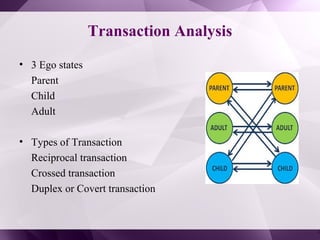
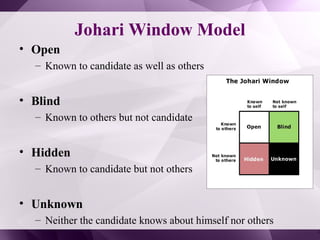
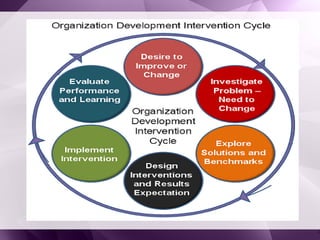
The document discusses organizational development (OD) interventions, which are structured actions aimed at enhancing organizational effectiveness through various techniques at individual, team, intergroup, and organizational levels. It highlights individual interventions such as sensitivity training, coaching, and stress management, detailing their objectives, advantages, and disadvantages. A case study on the self-renewal of a school system illustrates the application of these interventions to improve organizational dynamics and effectiveness.