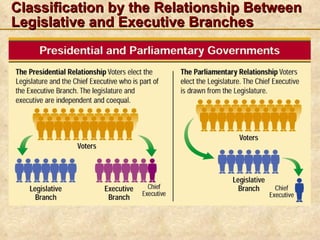
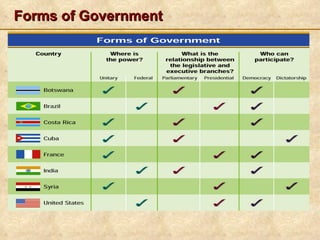
This document discusses different ways to classify forms of government. Governments can be classified based on who can participate (democracy vs dictatorship), the geographic distribution of power (unitary, confederate, federal), and the relationship between the legislative and executive branches. It provides examples of democracy (direct, indirect) and types of dictatorships (autocracy, oligarchy). The document includes review questions to check understanding of the classifications.