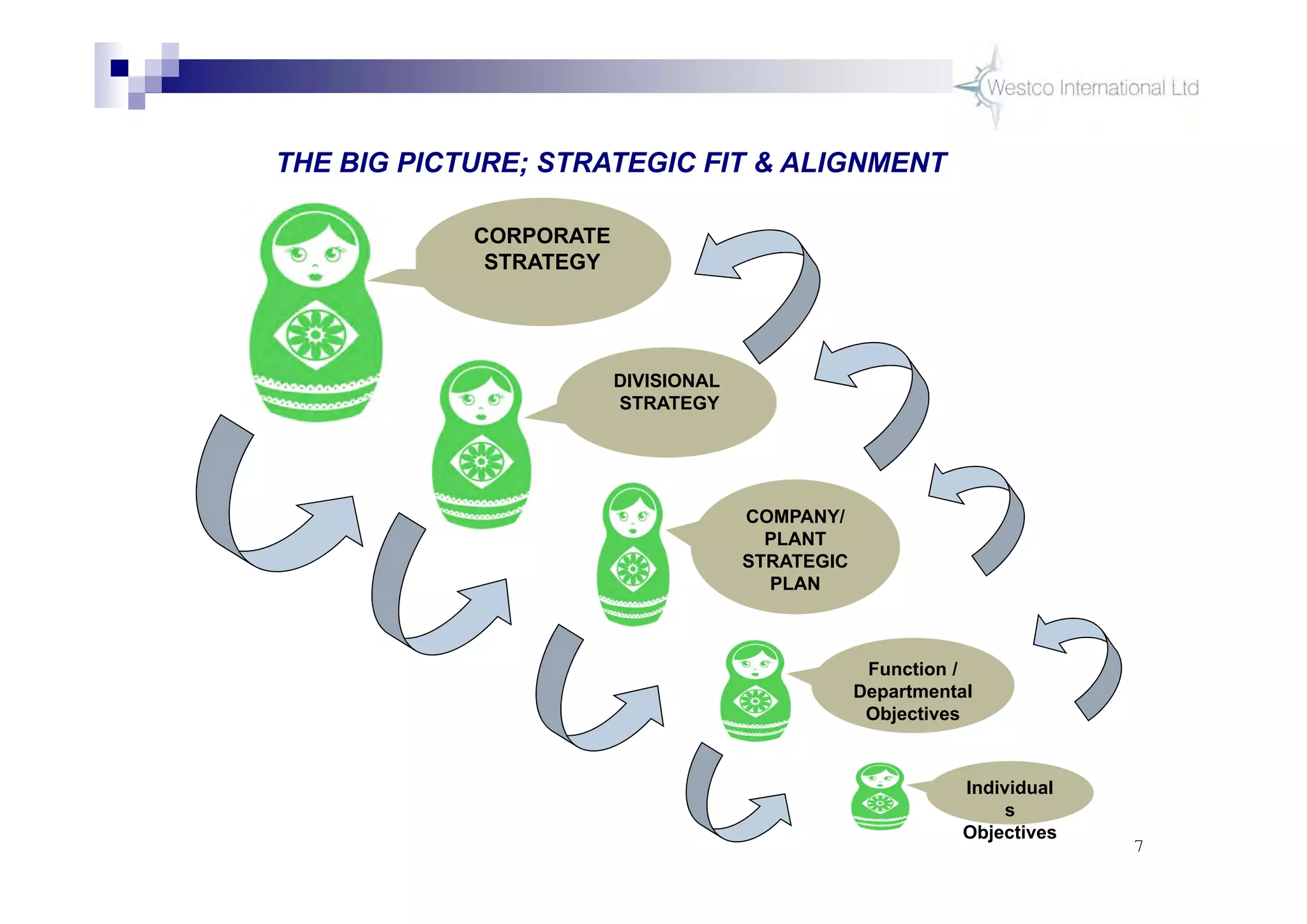
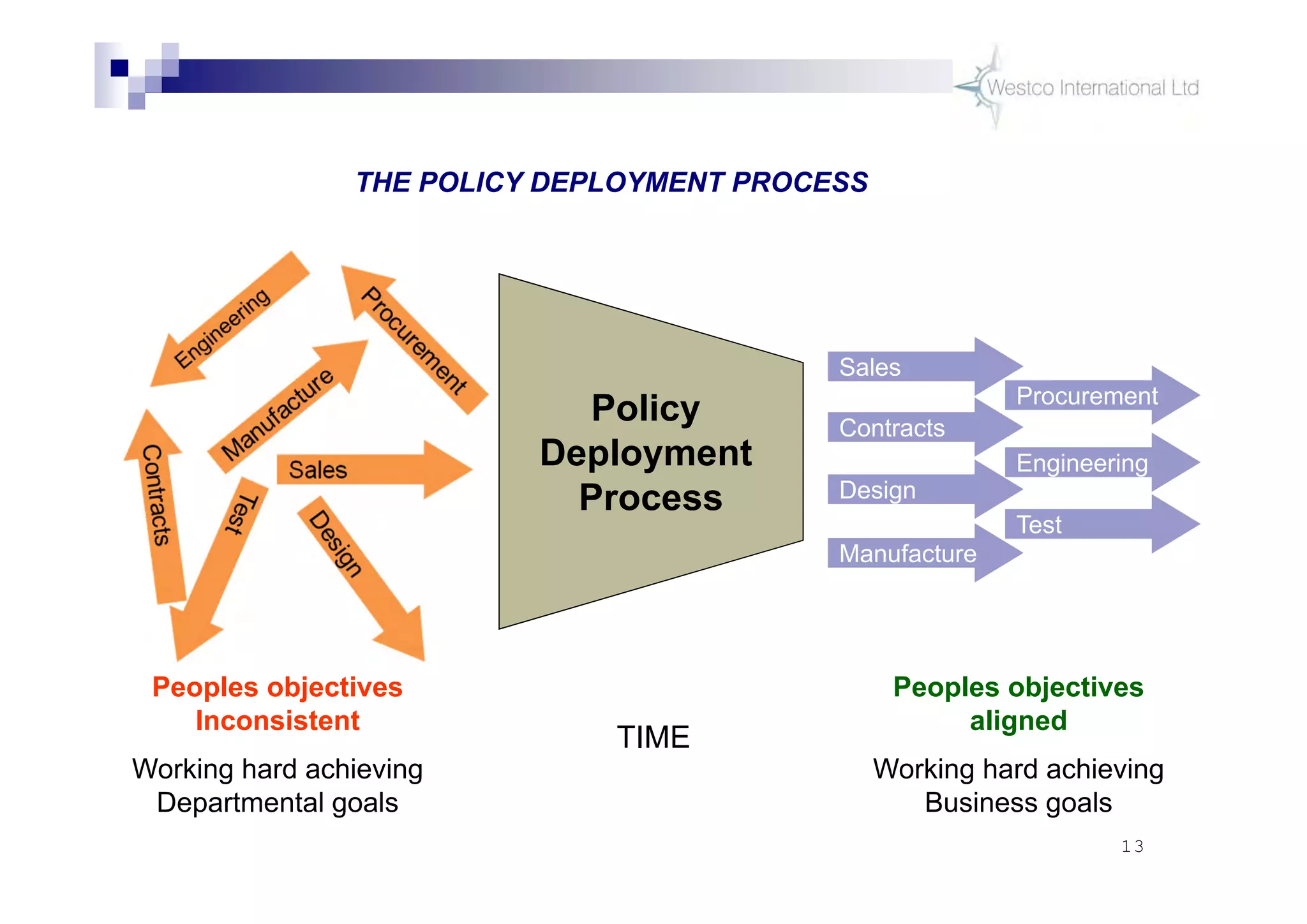
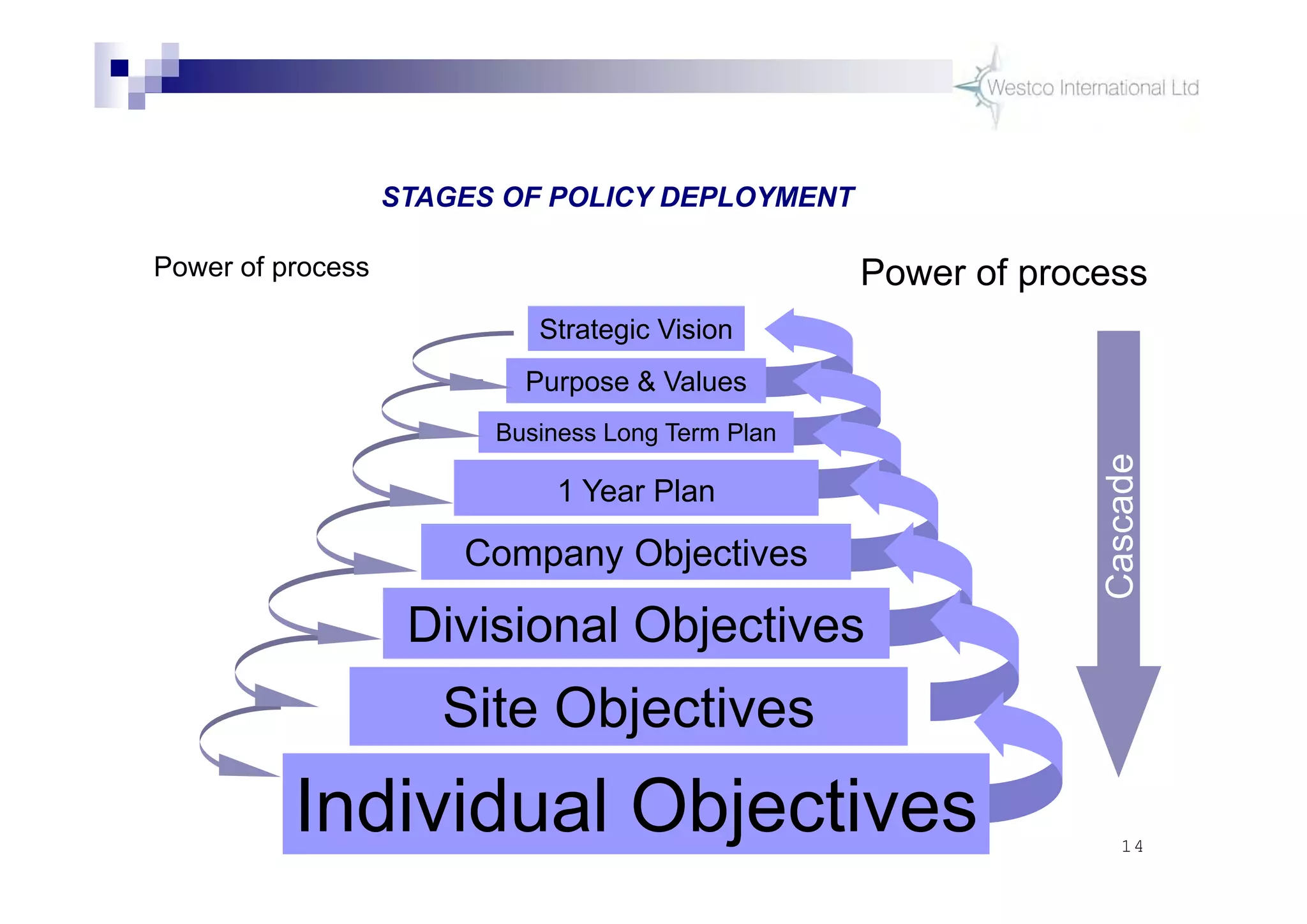
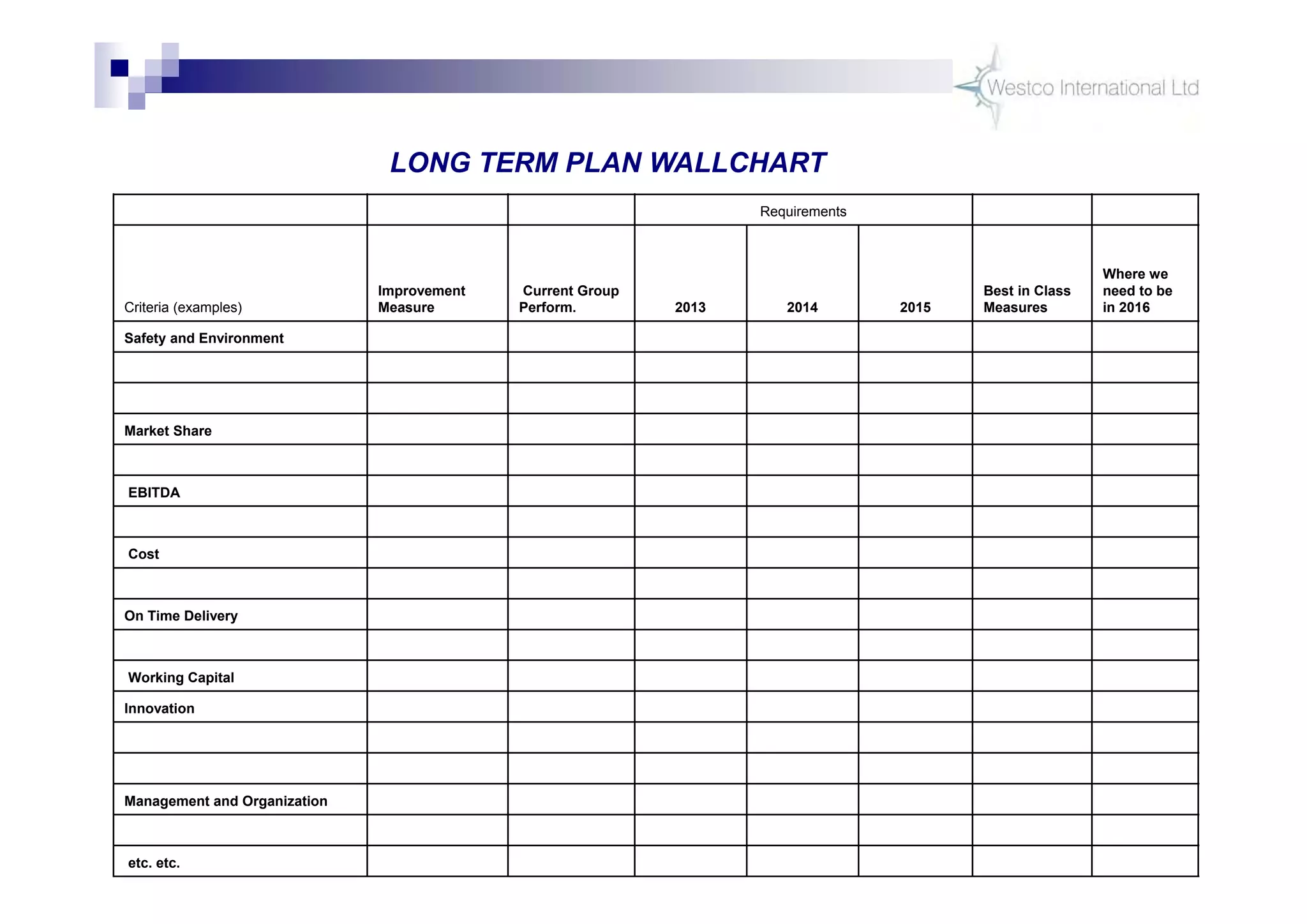
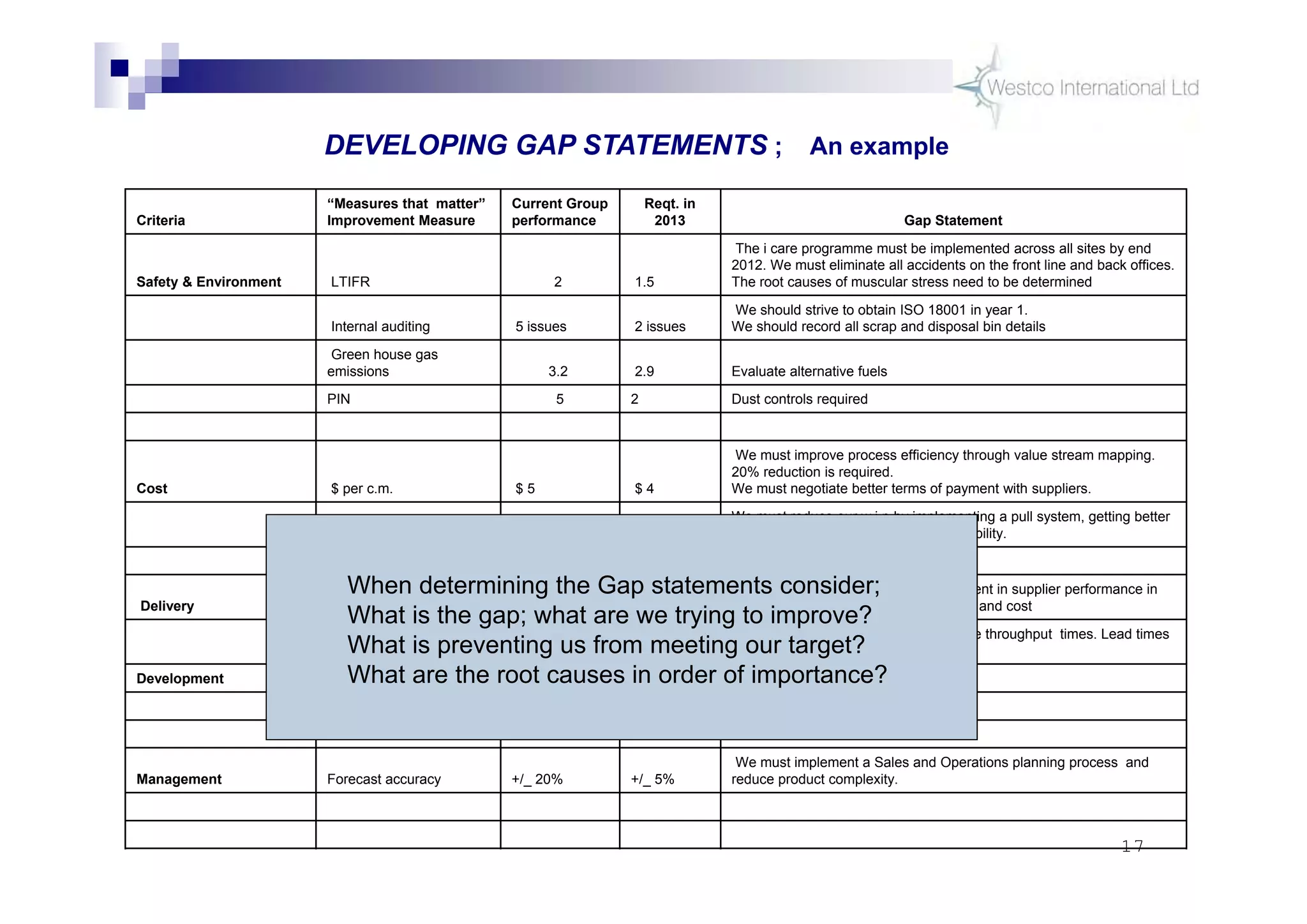
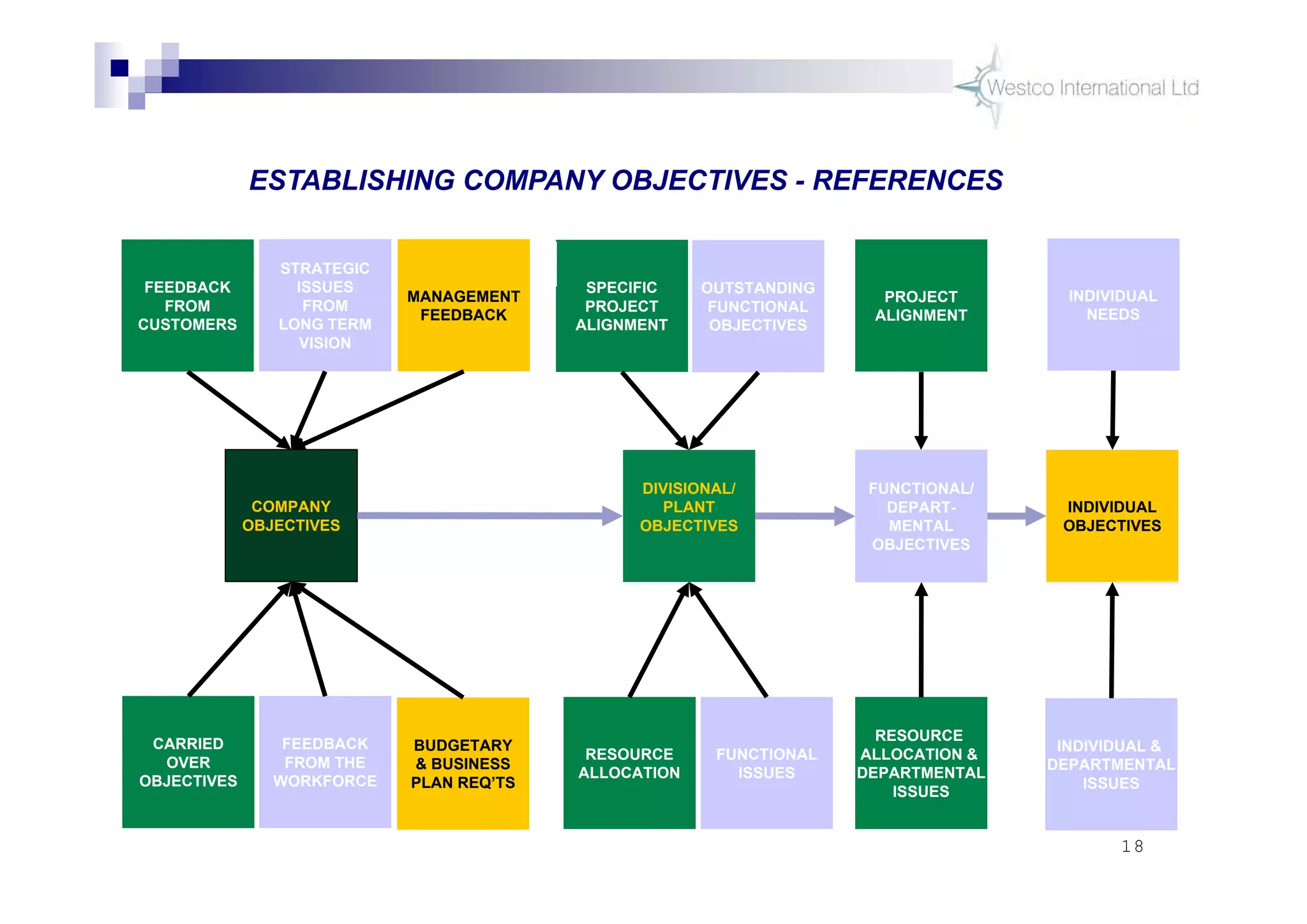
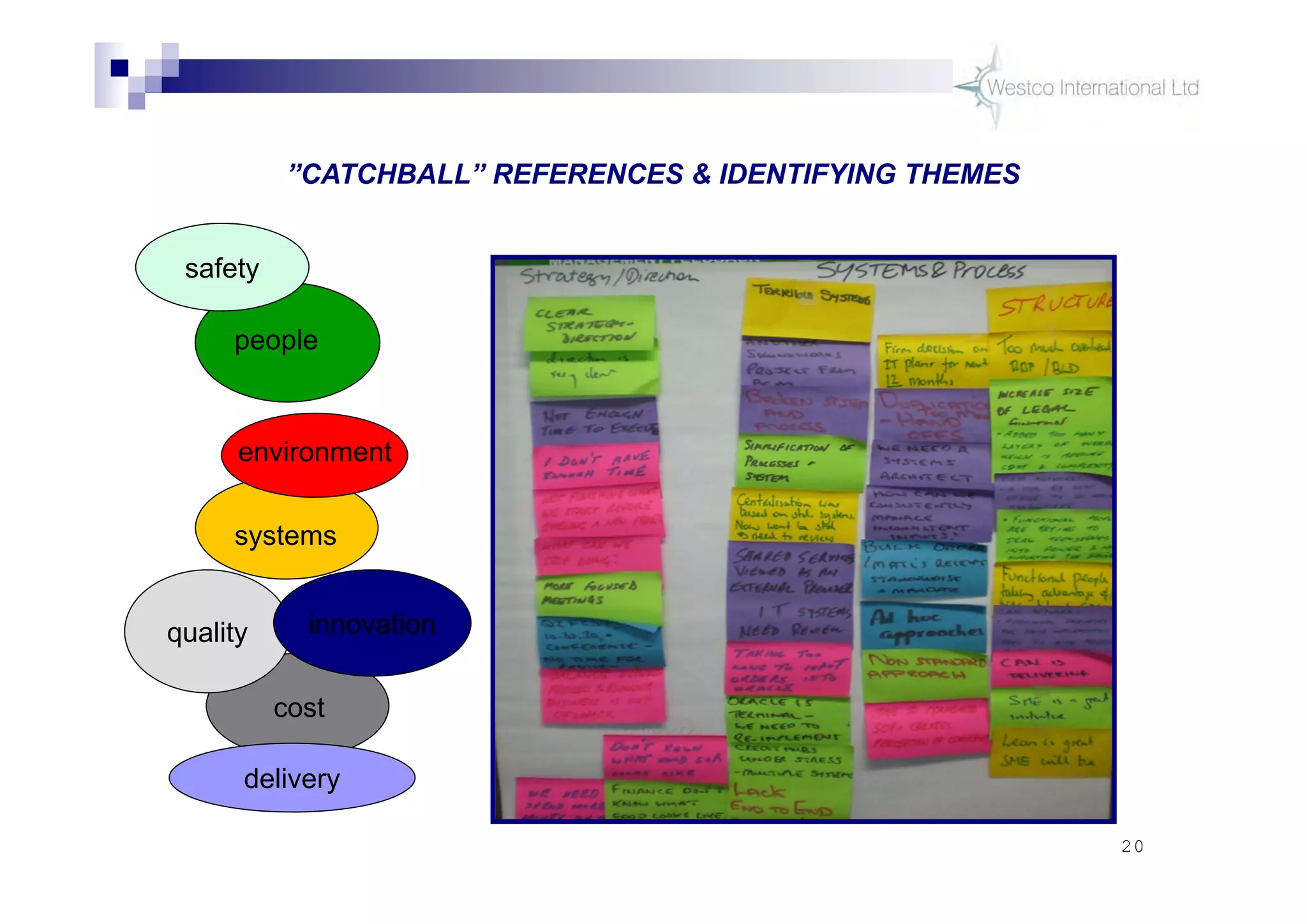
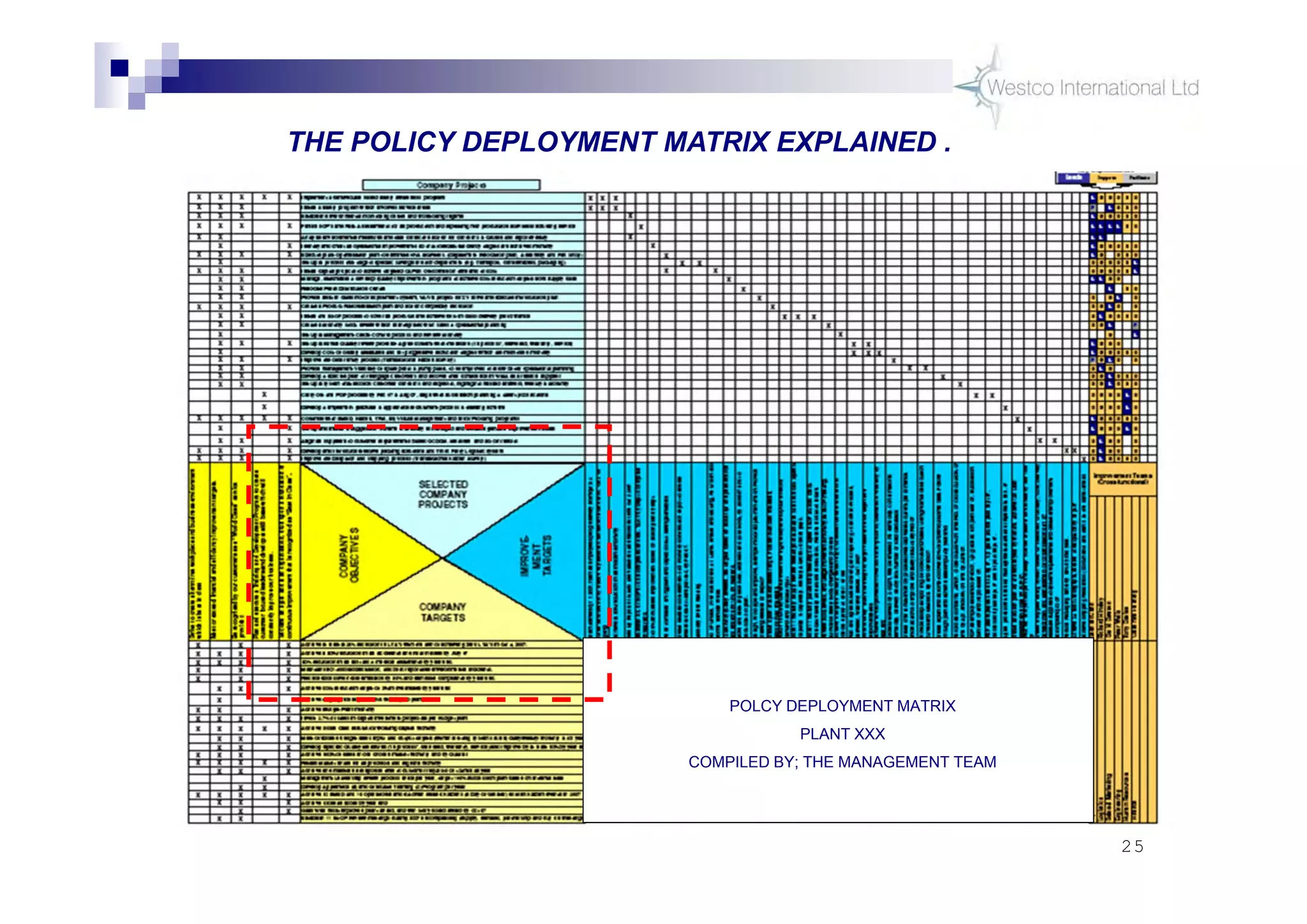
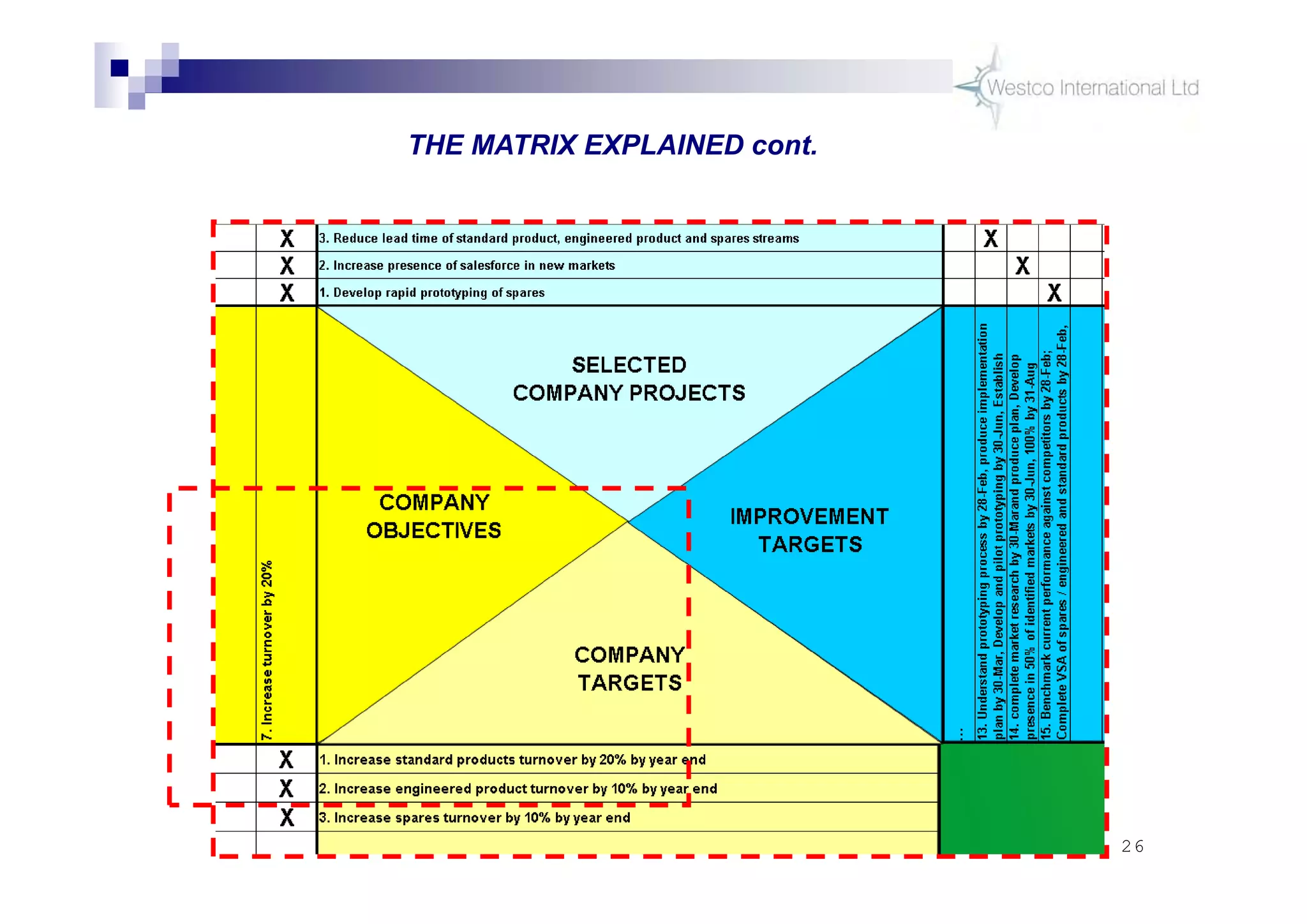
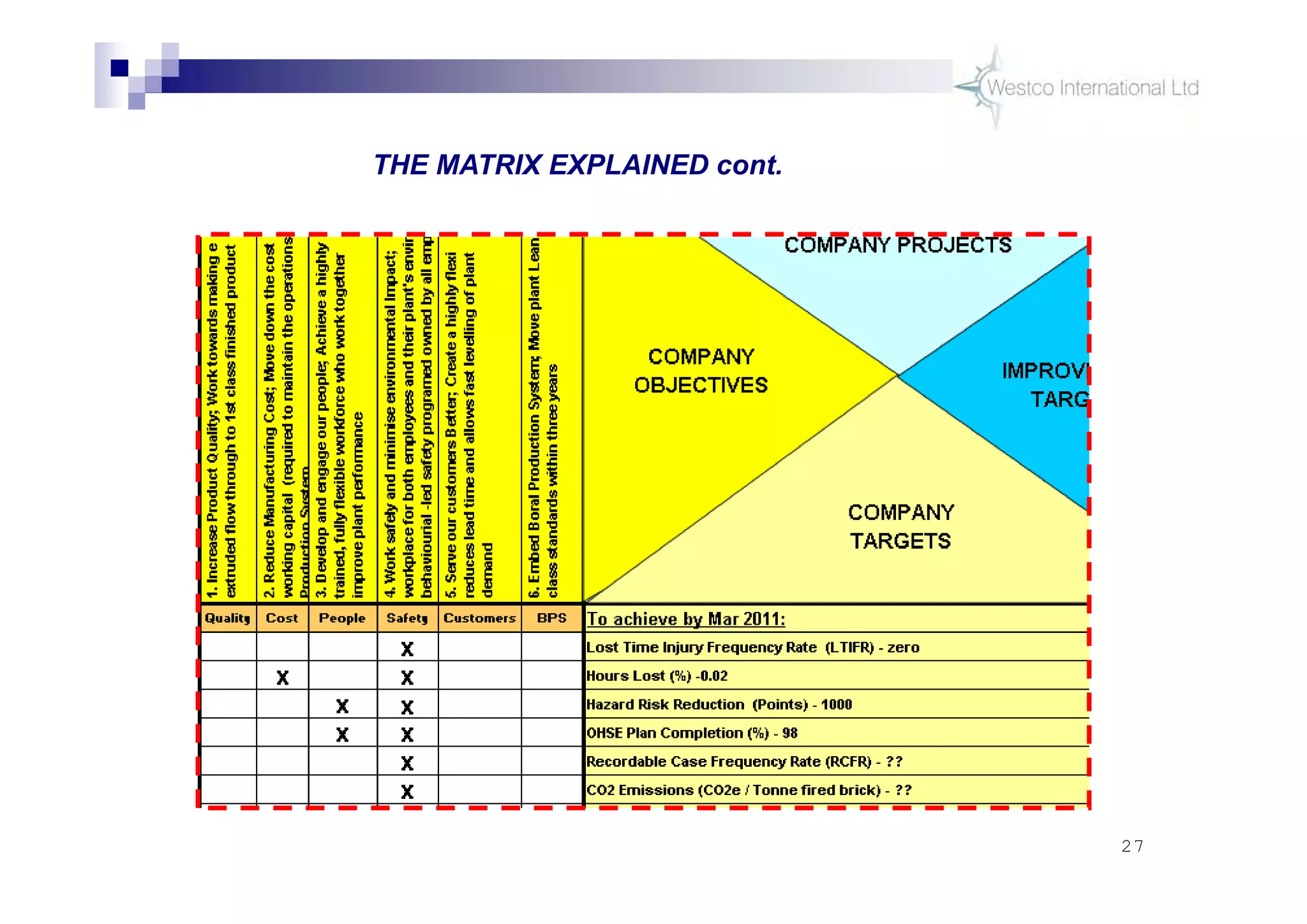
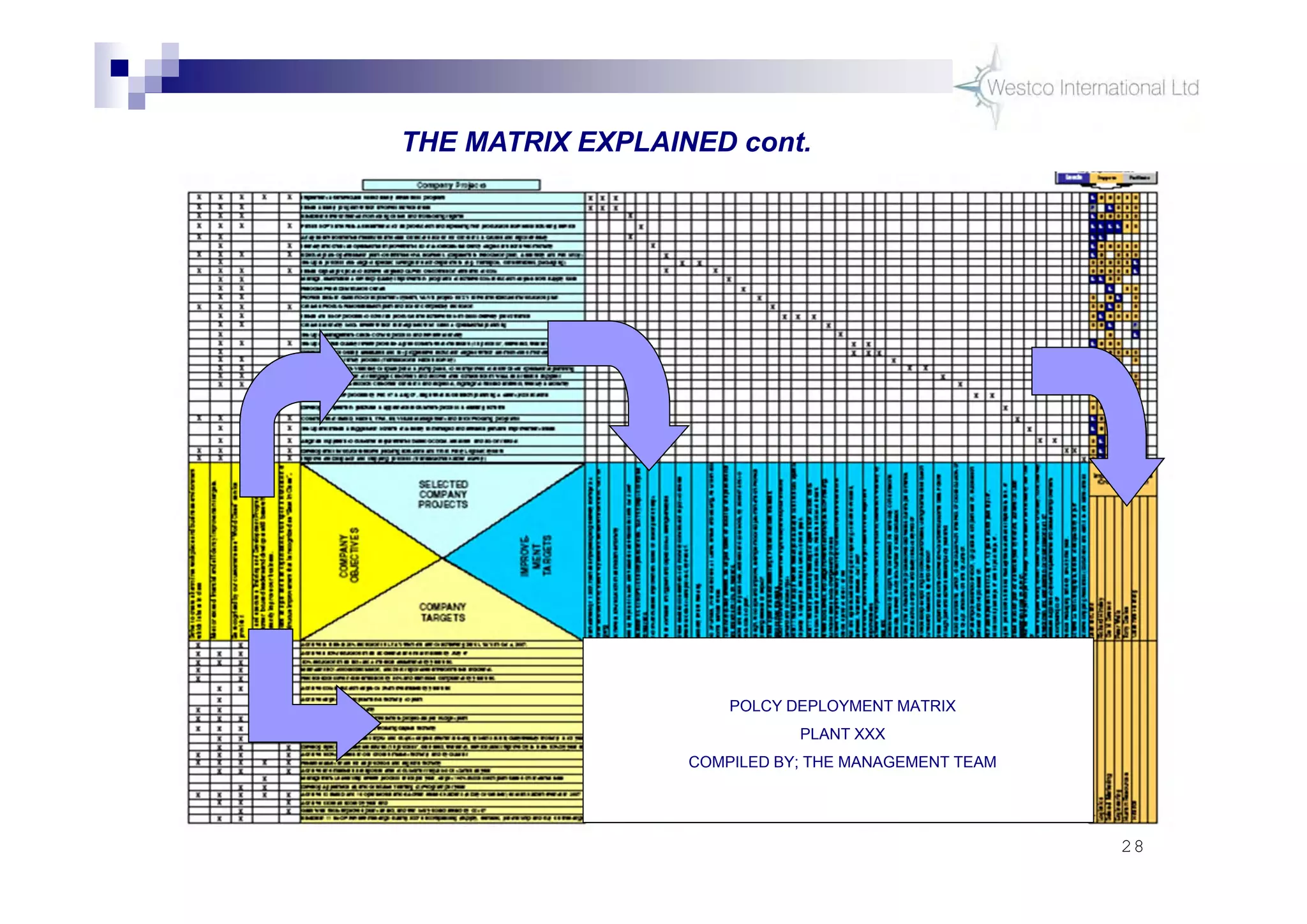
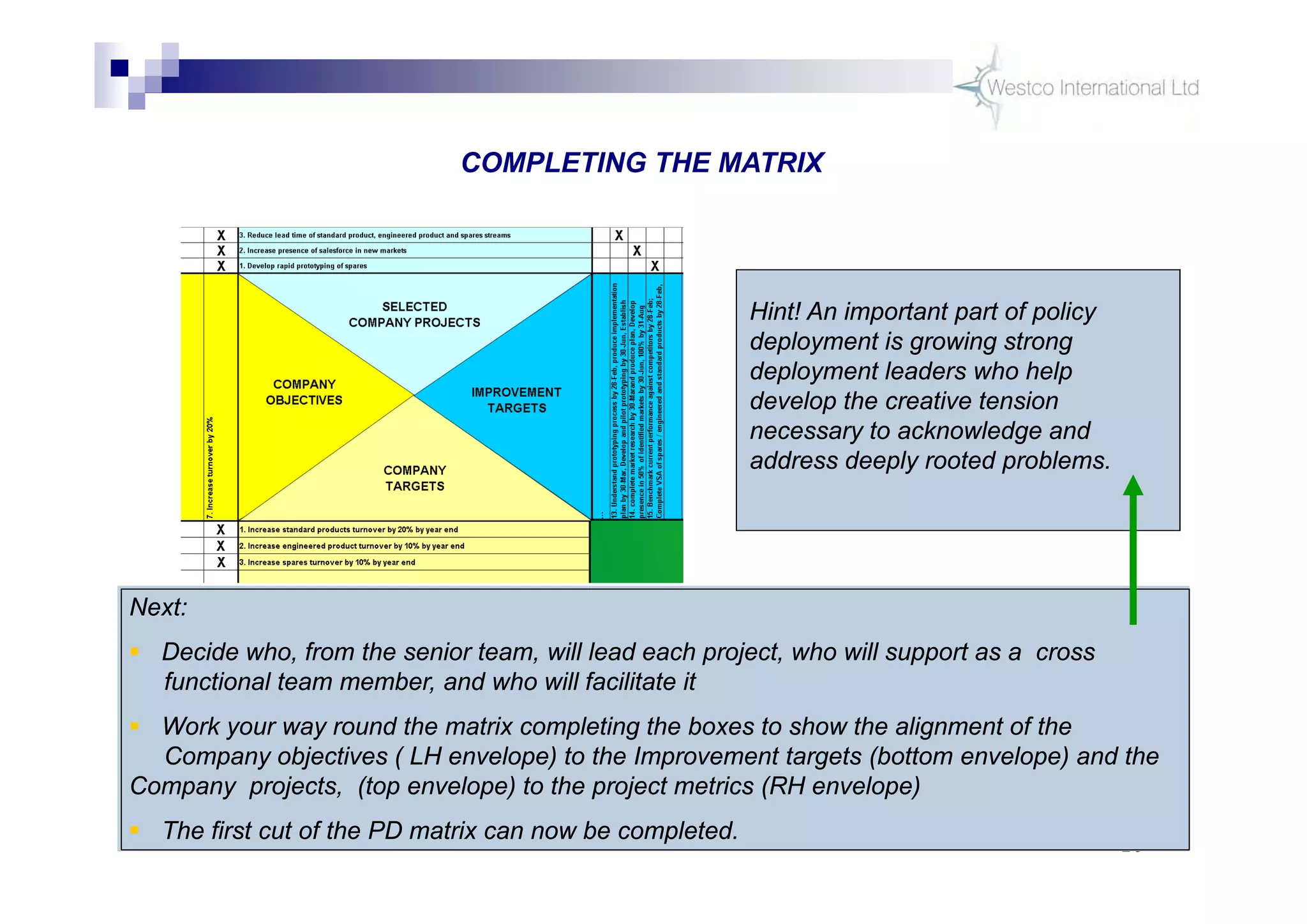
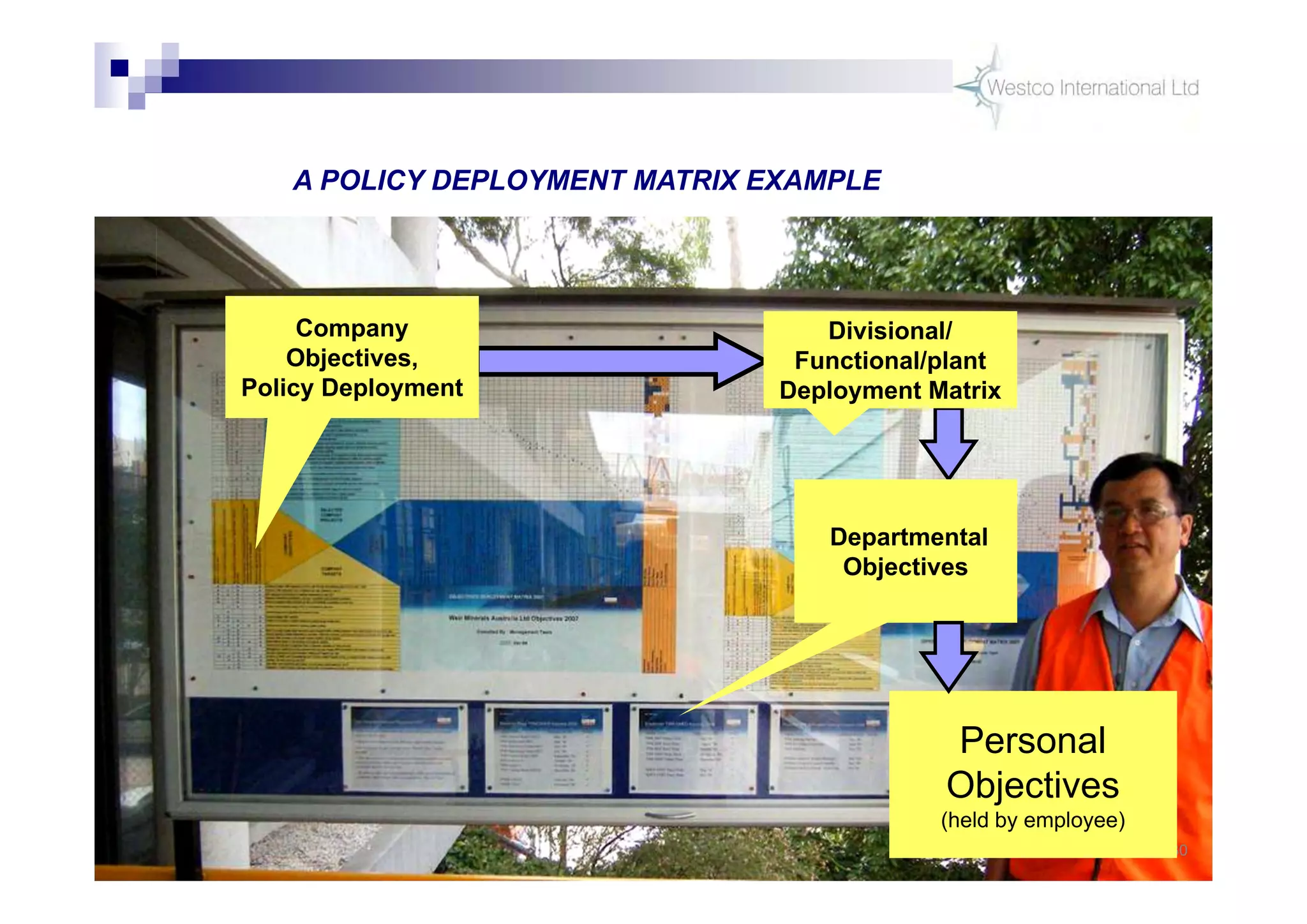
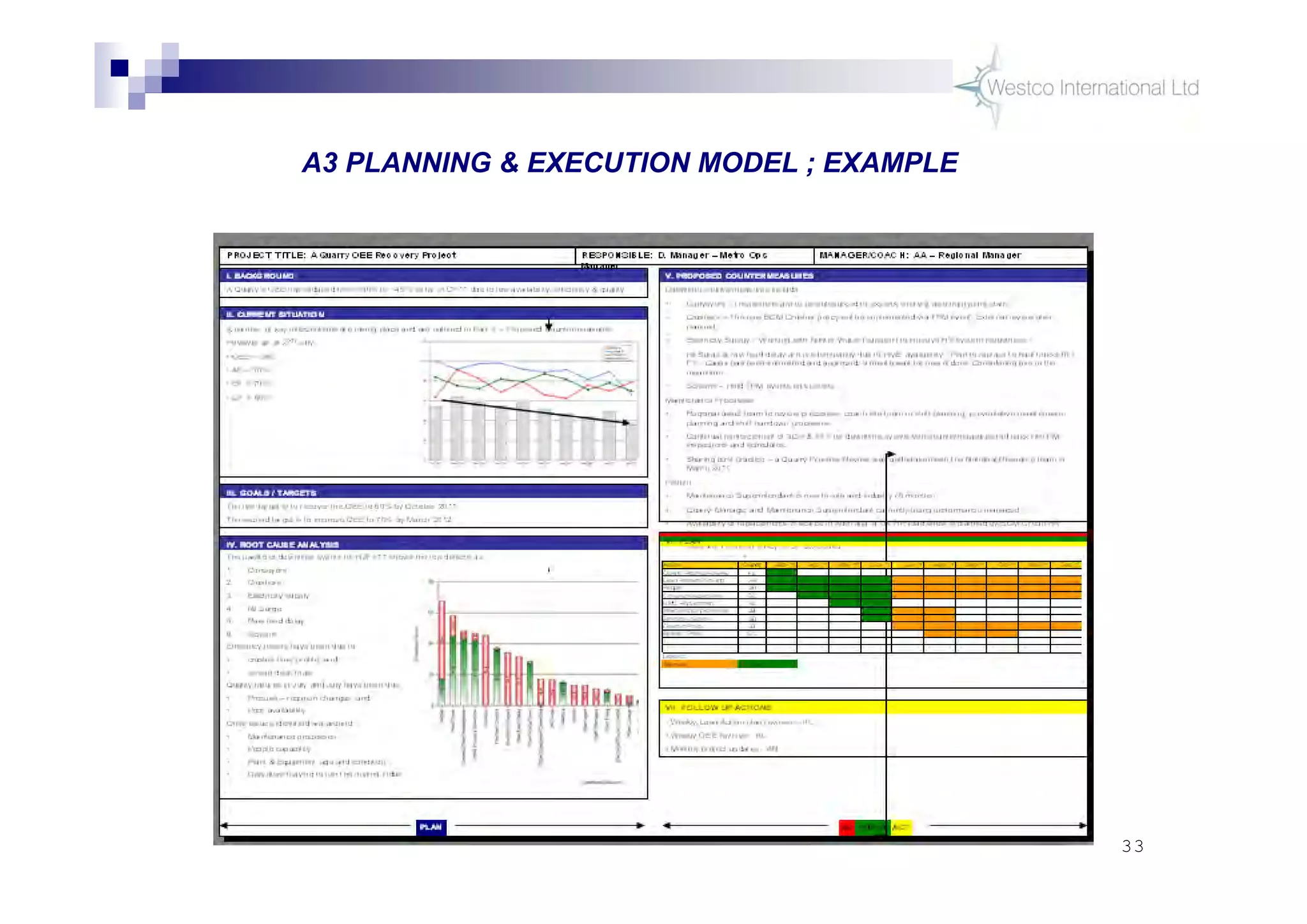
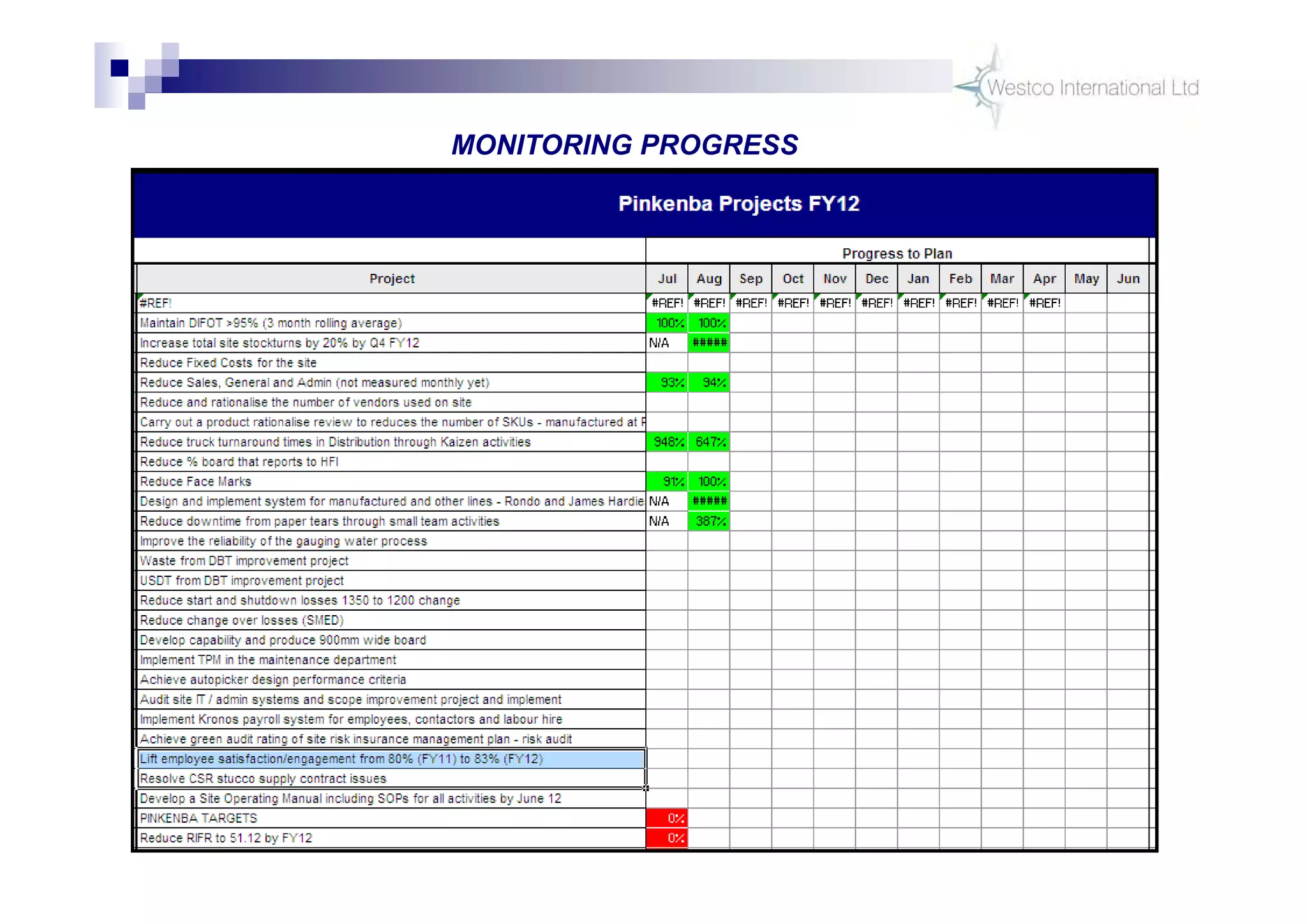
The document discusses policy deployment as a process for aligning strategy execution across an organization. It begins by explaining the importance of strategy and outlines the policy deployment process. This includes developing objectives at each level of the organization from corporate down to individual employee objectives. Projects are then selected and prioritized to achieve the objectives. Progress is monitored using metrics in a policy deployment matrix to ensure the strategy is executed successfully.