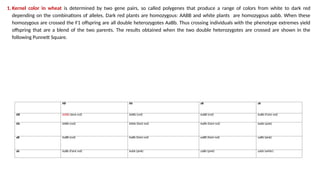
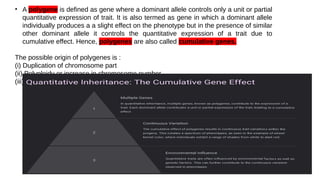
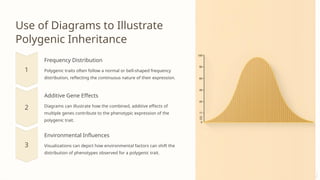
The document discusses two types of inheritance: qualitative inheritance, controlled by a single dominant gene resulting in discrete traits, and quantitative inheritance, influenced by multiple genes leading to continuous variation in traits. Examples of quantitative traits include plant height and fruit quality, with statistical methods used to analyze their genetic contributions. The document also emphasizes the role of environmental factors and genetic markers in the breeding and improvement of polygenic traits.