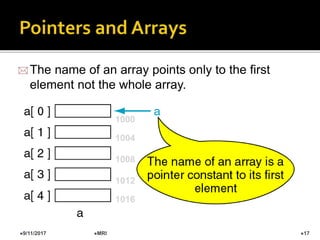
Pointer variables store memory addresses of other variables. A pointer variable contains the address of the memory location where another variable is stored. Pointers allow access and modification of the variable being pointed to using dereferencing operator (*). Arrays can also be treated as pointers, as the name of an array represents the address of its first element. Pointers provide benefits like dynamic memory allocation, passing arguments by reference, and building complex data structures.









![int A[5] - A is the address where the array starts (first
element), it is equivalent to &(A[0])
A is in some sense a pointer to an integer variable.
To determine the address of A[x] use formula:
(address ofA + x * bytes to represent int)
(address of array + element num * bytes for element size)
The + operator when applied to a pointer value uses
the formula above:
A + x is equivalent to &(A[x])
*(A + x) is equivalent to A[x]
9/11/2017 14MRI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11pointers-170911194309/85/Pointers-14-320.jpg)
![float A[6] =
{1.0,2.0,1.0,0.5,3.0,2.0};
float *theMin = &(A[0]);
float *walker = &(A[1]);
while (walker < &(A[6])) {
if (*walker < *theMin)
theMin = walker;
walker = walker + 1;
}
printf("%.1fn",*theMin);
9/11/2017 15MRI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11pointers-170911194309/85/Pointers-15-320.jpg)
![Array of Pointers & Pointers to Array
a
b
c
An array of Pointers
p
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3;
int *p[5];
p[0] = &a;
p[1] = &b;
p[2] = &c;
int list[5] = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5};
int *p;
P = list;//points to 1st entry
P = &list[0];//points to 1st entry
P = &list[1];//points to 2nd entry
P = list + 1; //points to 2nd entry
A pointer to an array
9/11/2017 16MRI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11pointers-170911194309/85/Pointers-16-320.jpg)
![When passing whole array as parameter use syntax
ParamName[], but can also use *ParamName
Still treat the parameter as representing array:
int totalArray(int *A, int N) {
int total = 0;
for (I = 0; I < N; I++)
total += A[I];
return total;
}
For multi-dimensional arrays we still have to use the
ArrayName[][Dim2][Dim3]etc. form
9/11/2017 18MRI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11pointers-170911194309/85/Pointers-18-320.jpg)

