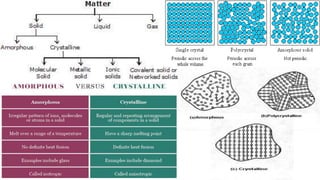
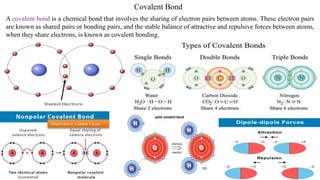
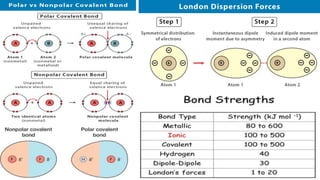
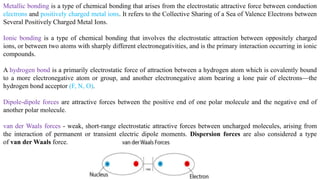
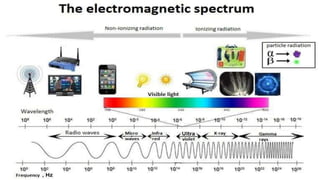
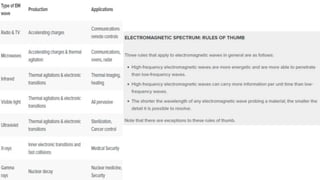
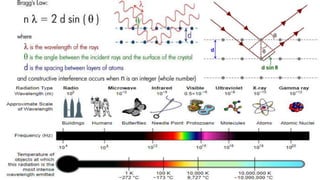
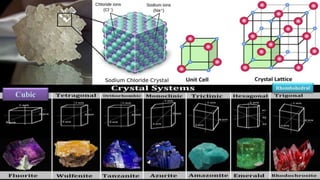
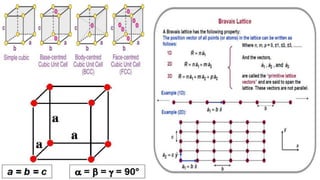
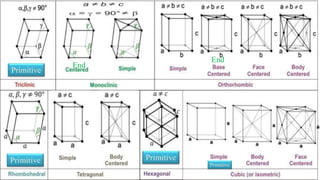
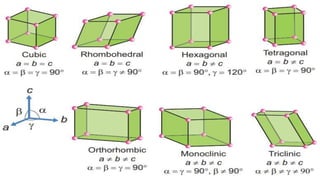
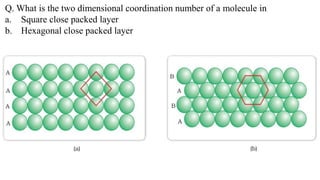
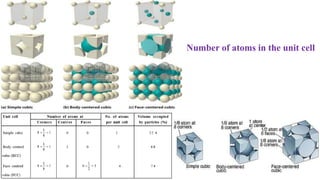
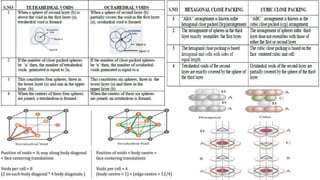
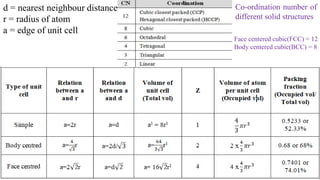
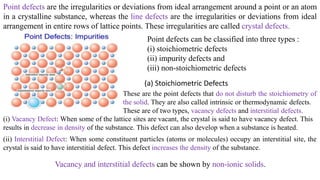
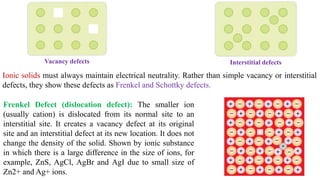
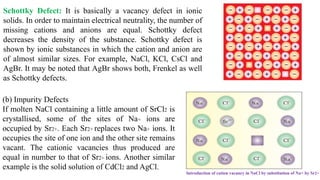
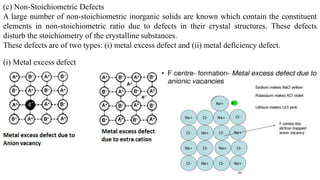
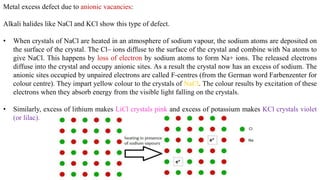
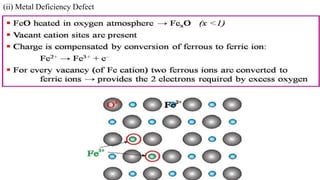
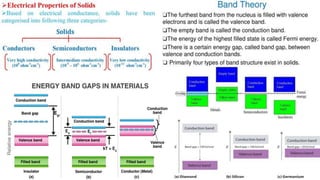
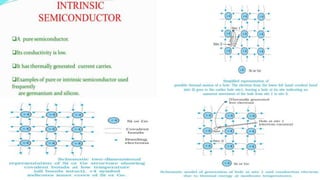
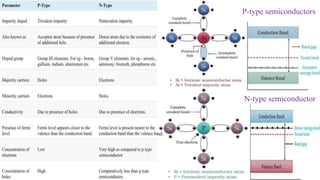
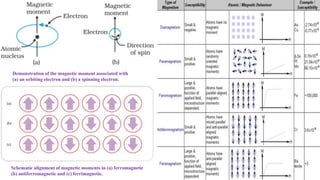
The document discusses various types of bonding and intermolecular forces found in solid state materials, including covalent bonding, metallic bonding, ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. It also describes different types of crystal defects such as point defects, line defects, stoichiometric defects, impurity defects, and non-stoichiometric defects. Finally, it covers topics like semiconductors, ferromagnetism, and the magnetic properties associated with orbiting and spinning electrons.