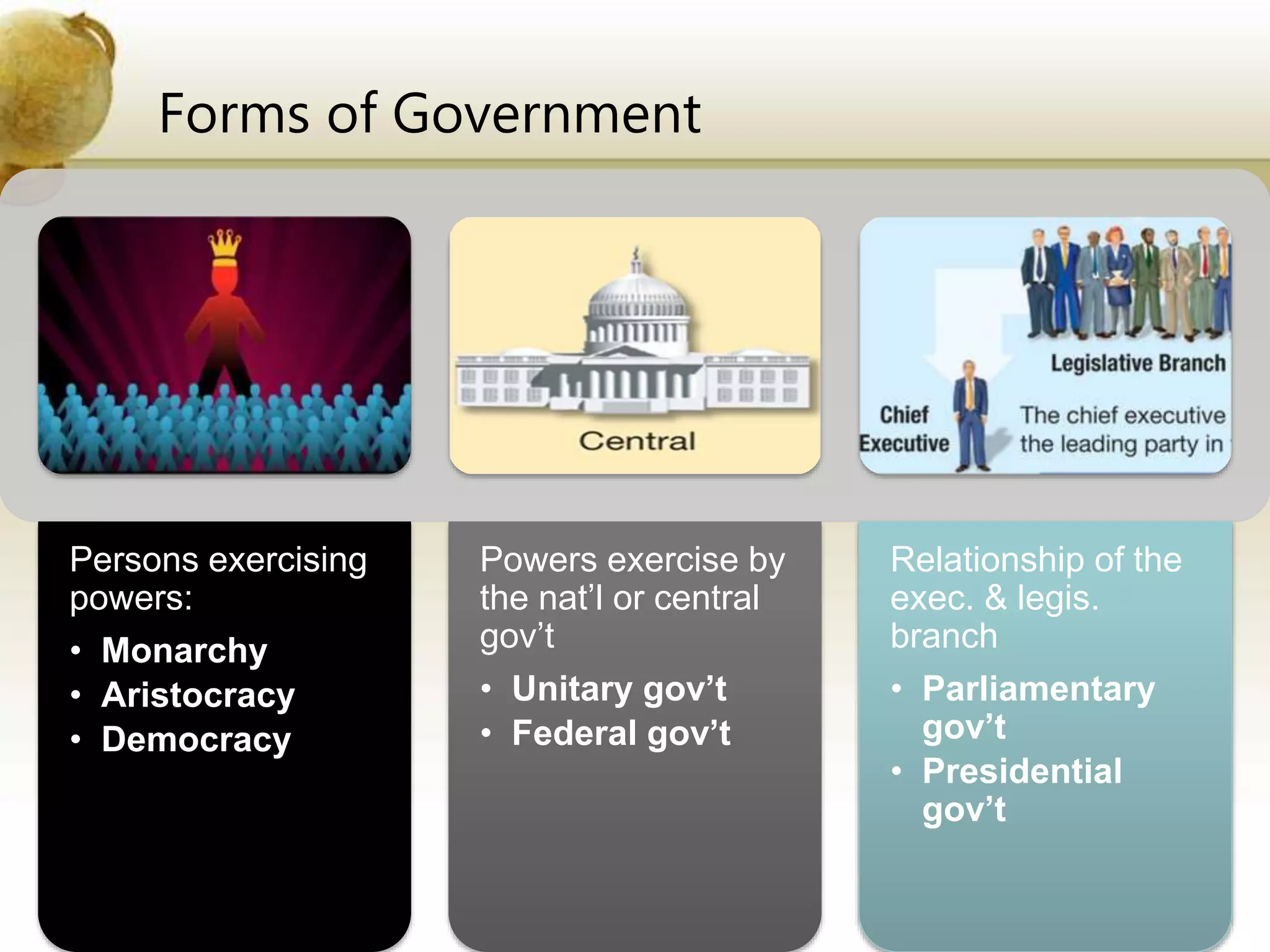
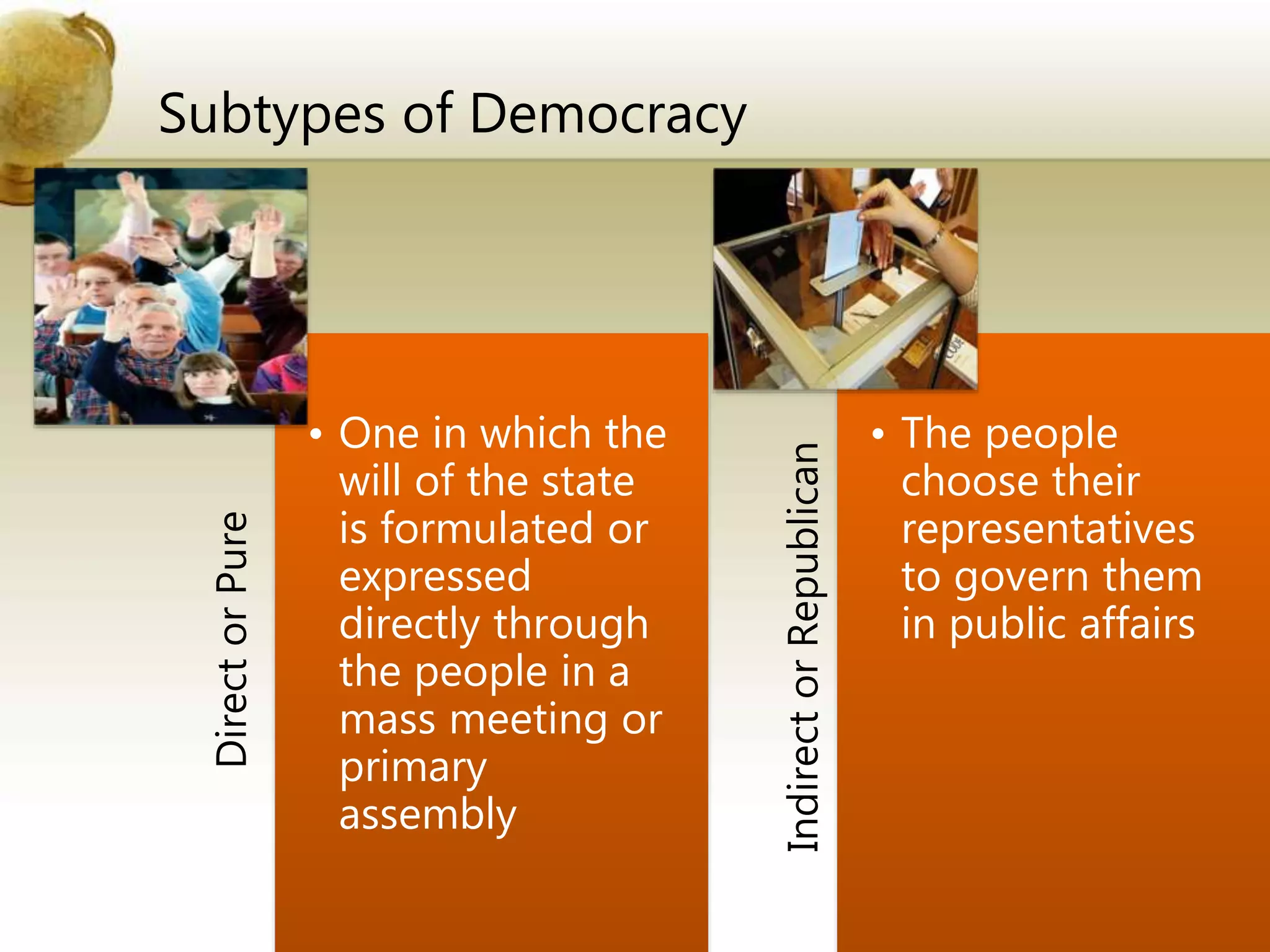
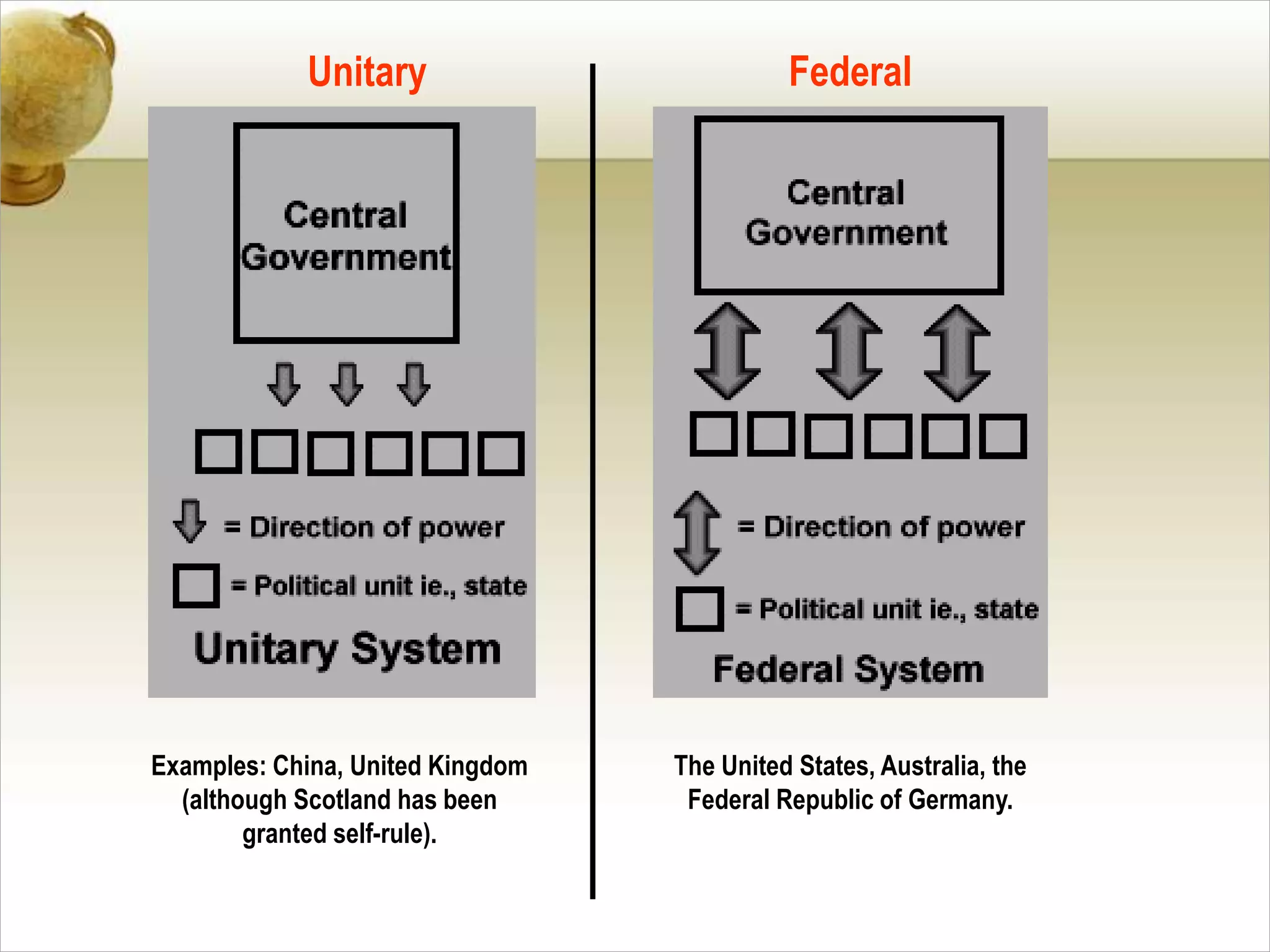
The document outlines various forms of government, including monarchy (absolute and limited), aristocracy, and democracy (direct and indirect). It also differentiates between unitary and federal governments, explaining the division of powers and the relationship between executive and legislative branches through parliamentary and presidential systems. Additionally, it provides specific details about Brazil's constitutional republic structure, including its bicameral legislature and state autonomy.