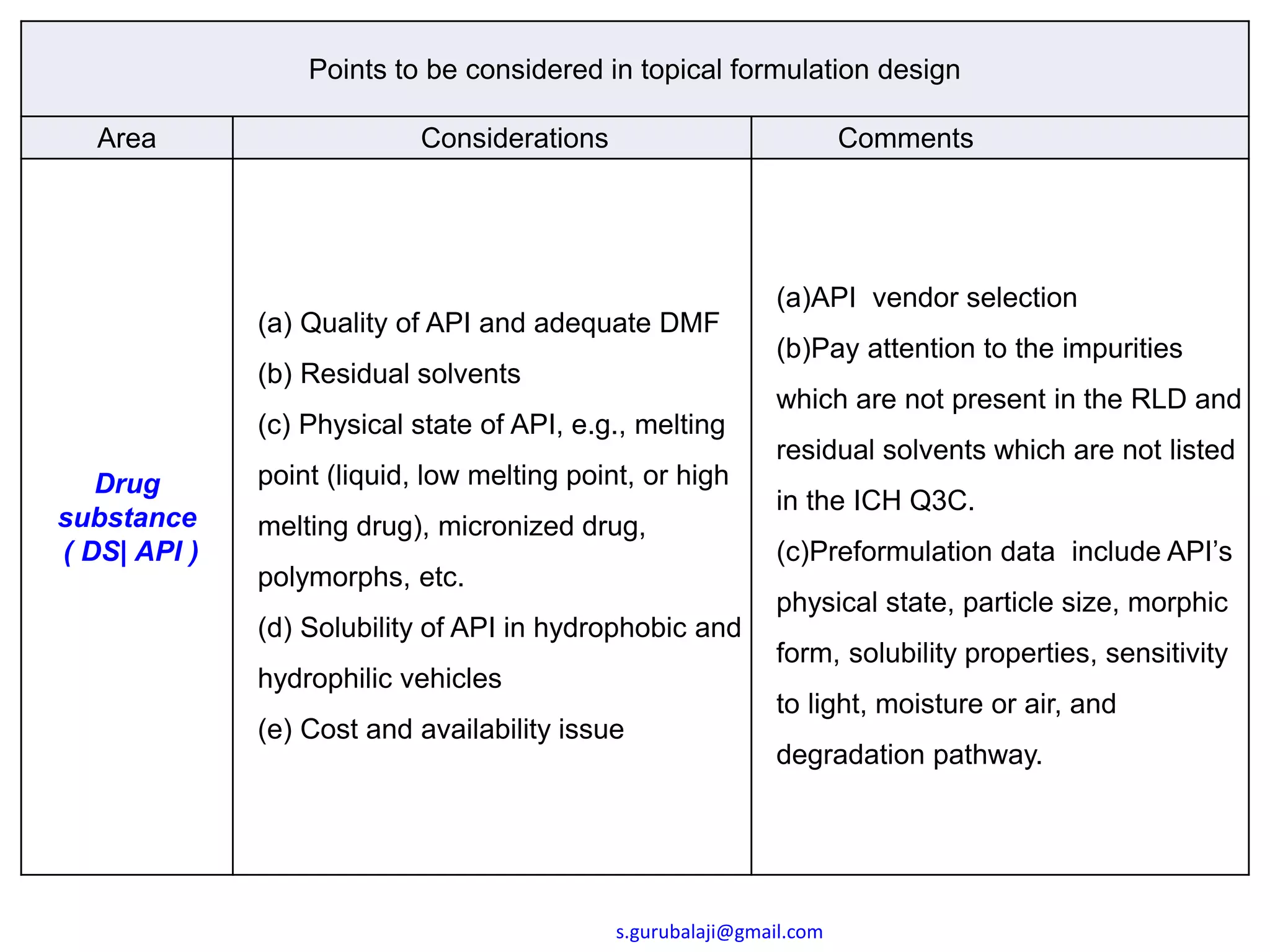
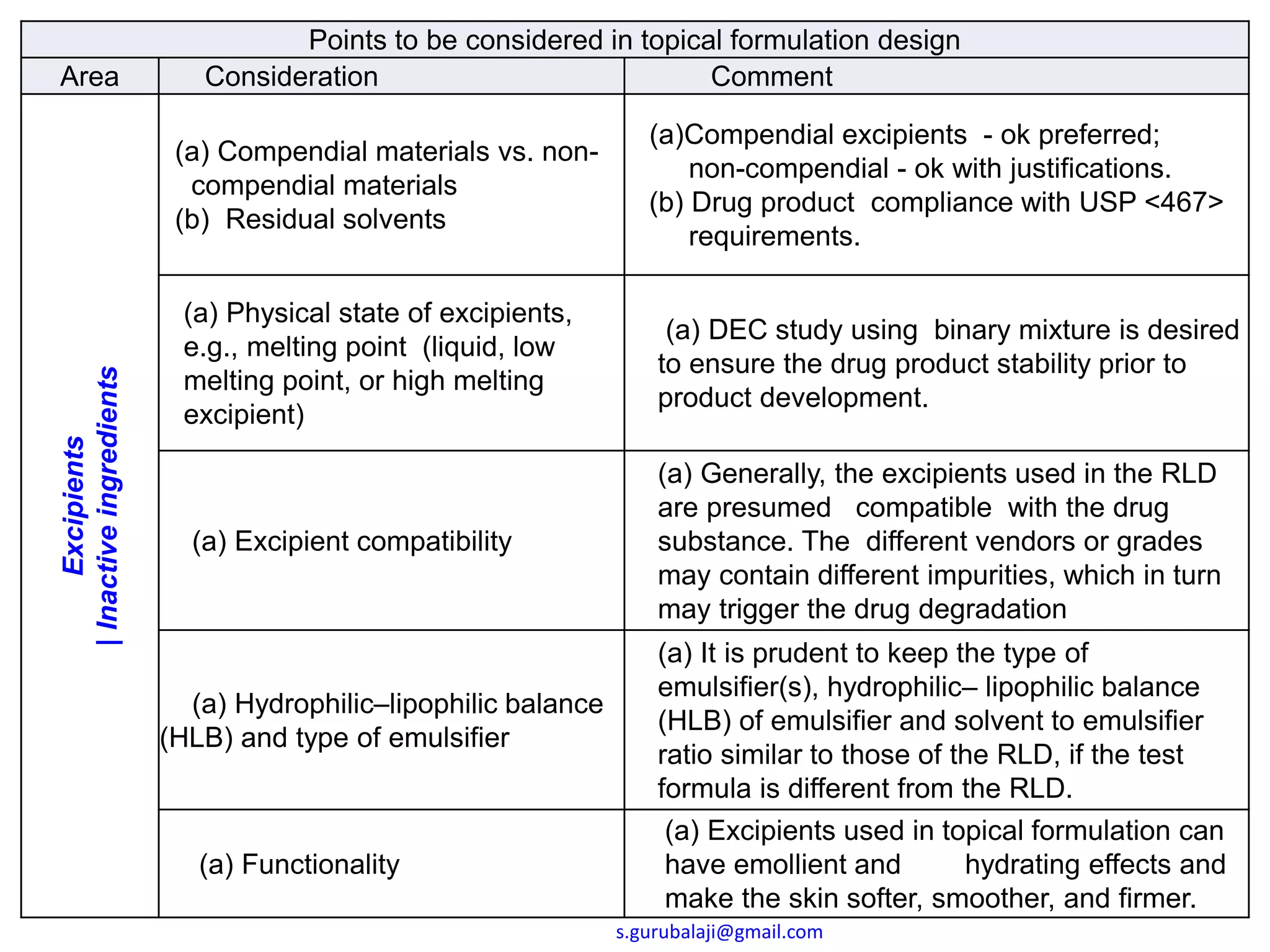
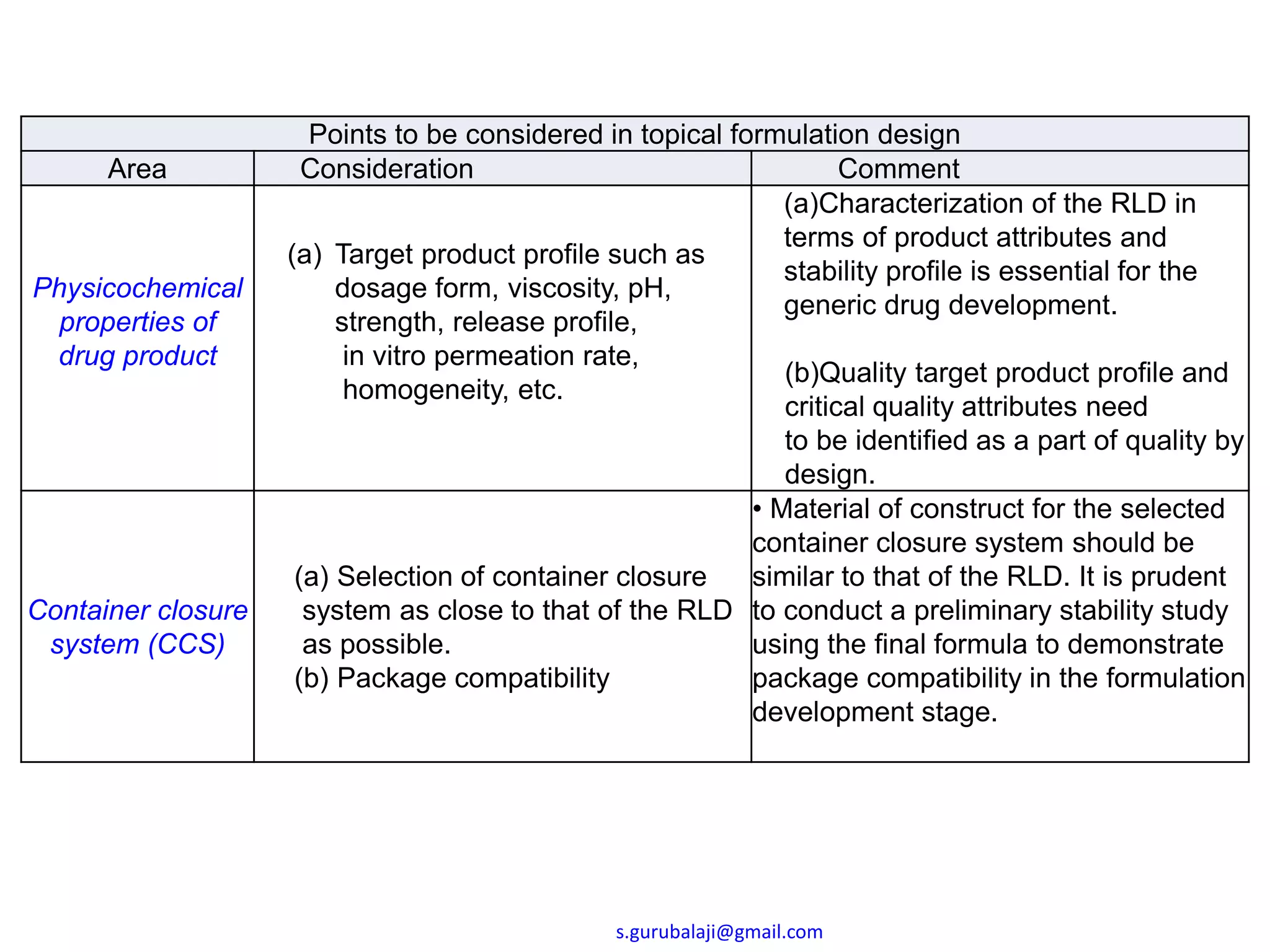
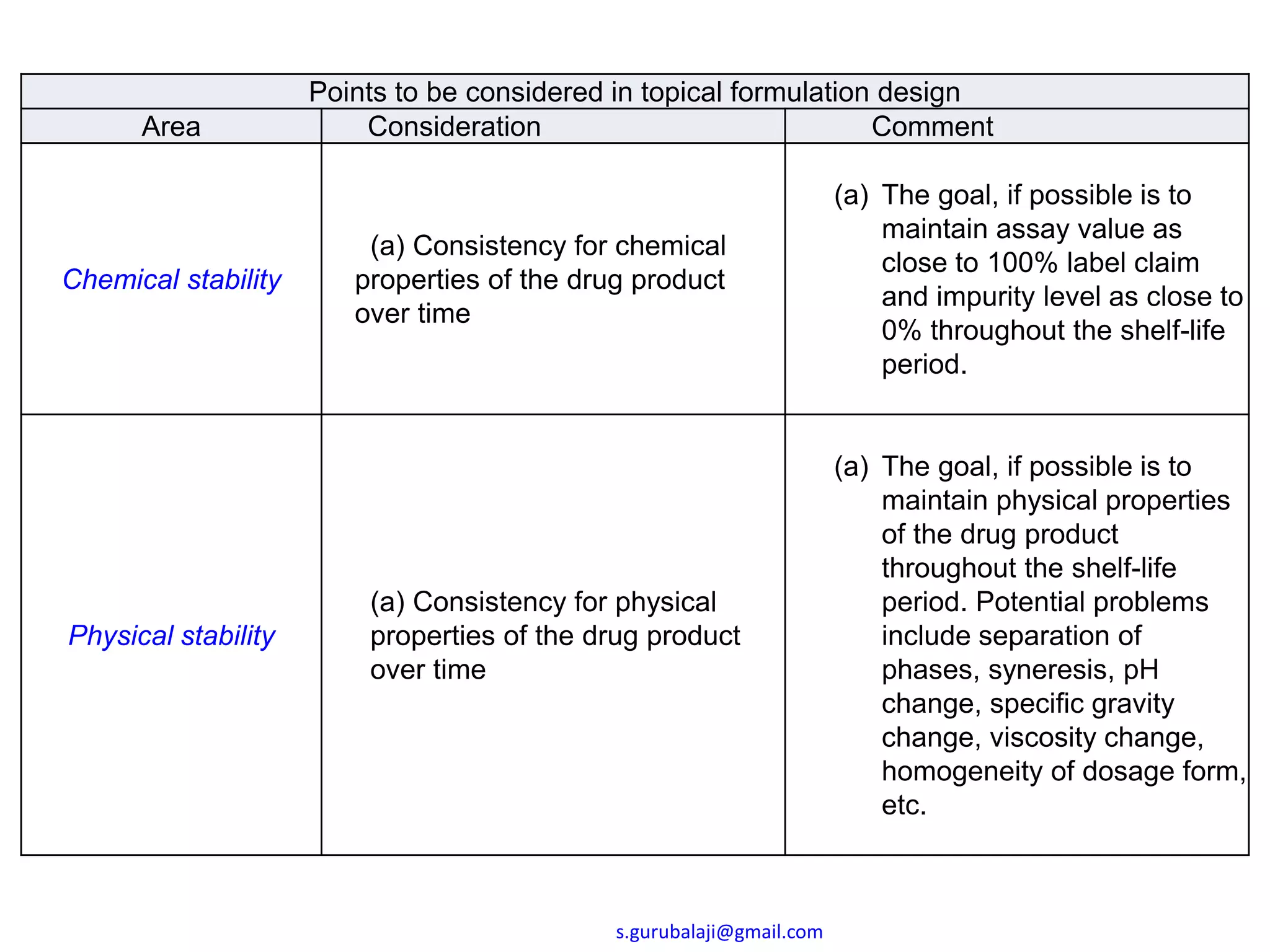
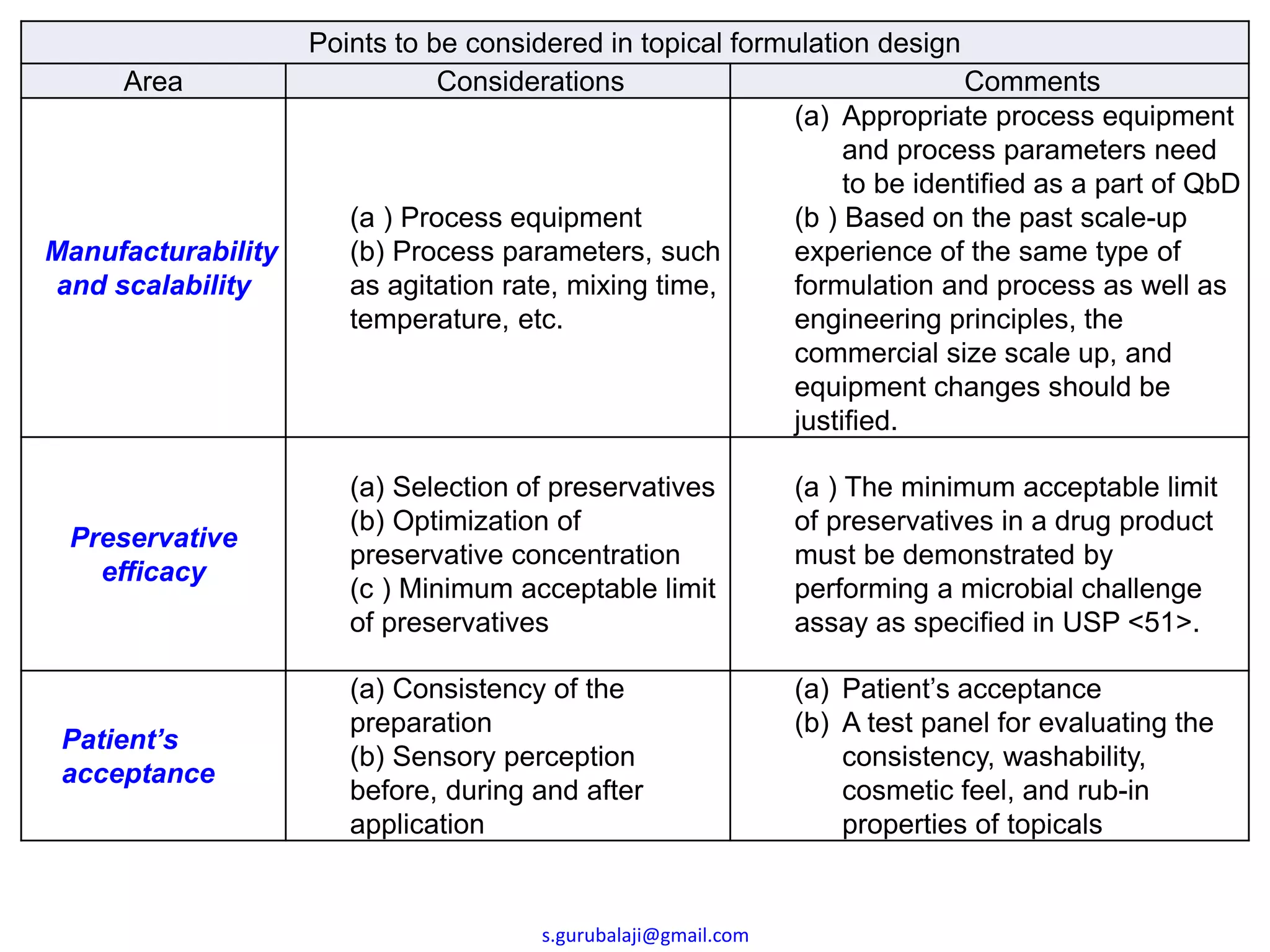
This document outlines key points to consider in topical formulation design, including the drug substance, excipients, physicochemical properties, container closure system, chemical and physical stability, manufacturability and scalability, preservative efficacy, and patient acceptance. Some important considerations are the quality and physical characteristics of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and excipients, ensuring compatibility between ingredients, and establishing a target product profile that maintains consistency of the formulation over time. Process parameters and equipment must also be identified during development to enable scalability and reproducibility of the commercial manufacturing process.