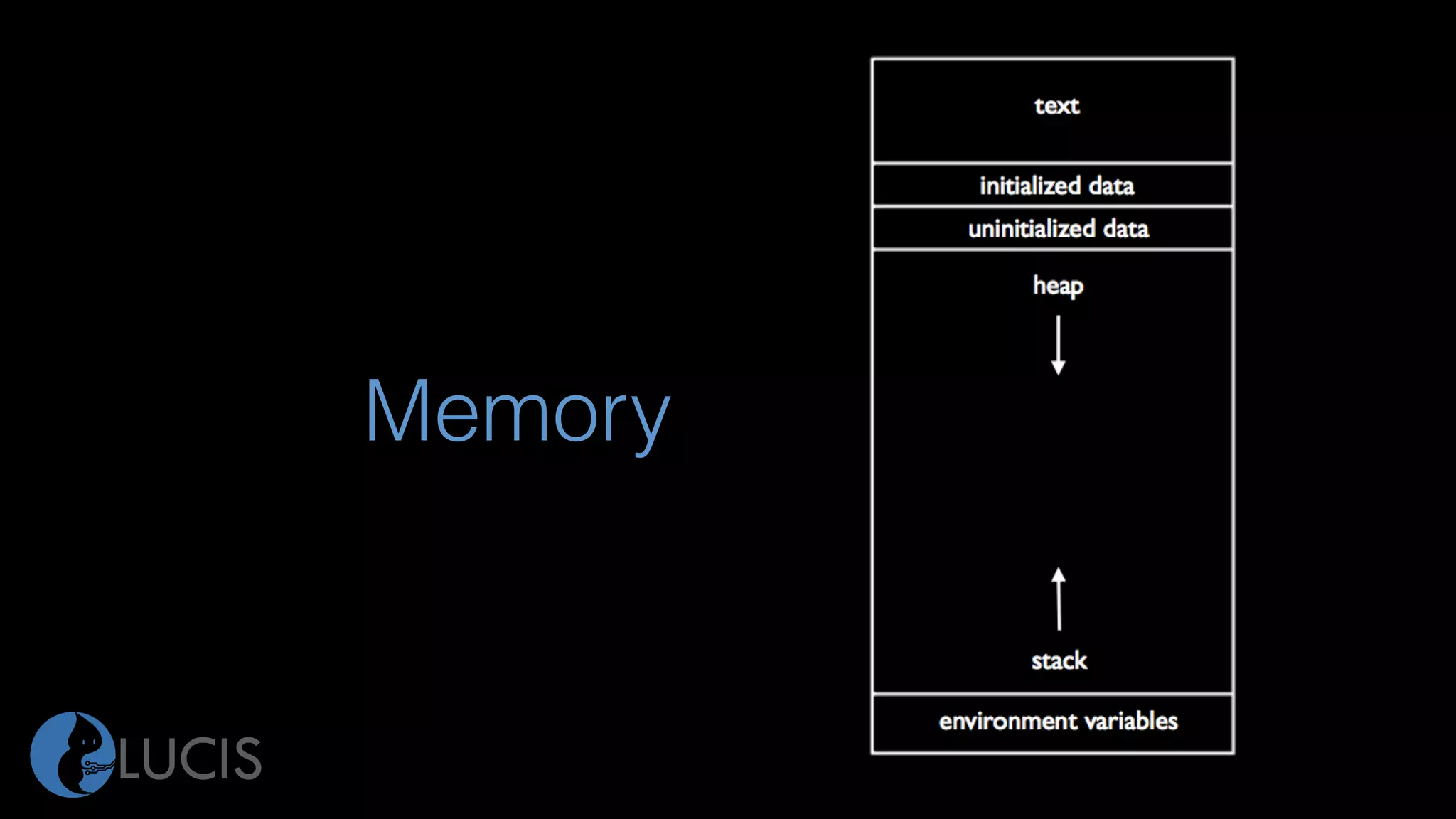
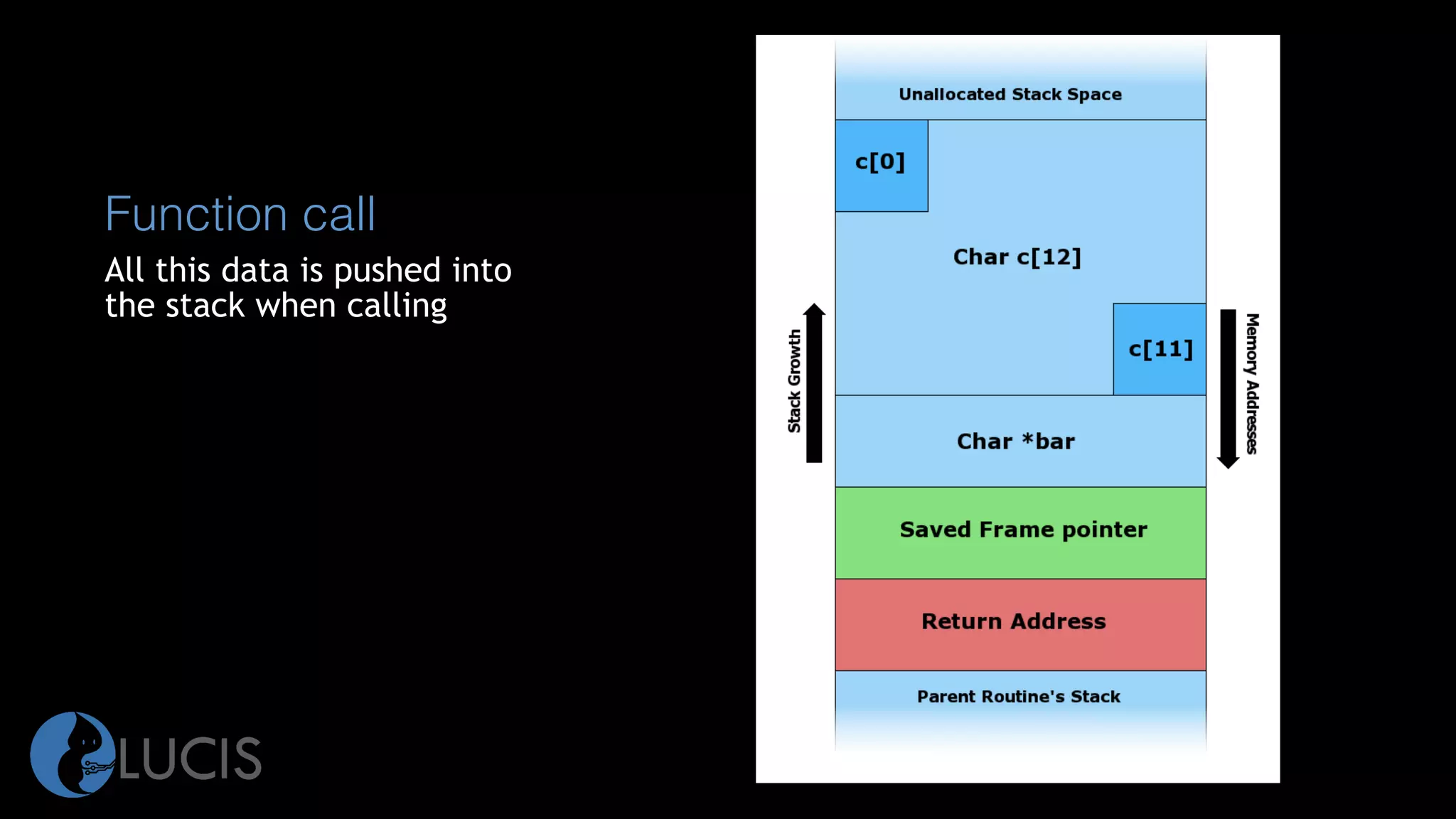
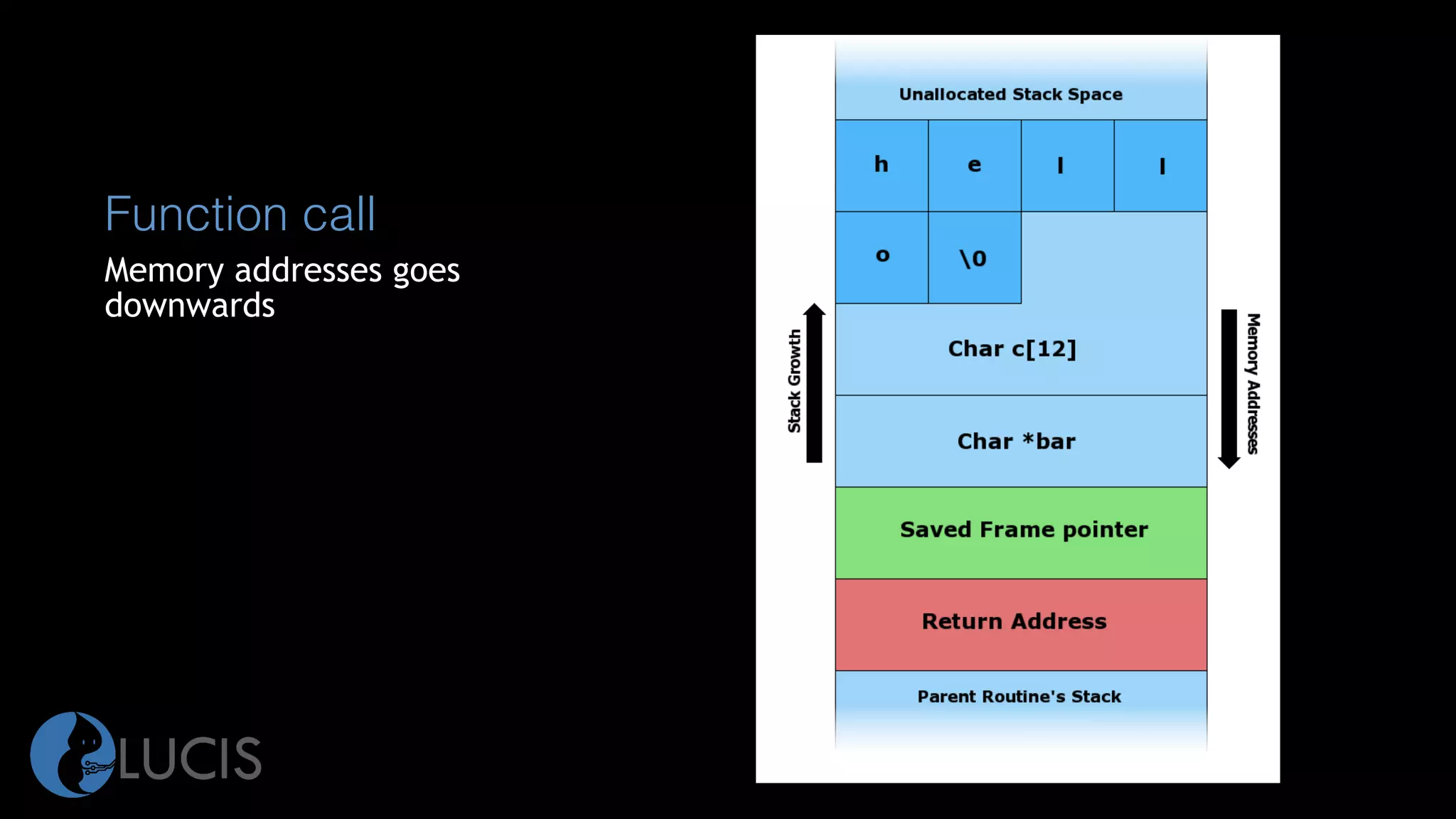
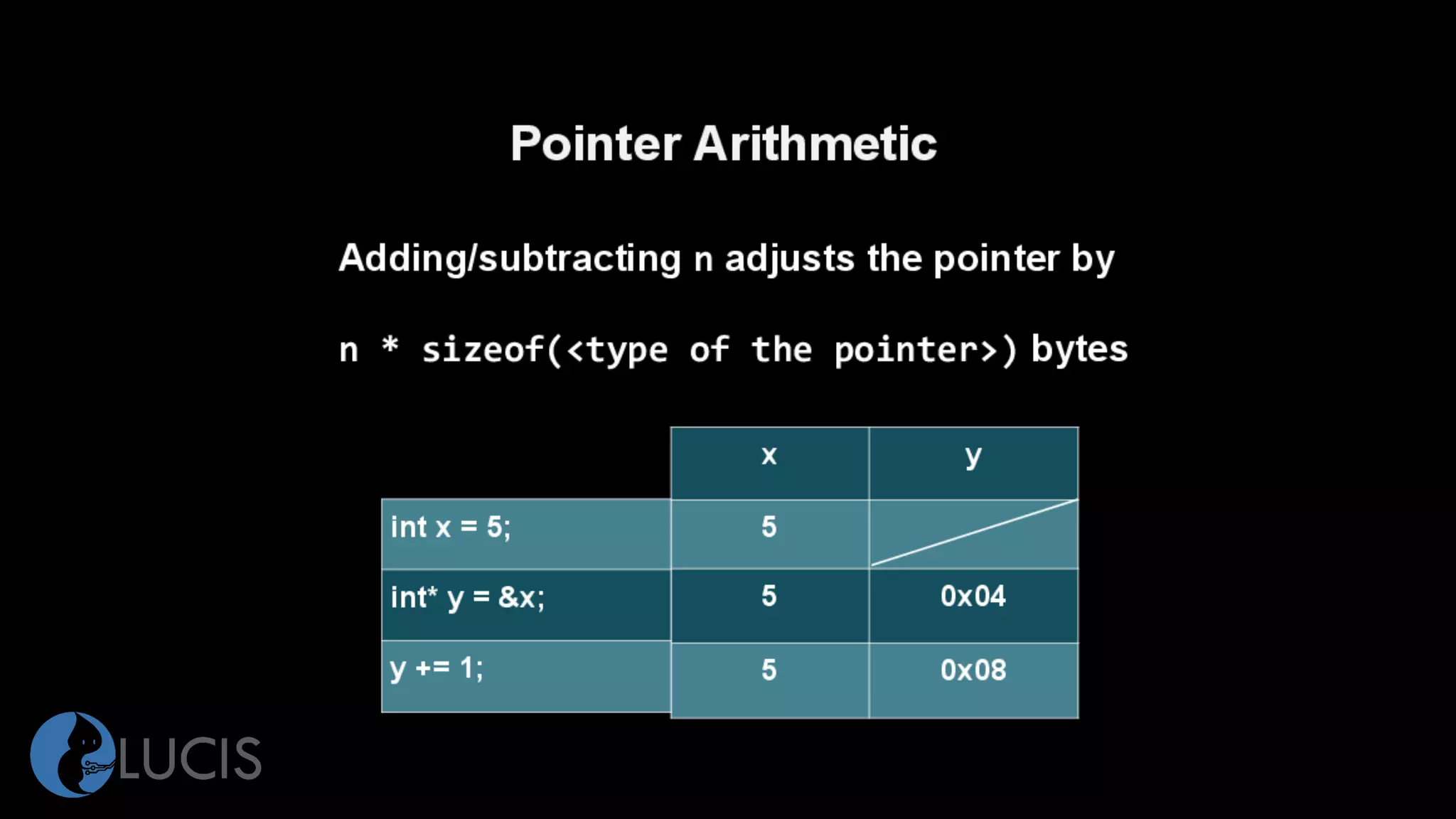
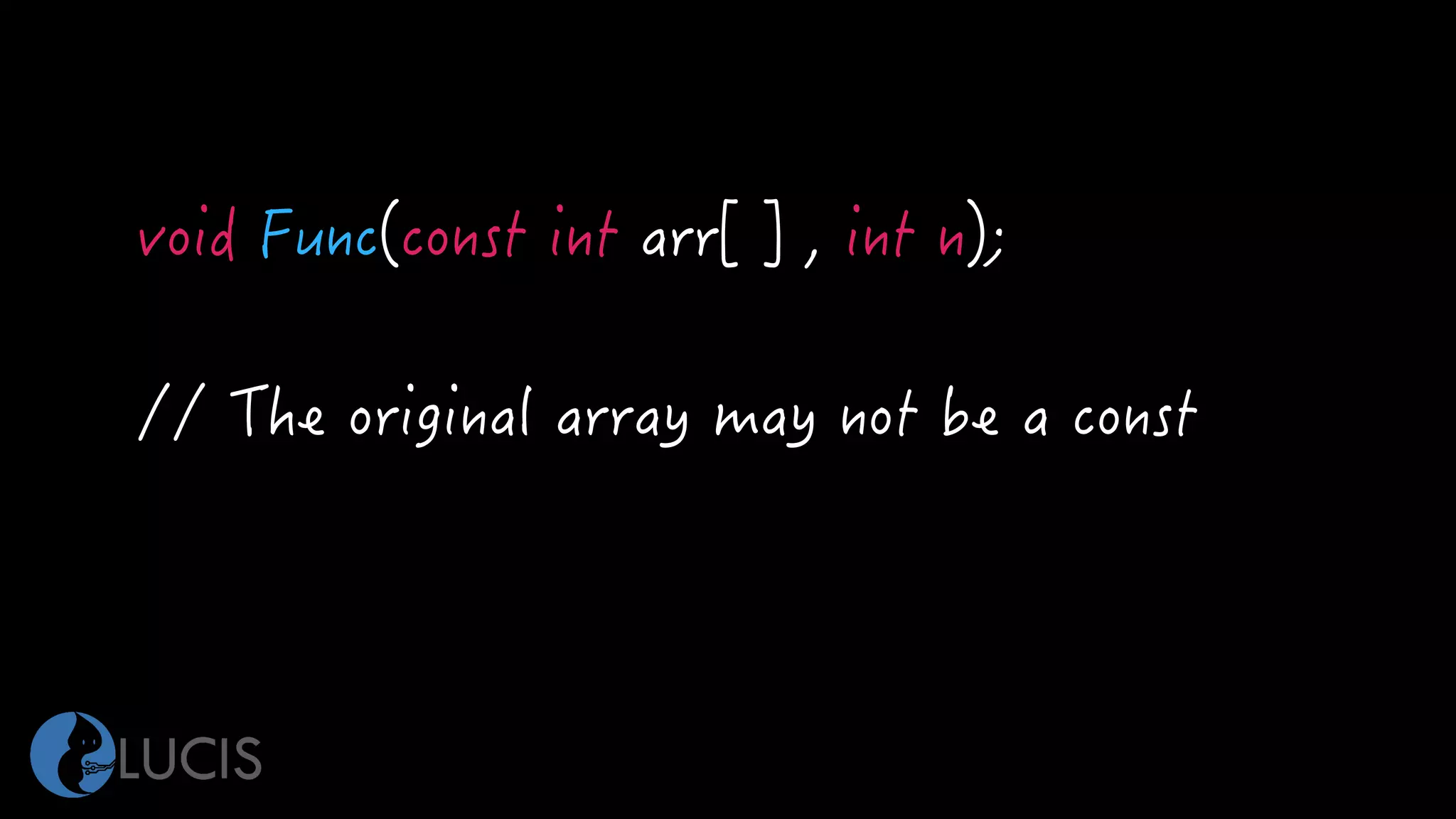
The document discusses pointers and arrays in C. It provides examples of declaring and initializing arrays, including multidimensional arrays. It also covers pointers, including declaring pointer variables, dereferencing pointers using * and &, pointer arithmetic, and how arrays are closely related to pointers since array names represent the address of the first element. Functions can accept arrays as arguments, and pointers allow accessing array elements within functions. Proper use of pointers is important to avoid errors like dereferencing uninitialized pointers or accessing out of bounds array indices.


















![Arrays
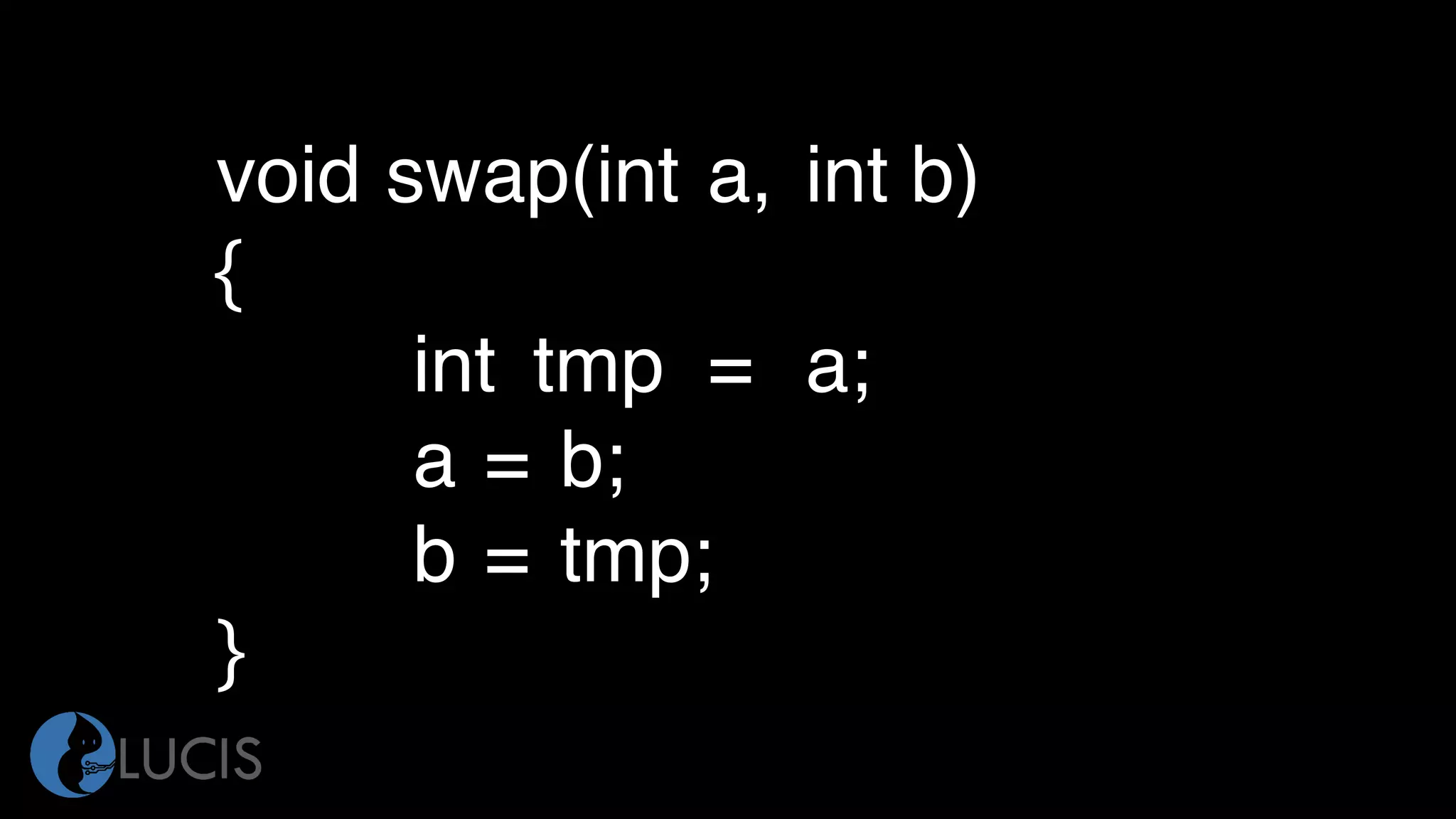
• Series of elements of one data type
• int grades[50];
• student[index] = 85;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-23-2048.jpg)
![Arrays Initialization
• int arr[4] = {11, 2, 4, 6};
• int arr[4];
• int arr[4] = {11, 2}; // " The rest are Zeros "
• int arr[ ] = {11, 2, 4, 6};
• int arr[150] = {[48] = 2, 4}; // " The rest are Zeros " C99
• int arr[ ] = {2, [7] = 3, 9};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-24-2048.jpg)

![sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-26-2048.jpg)




![Specifying an Array Size
• <Data Type> <Array Name>[int literal];
• int arr[<variable>]; //Not allowed before C99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-33-2048.jpg)

![Two-dimensional Arrays
• double x[5] [7];
• An array of arrays
• int arr[2][3] = {
{ 1, 3, 5 },
{ 4, 7, 8 }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-35-2048.jpg)








![Complicated Declarations
• int *arr [ ] ;
• float rain [5] [12];
• const double *p;
• double * const p;
• const double * const p;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointersc-180703005453/75/Pointers_c-46-2048.jpg)



