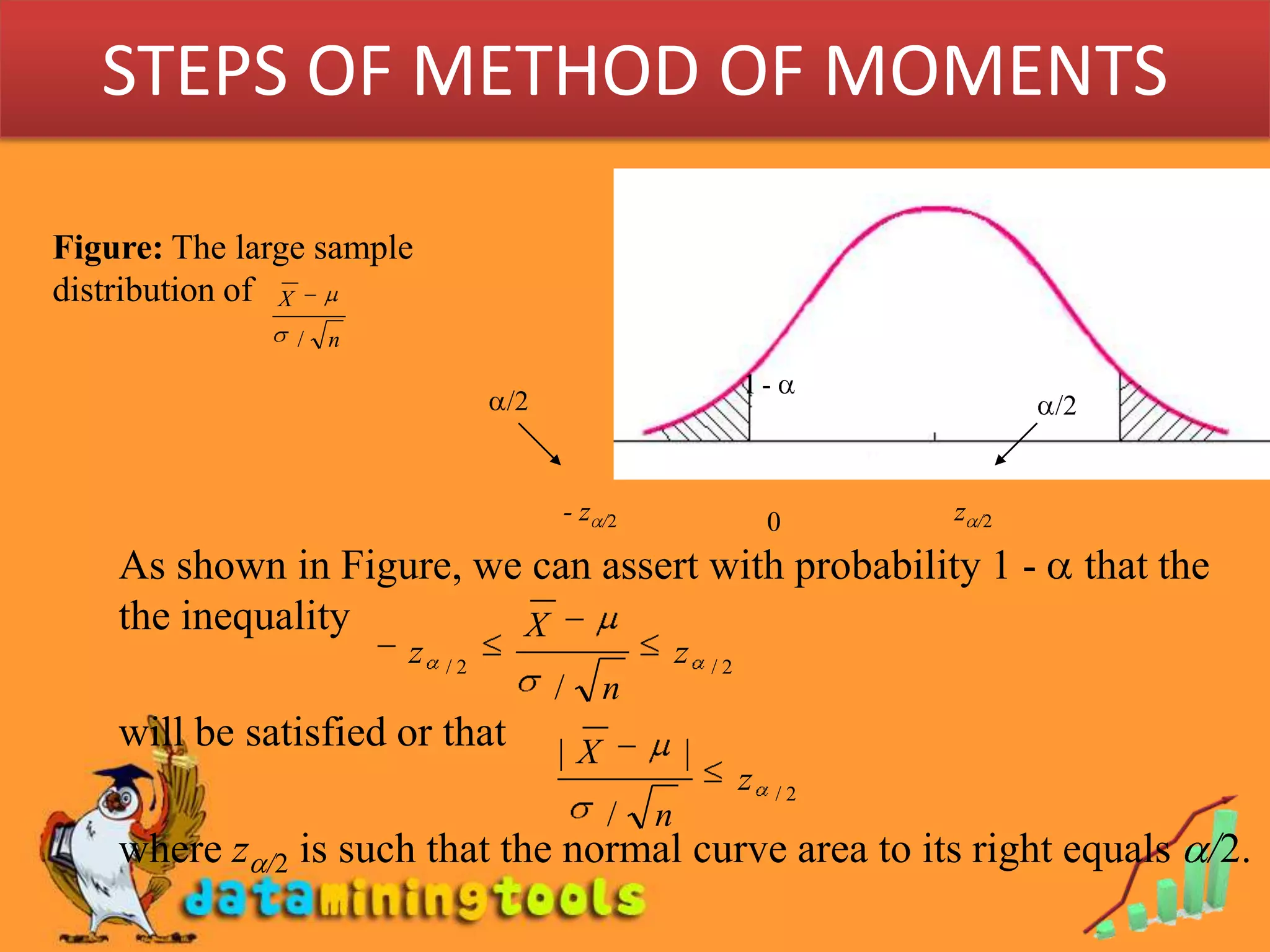
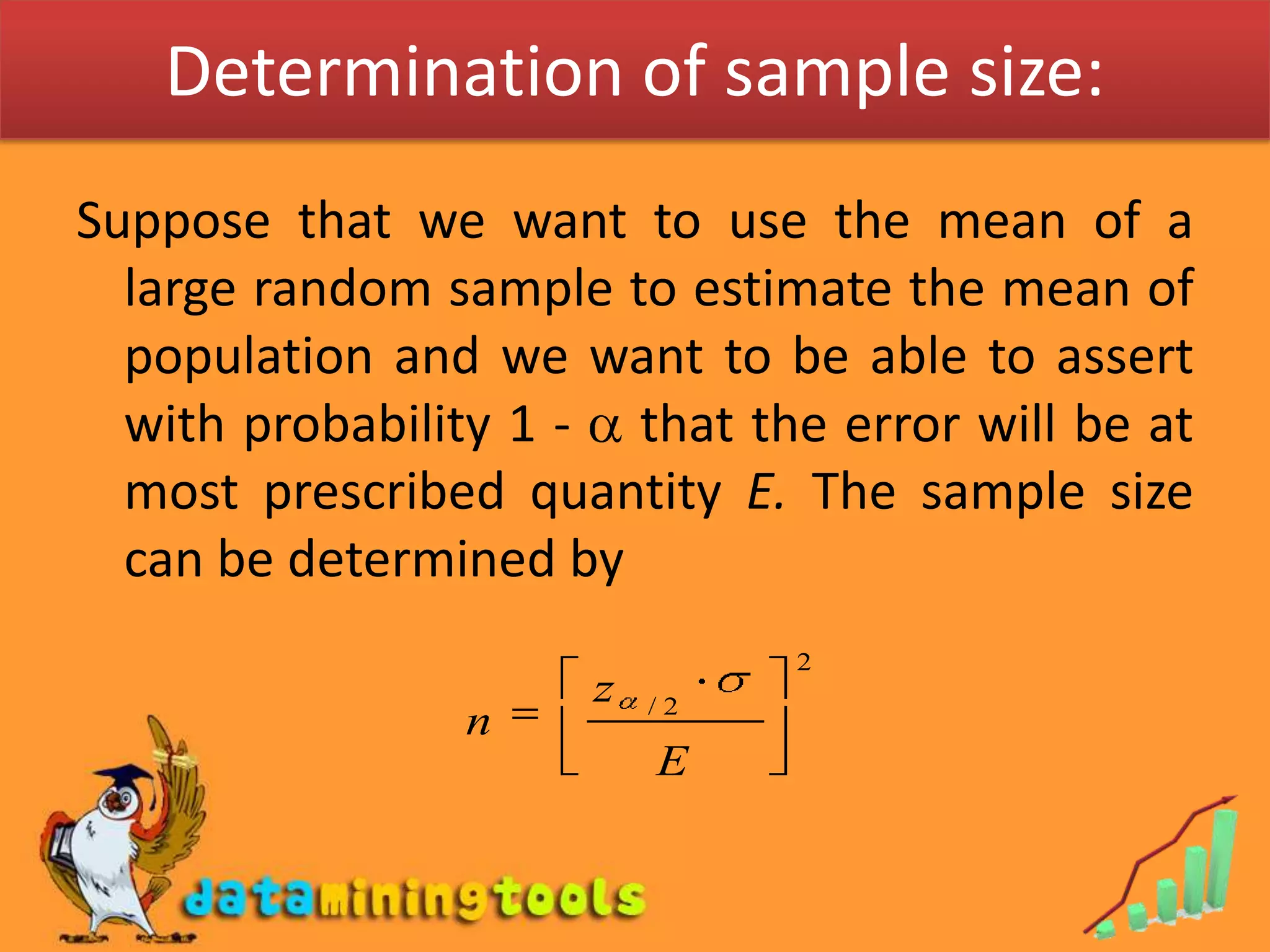
- Point estimation involves using sample data to calculate a single number (point estimate) that estimates an unknown population parameter.
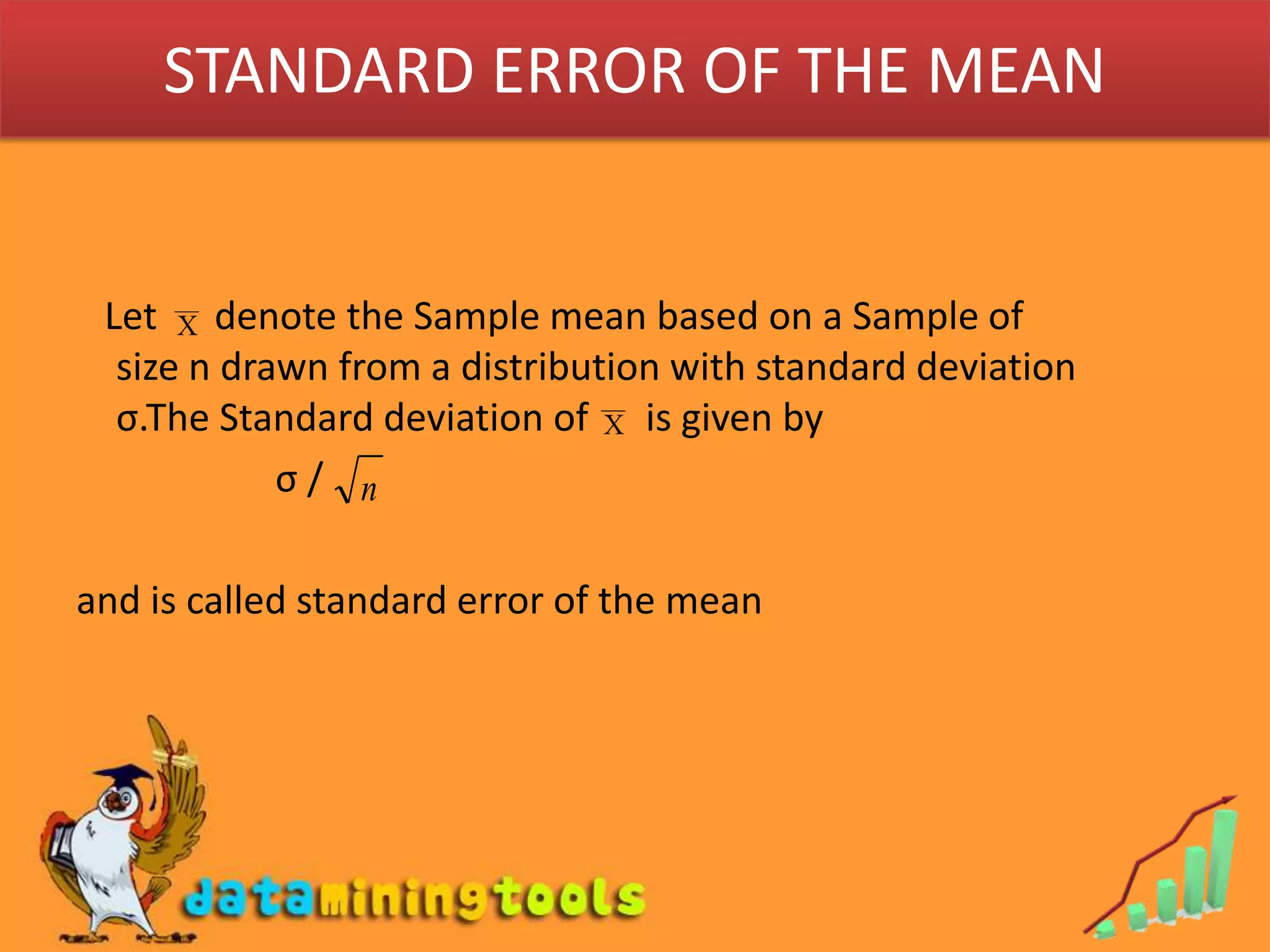
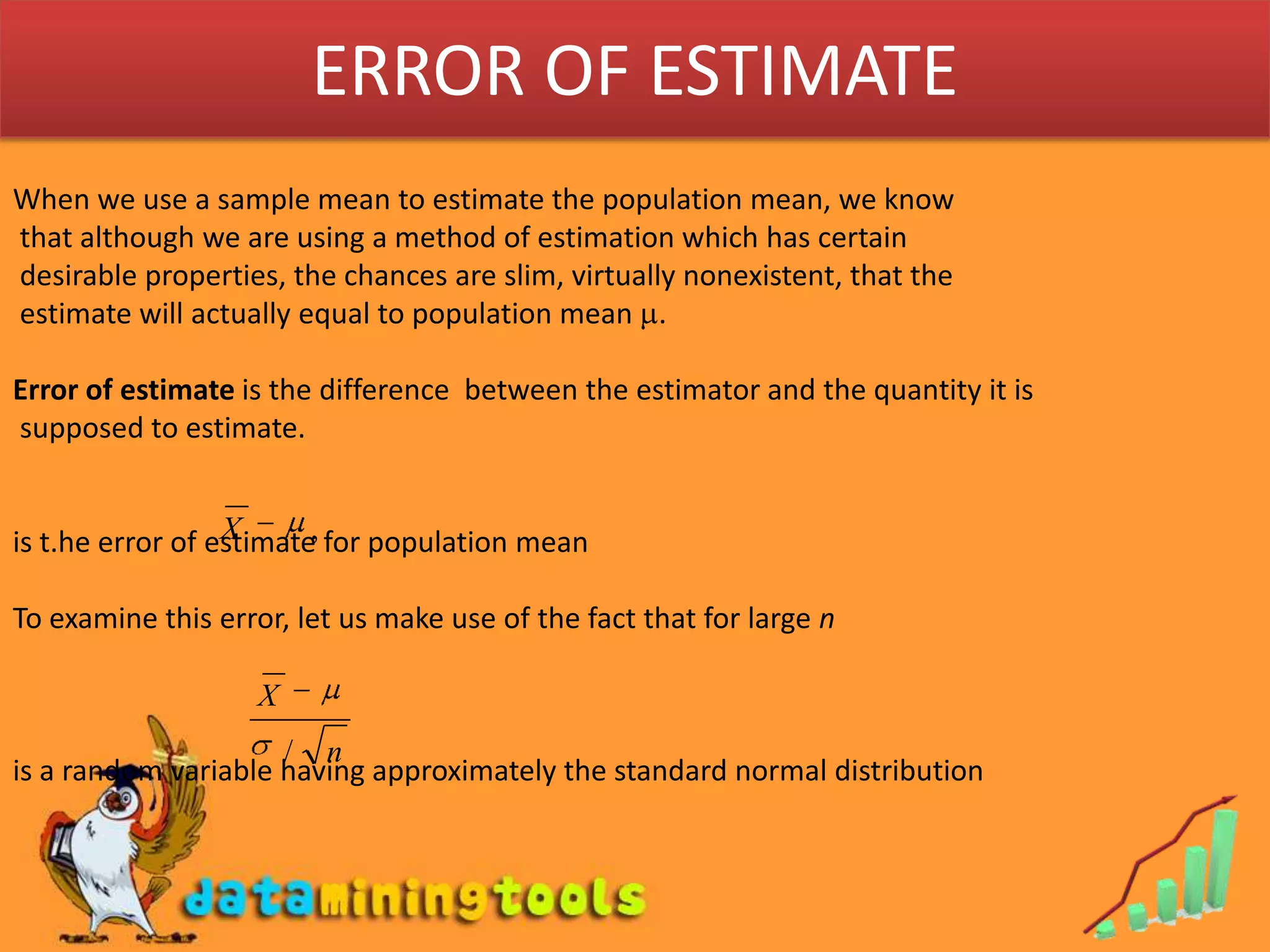
- A point estimator is a statistic used to calculate the point estimate. The sample mean is a common point estimator used to estimate the population mean.
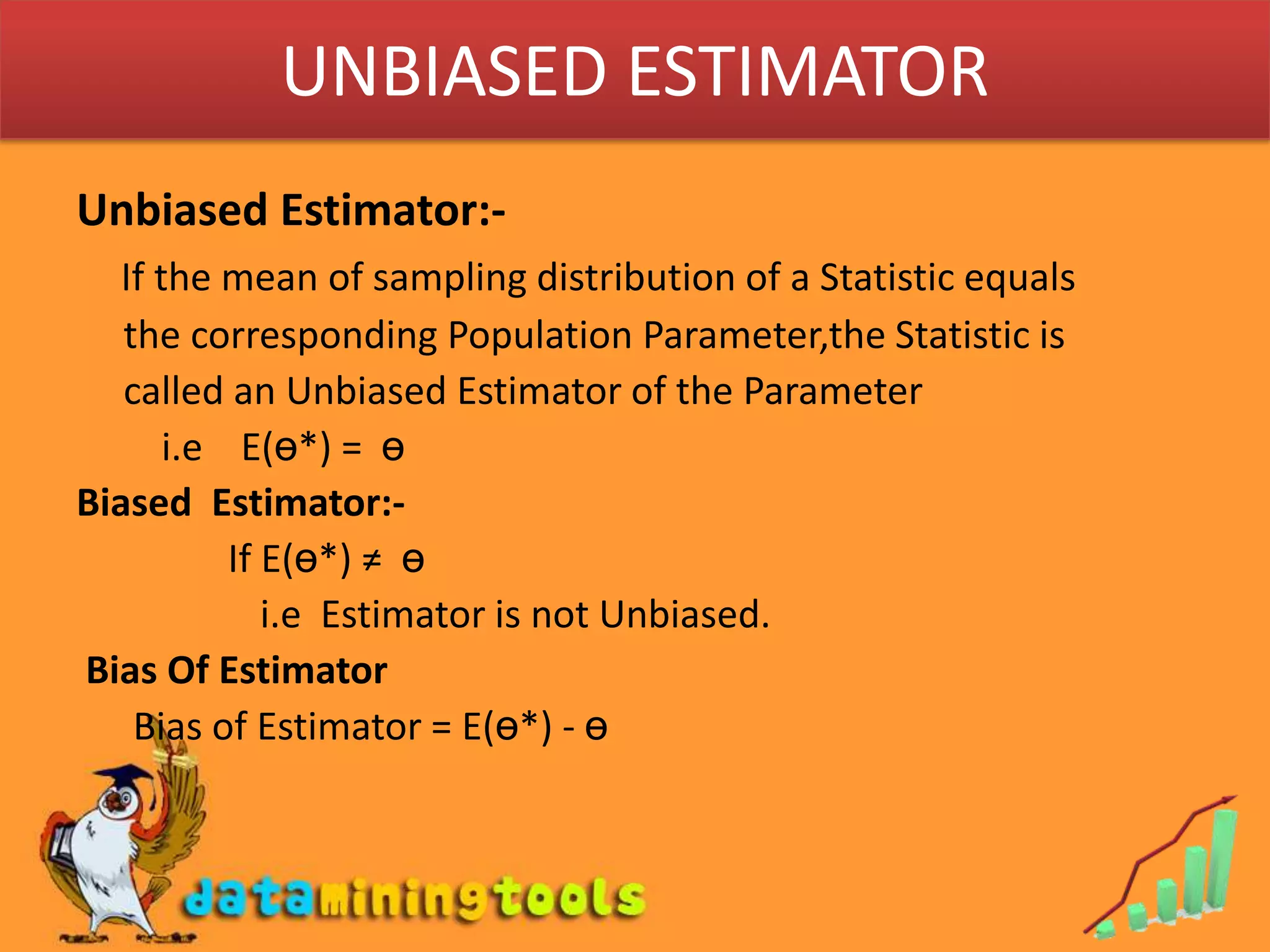
- An unbiased estimator has an expected value equal to the true population parameter. A biased estimator has an expected value that is not equal to the true parameter.
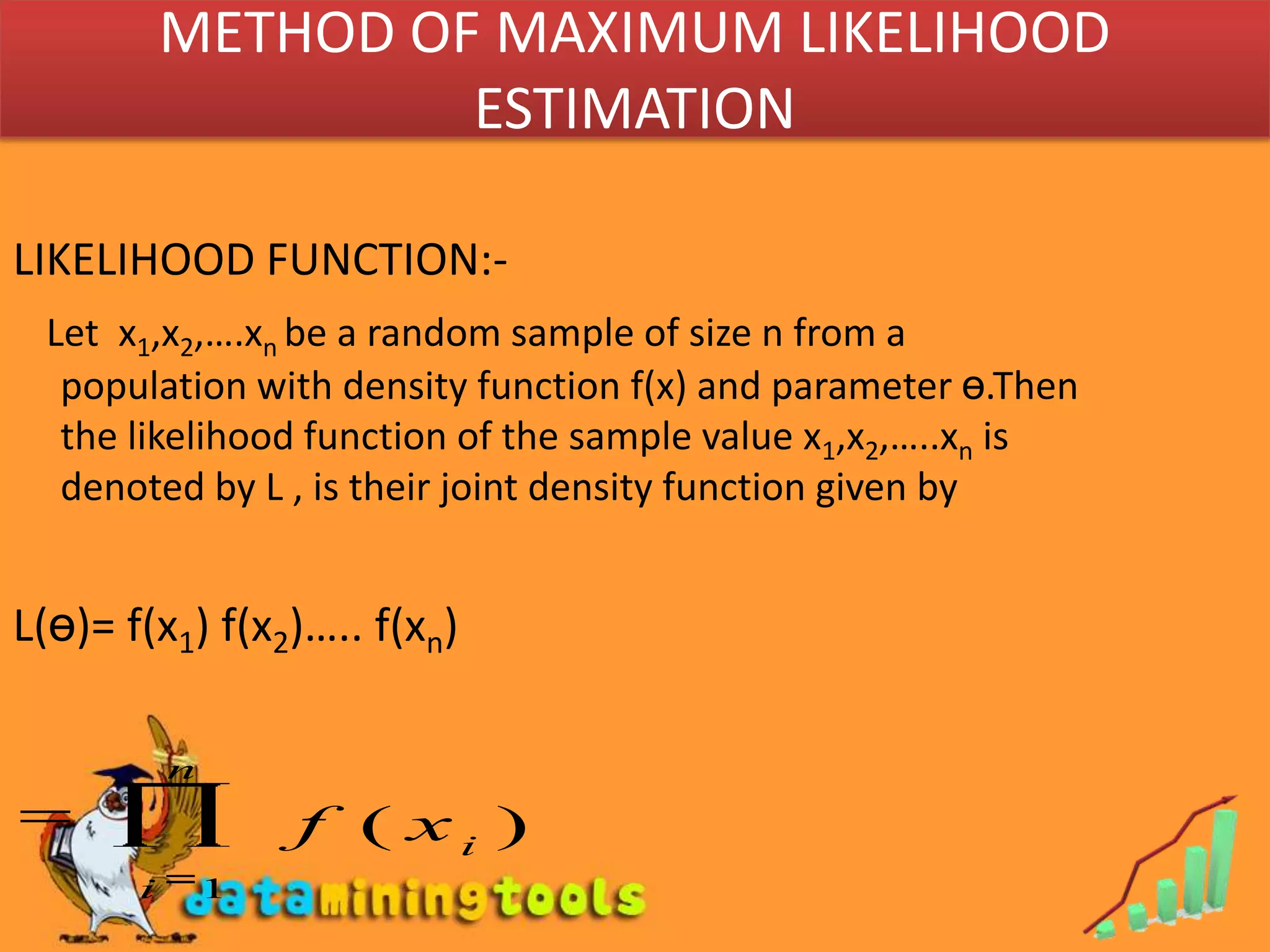
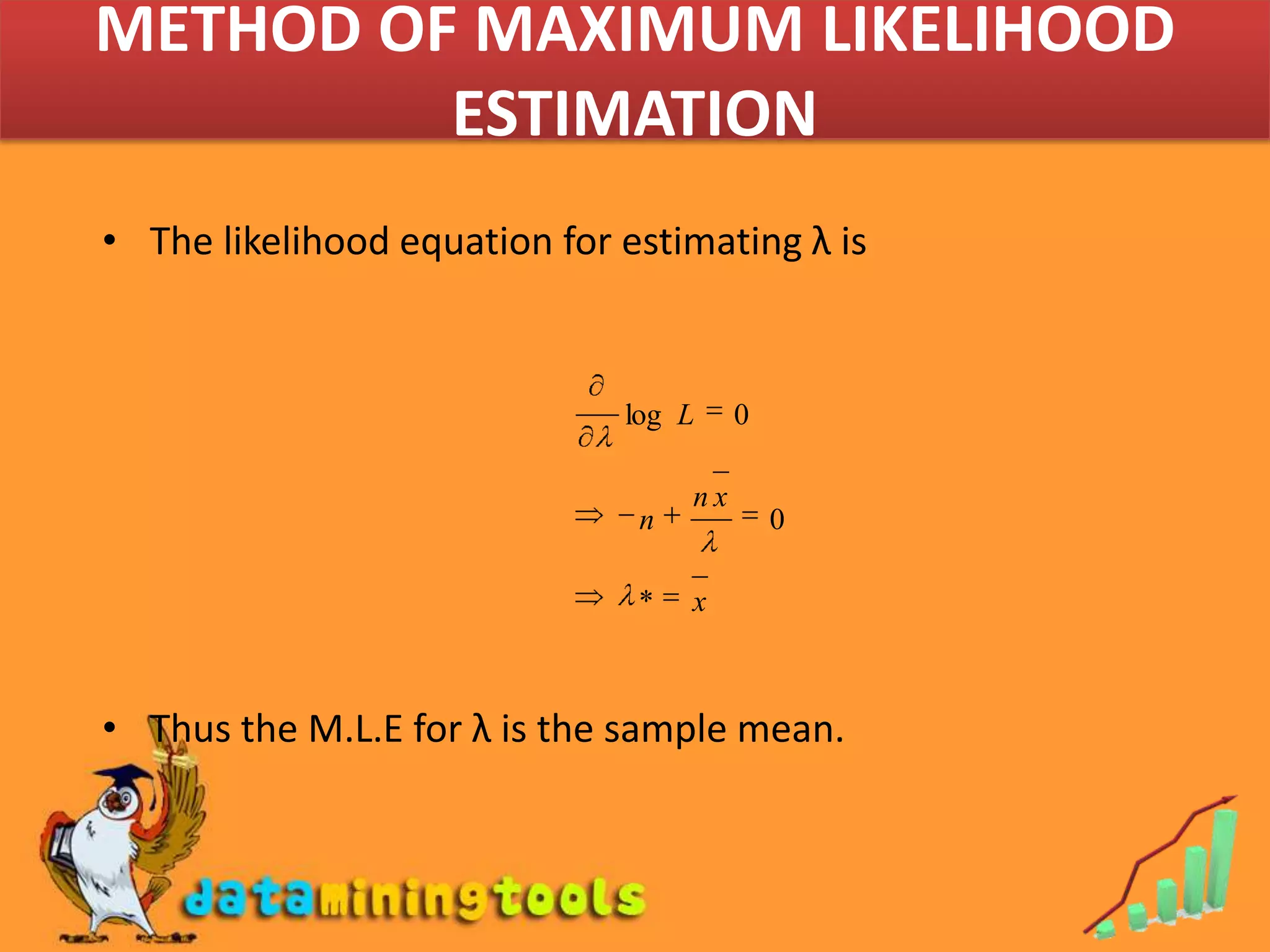
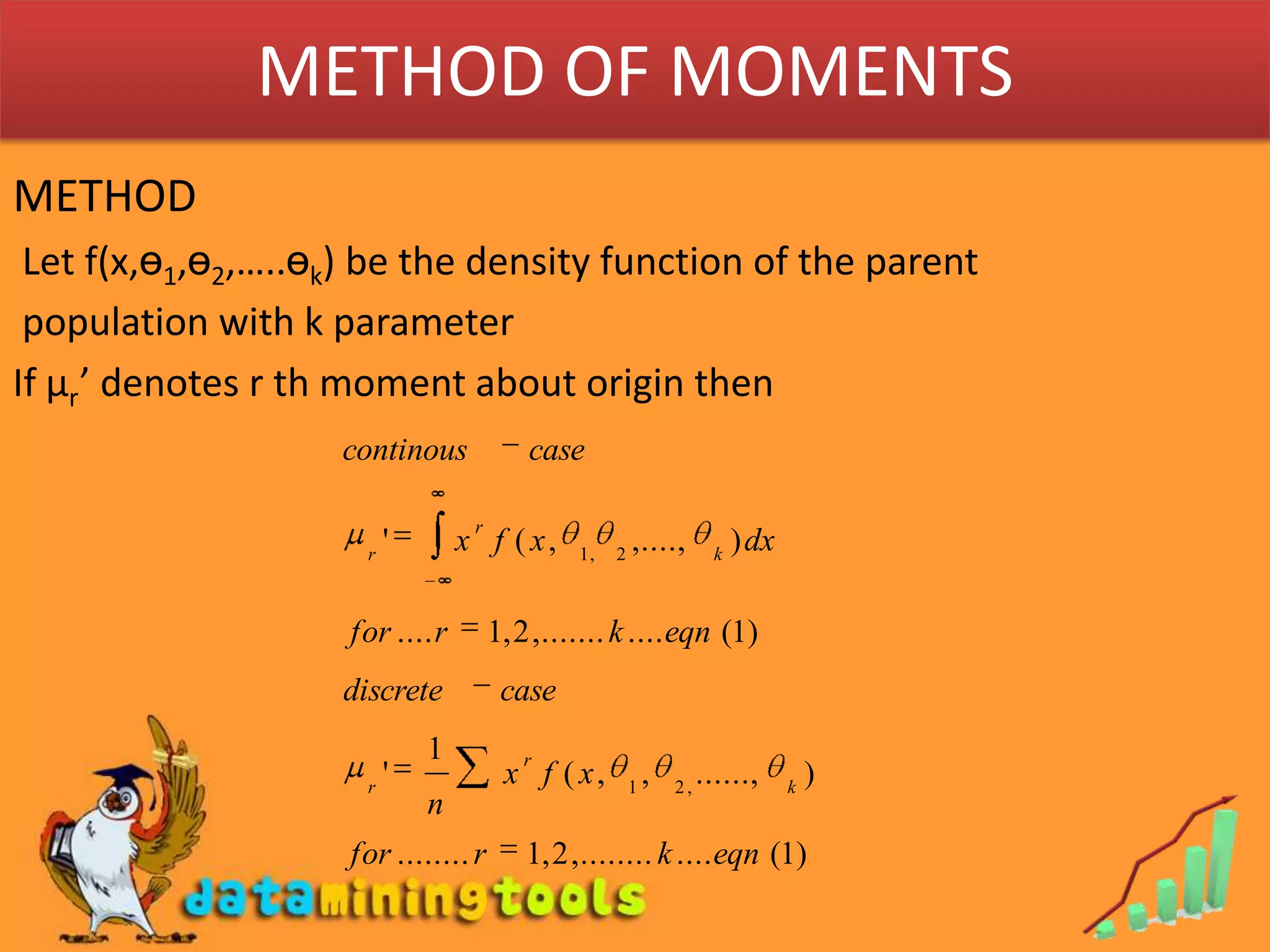
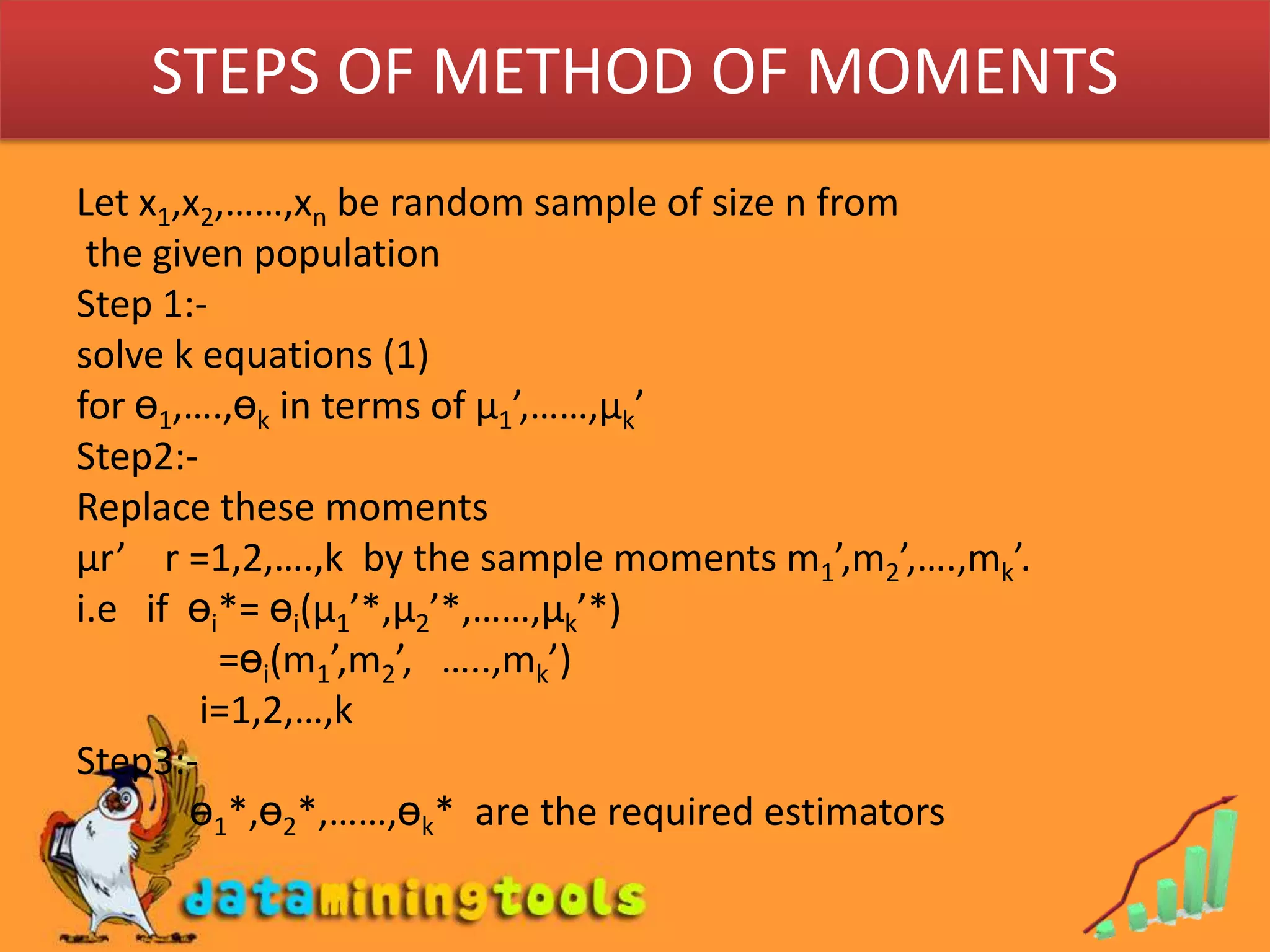
- Maximum likelihood estimation and the method of moments are two common approaches for finding estimators. Maximum likelihood estimation selects the value of the parameter that maximizes the likelihood function. The method of moments equates sample moments to population moments to estimate parameters.