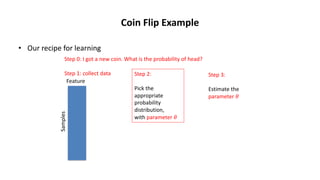
Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a technique for estimating parameters in a probabilistic model based on observed data. MLE finds the parameter values that maximize the likelihood function, or the probability of obtaining the observed data given the parameters. This involves writing the log likelihood function, taking its derivative with respect to the parameters, and solving for the parameter values that set the derivative to zero. MLE was demonstrated for Bernoulli, normal, Poisson, and Markov chain models using both theoretical examples and observed data. In practice, MLE provides a principled approach for learning probability distributions from samples.