraic expression of the form:
P(x) = a₀xⁿ + a₁xⁿ⁻¹ + ... + aₙ, where a₀, a₁, ..., aₙ are real numbers and n is a non-negative integer.
Types of Polynomials (by degree):
Zero polynomial: P(x) = 0
Constant polynomial: Degree = 0
Linear polynomial: Degree = 1 (e.g., 3x + 2)
Quadratic polynomial: Degree = 2 (e.g., x² – 4x + 3)
Cubic polynomial: Degree = 3 (e.g., x³ + x² – x + 1)
Degree of a Polynomial:
The highest power of the variable.
Zeroes of a Polynomial:
The value(s) of x for which P(x) = 0.
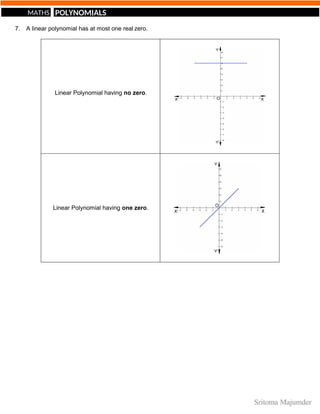
A linear polynomial has 1 zero.
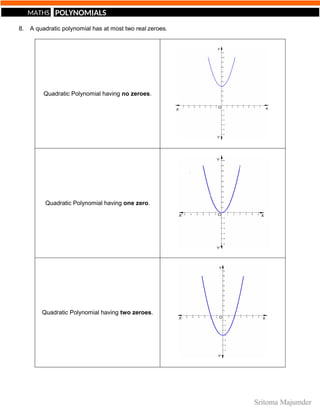
A quadratic polynomial has 2 zeroes.
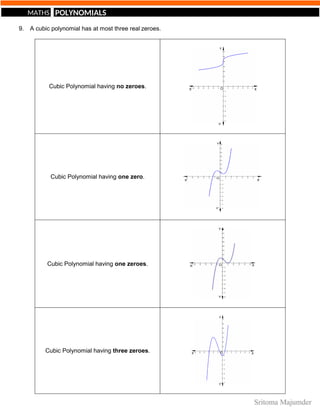
A cubic polynomial has 3 zeroes (at most).
Relationship between Zeroes and Coefficients:
For a quadratic polynomial:
ax² + bx + c, with zeroes α and β:
Sum of zeroes (α + β) = –b/a
Product of zeroes (αβ) = c/a
For a cubic polynomial:
ax³ + bx² + cx + d, with zeroes α, β, γ:
α + β + γ = –b/a
αβ + βγ + γα = c/a
αβγ = –d/a
Forming a Polynomial from Given Zeroes:
If α and β are zeroes, and leading coefficient is a, then:
P(x) = a(x – α)(x – β)
Division Algorithm for Polynomials:
For polynomials P(x) and G(x) (G(x) ≠ 0):
There exist Q(x) (quotient) and R(x) (remainder) such that:
P(x) = G(x) × Q(x) + R(x),
where deg(R(x)) < deg(G(x))

![POLYNOMIALS
MATHS
10. Relationship between zeroes and coefficients of a polynomial:
i. For a linear polynomial ax + b, a 0, the zero is x
b
. It can be observed that:
a
b
constant term
a Coefficient of x
ii. For a quadratic polynomial ax2
+ bx + c, a 0,
Sum of the zeroes = -
b
= -
a
Coefficient of x
Coefficient of x2
Product of the zeroes =
c
= constant term
a Coefficient of x2
iii. For a cubic polynomial ax3
+ bx2
+ cx + d = 0, a 0,
b
Coefficient of x2
Sum of zeroes =
a Coefficient of
x3
,
Sum of the product of zeroes taken two at a time =
c
a
Coefficient of x
,
Coefficient of x3
Product of zeroes = -
d
= - Constant term
a Coefficient of x3
11. The quadratic polynomial whose sum of the zeroes = ( + ) and product of zeroes = () is given by:
k [x2
- ( + ) x + ()], where k is real.
If a , b and g are the zeroes of a cubic polynomial f (x)= ax3
+ bx2
+ cx + d, a ¹ 0 , then
f (x)= k (x - a )(x- b )(x - g )
f (x)= k {x3
- (a + b + g )x2
+ (ab + bg + ga )x - abg },
where k is any non-zero real number.
12. Process of dividing a polynomial f(x) by another polynomial g(x) is asfollows:
Step 1: To obtain the first term of the quotient, divide the highest degree term of the dividend by the
highest degree term of the divisor. Then carry out the division process.
Step 2: To obtain the second term of the quotient, divide the highest degree term of the new dividend
by the highest degree term of the divisor. Then again carry out the division process
Step 3: Continue the process till the degree of the new dividend is less that the degree of the divisor.
This will be called the remainder.
13. Division Algorithm for polynomials: If f(x) and g(x) are any two polynomials, where g(x) ≠ 0, then
there exists the polynomials q(x) and r(x) such that f(x) = g(x) q(x) + r(x), where r(x) = 0 or degree of
r(x) < degree of g(x)
So, q(x) is the quotient and r(x) is the remainder obtained when the polynomial f(x) is divided by the
polynomial g(x).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-2polynomials-watermark-250601164301-48e8ec2f/85/CBSE-Grade-10-Mathematics-Ch-2-Polynomials-Notes-PDF-Format-6-320.jpg)
