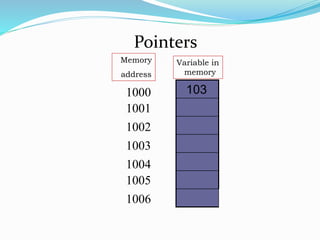
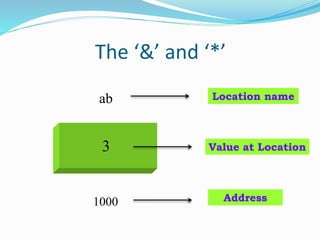
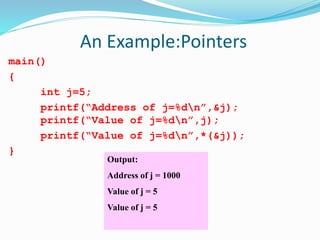
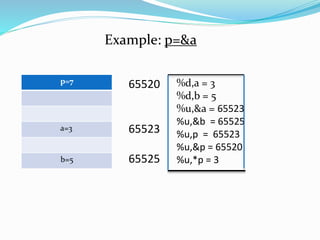
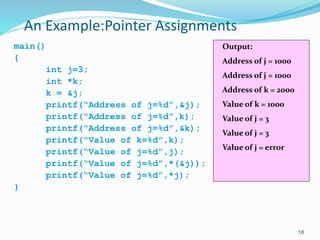
Pointer variables contain memory addresses that point to other variables in memory. A pointer contains the address of another variable. Pointers provide indirect access to data in memory. Pointer variables must be declared with a data type and the * symbol indicates it is a pointer. The & operator returns the memory address of a variable and * dereferences a pointer to access the value at that memory address. Pointers can be assigned, compared, and perform arithmetic operations like incrementing to point to the next memory location.




















![Array Of Pointers
An array of pointers can be declared as
data_type *pointer_name[size];
For ex:
int *p[10];
This declares an array of 10 pointers, each of which points to an integer.
The first pointer is called p[0], the second is p[1] and so on up to p[9].
Initially, these pointers are uninitialized and they can be used as below.
int a=10, b=100, c=1000;
p[0]=&a;
p[1]=&b;
p[2]=&c; and so on.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-27-320.jpg)
![Relationship between 1-D array and pointer
Array name by itself is an address or pointer.
It points to the address of the first element(0th element
of an array)
If x is 1D array, the address of the first element can be
expressed as &x[0] or as x.
Similarly address of second array element can be
written as &x[1]or x+1.
In general, address on an array element i can be
expressed as &x[i] or x+i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-28-320.jpg)
![• In general address of array element i can be
expressed as &x[i] or x+i
• x[i] and *(x+i) both represents represents the
content of the address.
Array x
Address of
first
array
element
can be
expressed as
&x[0] or
simply x
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3]
Array x
Address of
second
array
element
can be
expressed as
&x[1] or
simply x+1
x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-29-320.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int x[5]={20,40,60,80,100},k;
printf("narray element ttelements value
ttaddressn");
for(k=0;k<5;k++){
printf("x[%d]ttt%dttt%pn",k,*(x+k),x+k );
}
}
array
element
elements
value
address
x[0] 20 0x7fff5bb0
bbb0
x[1] 40 0x7fff5bb0
bbb4
x[2] 60 0x7fff5bb0
bbb8
x[3] 80 0x7fff5bb0
bbbc
x[4] 100 0x7fff5bb0
bbc0
To display array element with their address using array name as a pointer
OUTPUT
• Element k acts as the element number( 0,1,2,3,4)
• x acting array is added with k i.e k is added with the address of first
element, it points to the consecutive memory location.
• Thus &x[k] is same as *(x+k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-30-320.jpg)
![/* WAP to calculate average marks of 10 students in a subject
using pointer*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
float marks[10],sum=0;
int i;
float avg;
printf("Enter marks of 10 students: ");
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
scanf("%f",marks+i);
sum+=*(marks+i);
}
avg=sum/10;
printf("nThe average is=%fn", avg);
}
4/25/2017 Ashim Lamichhane 31
mark
s+0
mark
s+1
mark
s+2
mark
s+3
mark
s+4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-31-320.jpg)
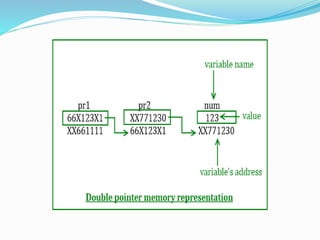
![Pointers and 2-D Arrays
A two dimensional array is actually a collection of one
dimensional arrays, each indicating a row (i.e. 2-D array can be
thought as one dimensional array of rows).
It is stored in memory in the row form. For ex.
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
• Is stored in the row major order in memory as illustrated
below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
a[0][0] a[0][1] a[0][2] a[1][1] a[1][2] a[2][0] a[2][1] a[2][2]
65500 65502 65504 65506 65508 65510 65512 65514 65516
a=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-32-320.jpg)
![Syntax for declaration of 2-D array
data_type (*ptr_var)[size2];
Instead of data_type array[size1][size2];
Ex: Suppose x is a two dimensional integer array having 4 rows
and 5 columns. We declare x as
int (*x)[5];
rather than
int x[4][5];
x points to the first 5 element array, which is actually first row of
the two dimensional array.
Similarly x+1 points to the second 5 element array, which is the
second row of the two dimensional array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-33-320.jpg)

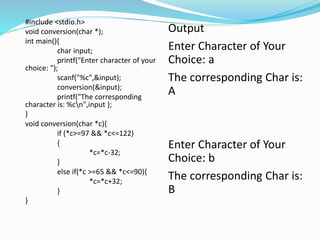
![String And Pointer
As strings are arrays and arrays are closely connected with
pointers, we can say that string and pointers are closely
related.
char name[5]=“shyam”;
As the string variable name is an array of characters, it is a
pointer to the first character of the string and can be used
to access and manipulate the characters of the string.
When a pointer to char is printed in the format of a string, it
will start to print the pointer character and then successive
characters until the end of string is reached.
Thus name prints “shyam”, name+1 prints “hyam”, name+2
prints “yam” and so on.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-170425035227/85/Pointers-36-320.jpg)
