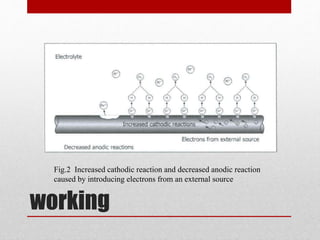
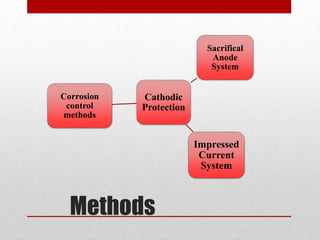
Cathodic protection (CP) is a method to prevent metal corrosion by making it the cathode in an electrochemical cell, typically using sacrificial anodes. There are two main methods of CP: sacrificial anode systems, which use more active metals like zinc or magnesium, and impressed current systems that apply a direct current. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, such as ease of installation for sacrificial anodes and higher driving voltage for impressed current systems.