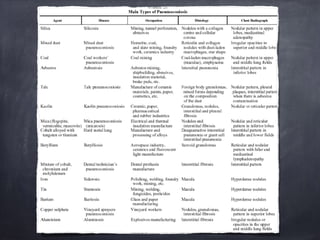
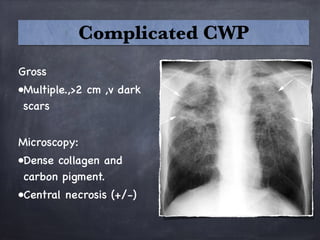
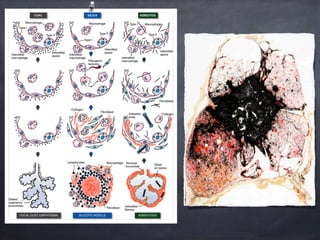
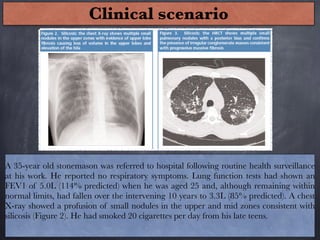
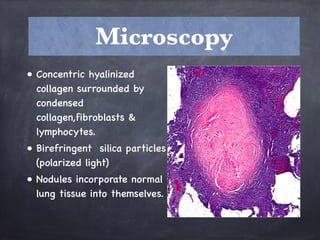
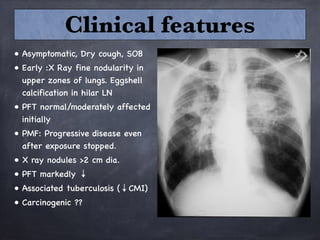
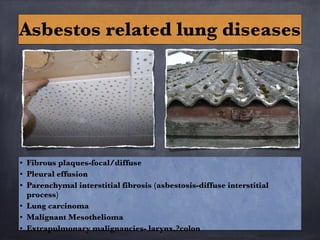
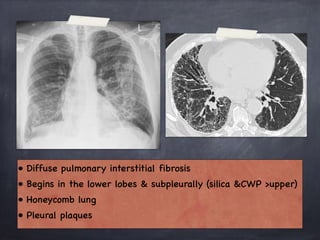
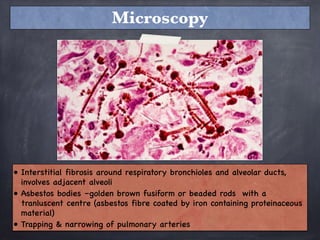
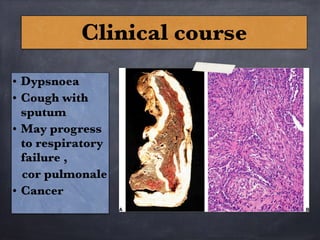
Pneumoconiosis is a non-neoplastic lung reaction caused by inhalation of mineral dusts and is critical to diagnose as an occupational lung disease. Key forms include silicosis, coal workers' pneumoconiosis, and asbestosis, with various pathophysiological mechanisms leading to fibrosis and lung dysfunction over time. The document details the clinical features, pathogenesis, diagnostic imaging findings, and preventative measures associated with these diseases.